- Oral Health and Dental Care | Colgate®
- Oral Health
- Mouth Anatomy Guide and Illustrations | Colgate® Oral Care


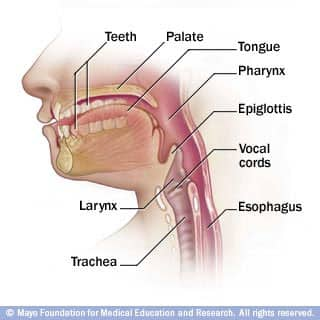
Oral health: What's behind your smile
You use your mouth to speak, eat, kiss and smile, among other tasks. The key to keeping everything working well is good oral health. Having healthy teeth and gums isn't a given, though. Preventing tooth decay and other oral health problems takes effort. Promote good oral health by understanding what's behind your smile — your teeth, gums, tongue and salivary glands.
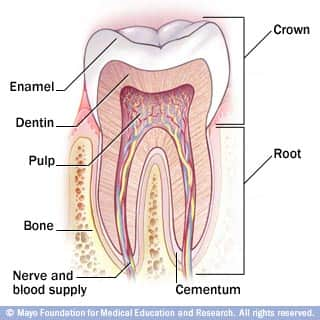
Teeth: From crown to root
Adults have 32 permanent teeth, including wisdom teeth. Each tooth has two main parts — the crown and the root. The crown is the part of the tooth you can see, and the root is hidden below your gums.
Other parts of the tooth include:
Enamel. This hard outer coating protects the crown of the tooth.
Dentin. This hard substance beneath the enamel makes up the bulk of the tooth.
Pulp. This soft tissue is located in the middle of the tooth.
Cementum. This hard tissue covers the root of the tooth and attaches it to the jawbone.
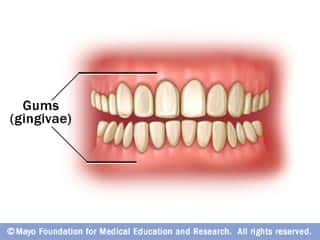
Gums: Pink means healthy
Your gums (gingivae) surround your teeth to help hold them in place. To keep your gums healthy, practice good oral hygiene — brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss your teeth once a day and schedule regular dental visits. If your gums become red and swollen or bleed easily, they could be infected. This is known as gingivitis. Prompt treatment can help restore good oral health. Left untreated, gingivitis can progress to severe gum disease (periodontitis) and possible tooth loss.
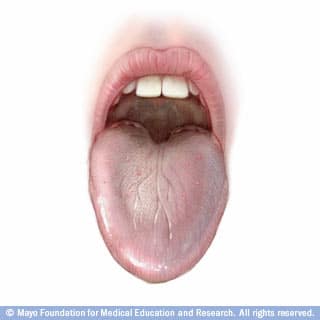
Tongue: From talking to tasting
Your tongue is a muscular organ that helps you speak and move food for chewing and swallowing. Small bumps called papillae (puh-PIL-e) cover your tongue's upper surface. Your taste buds are located in the papillae. Taste buds allow you to enjoy specific tastes, such as bitter, sour, salty and sweet. Your tongue also plays a role in oral health. Food particles can stick to your tongue, causing bad breath and promoting tooth decay. To take good care of your tongue, simply brush your tongue whenever you brush your teeth.
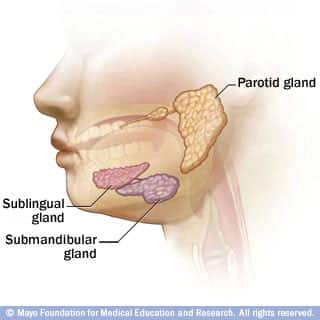
Salivary glands: Aiding digestion, preventing decay
Your mouth has three major pairs of salivary glands — the parotid, sublingual and submandibular glands — as well as many smaller glands. Salivary glands produce and secrete saliva. In addition to helping you swallow and digest food, saliva promotes oral health by:
Flushing food away from your mouth
Stopping acids that can attack tooth enamel
Replenishing minerals in tooth enamel
Killing or reducing disease-causing organisms
© 1998-2017 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved.
2/3/2014
Related Products

Helping dental professionals
More professionals across the world trust Colgate. Find resources, products, and information to give your patients a healthier future













