How do I Know if I Need Orthodontics?
Only your dentist or orthodontist can determine whether you can benefit from orthodontics. Based on diagnostic tools that include a full medical and dental health history, a clinical exam, plaster models of your teeth, and special X-rays and photographs, an orthodontist or dentist can decide whether orthodontics are recommended, and develop a treatment plan that's right for you.
If you have any of the following, you may be a candidate for orthodontic treatment:
- Overbite, sometimes called "buck teeth" — where the upper front teeth lie too far forward (stick out) over the lower teeth
- Underbite — a "bulldog" appearance where the lower teeth are too far forward or the upper teeth too far back
- Crossbite — when the upper teeth do not come down slightly in front of the lower teeth when biting together normally
- Open bite — space between the biting surfaces of the front and/or side teeth when the back teeth bite together
- Misplaced midline— when the center of your upper front teeth does not line up with the center of your lower front teeth
- Spacing — gaps, or spaces, between the teeth as a result of missing teeth or teeth that do not "fill up" the mouth
- Crowding — when there are too many teeth for the dental ridge to accommodate
How Does Orthodontic Treatment Work?
Many different types of appliances, both fixed and removable, are used to help move teeth, retrain muscles and affect the growth of the jaws. These appliances work by placing gentle pressure on the teeth and jaws. The severity of your problem will determine which orthodontic approach is likely to be the most effective.
Fixed appliances include:
- Braces — the most common fixed appliances, braces consist of bands, wires and/or brackets. Bands are fixed around the teeth or tooth and used as anchors for the appliance, while brackets are most often bonded to the front of the tooth. Arch wires are passed through the brackets and attached to the bands. Tightening the arch wire puts tension on the teeth, gradually moving them to their proper position. Braces are usually adjusted monthly to bring about the desired results, which may be achieved within a few months to a few years. Today's braces are smaller, lighter and show far less metal than in the past. They come in bright colors for kids as well as clear styles preferred by many adults.
- Special fixed appliances — used to control thumb sucking or tongue thrusting, these appliances are attached to the teeth by bands. Because they are very uncomfortable during meals, they should be used only as a last resort.
- Fixed space maintainers — if a baby tooth is lost prematurely, a space maintainer is used to keep the space open until the permanent tooth erupts. A band is attached to the tooth next to the empty space, and a wire is extended to the tooth on the other side of the space.
Removable appliances include:
- Aligners — an alternative to traditional braces for adults, serial aligners are being used by an increasing number of orthodontists to move teeth in the same way that fixed appliances work, only without metal wires and brackets. Aligners are virtually invisible and are removed for eating, brushing and flossing.
- Removable space maintainers — these devices serve the same function as fixed space maintainers. They're made with an acrylic base that fits over the jaw, and have plastic or wire branches between specific teeth to keep the space between them open.
- Jaw repositioning appliances — also called splints, these devices are worn on either the top or lower jaw, and help train the jaw to close in a more favorable position. They may be used for temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ).
- Lip and cheek bumpers — these are designed to keep the lips or cheeks away from the teeth. Lip and cheek muscles can exert pressure on the teeth, and these bumpers help relieve that pressure.
- Palatal expander — a device used to widen the arch of the upper jaw. It is a plastic plate that fits over the roof of the mouth. Outward pressure applied to the plate by screws force the joints in the bones of the palate to open lengthwise, widening the palatal area.
- Removable retainers — worn on the roof of the mouth, these devices prevent shifting of the teeth to their previous position. They can also be modified and used to prevent thumb sucking.
- Headgear — with this device, a strap is placed around the back of the head and attached to a metal wire in front, or face bow. Headgear slows the growth of the upper jaw, and holds the back teeth where they are while the front teeth are pulled back.
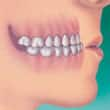 | 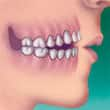 | 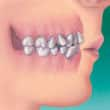 |
| Underbite | OpenBite | Crowding |
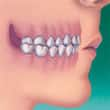 |  |
| Crossbite | Overbite |
11/15/2010










