All oral health articles
561 results





Fluoride
What Does Fluoride Do To Protect Your Smile?
If you've ever wondered what fluoride does to improve your oral health and fight cavities, here's what you need to know.
Read More





















Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Dry Mouth and Bad Breath: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
Some people, however, suffer with bad breath from dry mouth problems, which have little to do with poor hygiene. The good news is, you can take steps to identify and treat the problem, as well as prevent it from recurring.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
3 Foods That Cause Bad Breath and Tips to Fight It
There are many ways to combat it and still enjoy the foods you love. Here are some foods that cause bad breath, and how to control or prevent them from affecting your oral hygiene.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
How To Manage Alcohol Breath
Drinking too much alcohol is bad news for your body and also for your breath. Find out how you can manage and get rid of alcohol breath, here.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
How To Get Rid Of Garlic Breath
Fortunately, there are many things you can do to quickly get your breath under control. Here's how to get rid of garlic breath before an important event.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Using A Tongue Cleaner For A Cleaner Mouth
In addition to using a toothbrush to clean your teeth, you can improve your mouth's freshness by using a tongue cleaner.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Trimethylaminuria And The Fishy Odor
Bad breath, or "mabahong hininga" may be caused by a genetic condition known as trimethylaminuria. Find out more about the causes of trimethylaminuria, treatment, and more.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
What Causes Morning Breath and How to Prevent It
The phone alarm sounds each morning waking you from a restful night's slumber. You rub the sleep from your eyes and then you notice it: morning breath.
Read More
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
How to Clean Your Tongue to Avoid Bad Breath
Cleaning your tongue can leave you feeling refreshed. Learn how cleaning your tongue can improve your breath and discover simple tongue cleaning techniques.
Read More











Cavities
Your Guide to Tooth Decay Stages
Decay worsens over time, and more advanced tooth decay stages require more extensive treatments. If caught early on, you can stop decay in its tracks.
Read More
Cavities
What Is A Gumline Cavity?
Did you know that cavities can form in the holes & grooves of the molars, between teeth, or even along the gumline. Learn more about gumline cavities here.
Read More
Cavities
What Are Incipient Caries?
Incipient caries are the beginning stages of a cavity. Find out more about incipient caries and how you can stop them in their tracks and avoid the drill.
Read More
Cavities
Rampant Caries: What Are They?
Anyone of any age is susceptible to rampant caries, but luckily there are treatments that can restore your oral health. Find out more about rampart caries.
Read More
Cavities
Enamel Decay: How It Starts And How To Stop It
When lactic acid attacks the minerals in your enamel, it turns white – but unfortunately not the white you want. This is the first sign of enamel decay.
Read More
Cavities
What Does Sugar Do To Teeth?
It's not the sugar itself that does the damage, but rather the chain of events that takes place after. Here's how you can prevent tooth decay from hijacking your family's oral health.
Read More
Cavities
5 Ways to Reverse Tooth Decay
If your dentist has told you that you have cavities, it's time to start thinking about ways to reverse tooth decay.
Read More
Cavities
Pit And Fissure Cavity: How To Prevent
Pit and fissure cavity prevention can start right at home. Make sure to brush your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes each session.
Read More
Cavities
What Are The Classes Of Cavities?
In fact, there are six classes of cavities based on the tooth type and the location of the decay, as well as four classifications that describe the severity of decay.
Read More
Cavities
What Does A Cavity Feel Like?
Your teeth might feel sensitive and you might feel some pain, especially after eating sweets, hot foods or cold foods. Learn more here.
Read More
Cavities
Preventing Tooth Decay Disease
The main culprit in tooth decay disease is acid. When food is frequently left on your teeth, bacteria that lives in the mouth wi...
Read More
Cavities
Do Cavity Fillings Hurt?
Do cavity fillings hurt? They shouldn't, although you can expect some tenderness and soreness during the first few days after you get a tooth filled.
Read More
Cavities
Is Your Toothache Caused by a Toothworm?
Once upon a time, dental patients believed a toothache was caused by a tooth worm eating away their tooth from the inside out. Do tooth worms really exist?
Read More
Cavities
Watch Out for These Signs of a Cavity
You bite down and feel a slight twinge in your mouth. Learn all the signs and symptoms of a cavity and why maintaining dental appointments is essential.
Read More
Cavities
What Causes a Cavity on The Front Tooth?
If your child has a cavity on the front tooth or you have one yourself, you may be wondering why it happened and how your dentist might treat it.
Read More
Cavities
What Is a Root Cavity and How Can You Prevent It?
A root cavity occurs on the root of your tooth rather than the enamel. Learn more about how to prevent and treat this type of cavity.
Read More
Cavities
What Is a Smooth Surface Cavity?
A smooth surface cavity is a type of cavity that appears on the sides of the teeth. Here's what you should know about this type of dental decay.
Read More
Cavities
What Should You Do About a Wisdom Tooth Cavity?
If you have a wisdom tooth cavity, you may be wondering if you should get the tooth extracted or filled. Here's what to consider.
Read More
Cavities
Dealing with Dental Pain: When are Antibiotics Necessary?
It's important to get treatment for tooth pain. In some cases, you may need antibiotics for a toothache. Here's what to know before seeing your dentist.
Read More
Cavities
Arrested Caries: What to Know About This Type of Dental Decay
When examining your teeth, your dentist looks for different types of cavities, including arrested caries. Here's what to know about this type of decay.
Read More
Cavities
How To Remineralize Your Teeth
Advertisements have flooded the dental market recently with products that claim to remineralize teeth. But are these items effective? Get your answers here!
Read More






Dry Mouth
Causes Of Dry Mouth And The Problems It Can Create
There are many causes of dry mouth, not to mention a number of related dental problems that it can lead to.
Read More
Dry Mouth
What Is Saliva And Why Is It Important?
What is saliva? You might be surprised to know that it contains much more than just water and serves a host of functions for your health! Learn more.
Read More
Dry Mouth
Dry Mouth At Night: Causes, Symptoms and Home Remedies
Have you ever woken up from a sound sleep with a dry mouth at night? Dry mouth, or xerostomia, can be caused by a variety of conditions and habits.
Read More
Dry Mouth
10 Home Remedies for Dry Mouth
Dry mouth can develop for many reasons: medications, nutritional deficiencies, stress, cancer treatment, and even some systemic diseases. Learn how to help dry mouth here.
Read More
Dry Mouth
How Do Dry Mouth Lozenges Work?
Saliva plays an important role in keeping your mouth healthy. If you have dry mouth, dry mouth lozenges may help stimulate your saliva production.
Read More
Dry Mouth
Dry Mouth And Diabetes: Four Tips for Prevention
Dry mouth and diabetes often go hand in hand, but here are four tips for managing the problem.
Read More
Dry Mouth
Dry Mouth Toothpaste 101: What Is It And How Does It Work?
Dry mouth toothpaste can stave off discomfort and potential health issues. Find out if dry mouth toothpaste can be the remedy for your dry mouth.
Read More






Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom Tooth Extraction
A wisdom tooth extraction is a surgical procedure to remove one or more of your wisdom teeth. Learn what to expect, before during and after the surgery.
Read More







Mouth & Teeth Anatomy
How To Get Rid of A Dry Throat
How To Get Rid Of A Dry Throat Learn about some of the common causes, including allergies, dehydration, the common cold and more.
Read More
Mouth & Teeth Anatomy
What Are The Different Parts Of A Tooth?
Understanding the function of each part of a tooth and the steps required to keep teeth healthy with regular checkups are important components of oral health education for you and your family.
Read More
Mouth & Teeth Anatomy
Do You Know All The Human Teeth Names?
Get a better understanding of the human teeth names, each tooth's location in the mouth and how you use them in daily functions.
Read More














Teeth Whitening
How Does Coffee Stain Teeth & How You Can Prevent It
Most of us can't live without a daily dose of coffee to jump start the day, but could the beverage that puts morning smiles on… Read more at Colgate.com
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Does Tea Stain Teeth?
We know that coffee can stain those pearly whites, but does tea stain teeth? The answer is yes. In fact, tea might be even more… Read more at Colgate.com
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Are Teeth Whitening Strips Your Best Option?
Everybody wants that million-dollar smile, and with new teeth whitening products debuting on the market every year, companies ar...
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Does Charcoal Teeth Whitening Work?
Charcoal toothpaste is a hot topic, but does charcoal whiten teeth? But does charcoal teeth whitening work?
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How to Whiten Yellow Teeth: 5 Top Tips
Whether the discoloration is due to staining or other factors, learn how to get rid of yellow teeth through over-the-counter products and professional whitening from the dentist.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Should You Try DIY Teeth Whitening Paste?
Tooth whitening is the process which lightens teeth, helps remove stains, and corrects tooth discoloration. Learn more on teeth whitening procedures, types, risks, and more.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Professional Teeth Whitening at the Dentist: What to Ask
One of the most popular dental procedures now desired by patients is professional teeth whitening as it is known as. With patients retaining their teeth...
Read More
Teeth Whitening
What Causes Green Tooth and Other Tooth Discoloration?
Tooth discoloration like a green tooth can occur under many circumstances. These stains may be extrinsic or intrinsic.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How To Whiten With Braces
Knowing how to whiten teeth with braces on isn't impossible, but special care must be taken to ensure treatment is successful. Here are three options.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is LED Teeth Whitening Right For You?
The process is minimally invasive and can offer great results. LED teeth whitening is a popular option for achieving a brighter smile, but is it the best at-home treatment for you?
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is The Cost Of Professional Teeth Whitening Worth It?
If you've considered whitening your teeth, you may already know the professional teeth whitening cost can be high — much more expensive than at-home alternatives. Learn more here.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is Teeth Whitening Safe?
Many people wish their teeth were whiter, but are nervous about bleaching treatment. So, is teeth whitening safe? Yes, save three common side-effects.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is UV Teeth Whitening Safe?
Is UV teeth whitening safe to do yourself at home? Find out more about UV teeth whitening including safety information and alternatives.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is Professional Teeth Whitening Right For You?
Professional teeth whitening can give excellent results for many of us who have healthy teeth with stubborn stains and yellowing.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Five Foods that Cause Stains and Six Foods that Prevent Them
Watch what you eat and drink because certain foods and beverages cause discolored teeth.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Breaking Down Laser Teeth Whitening Cost
Laser teeth whitening is a highly effective way to whiten your teeth. It's becoming more popular among average people.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
The Best Whitening Mouthwash: What to Look For
What is the best whitening mouthwash out there and is using it going to help you get a brighter smile? Find out here!
Read More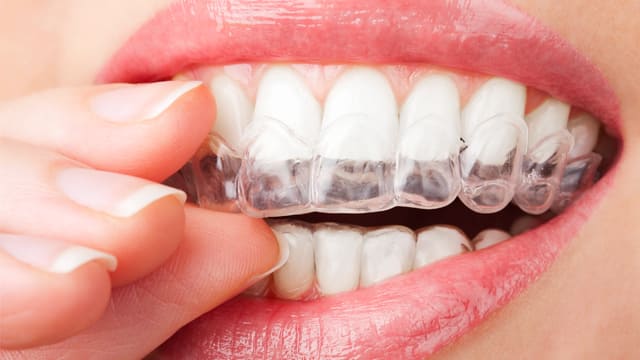
Teeth Whitening
How Custom Whitening Trays Brighten Your Smile
If your teeth aren't as white as you'd like, there are safe and simple ways to improve it. One of them involves custom whitening trays.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How To Maintain White Teeth
Whether you already have white teeth or you've just completed a whitening treatment, keep in mind that you've still got some wor...
Read More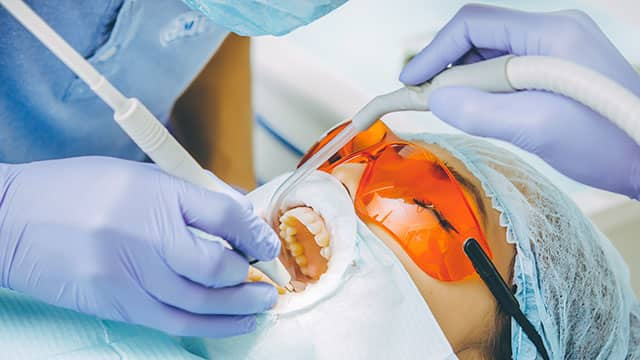
Teeth Whitening
What are the best Instant Teeth Whitening Options?
Here are your options, including the fastest teeth whitening treatments, and the ones that take some time.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
3 Tips For Preventing Teeth Stains From Braces
Learn about our top 3 tips for preventing teeth stains from braces and whitening your teeth evenly once they come off.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How to Safely Use a Tooth Whitening Gel at Home
With the guidance of your dentist you can safely and effectively brighten your smile at home with a tooth whitening gel. Over-the-counter gels or a gel...
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Is Laser Teeth Whitening an Option For You?
Laser teeth whitening may be an option available at your dental office, but the treatment is not for everyone. Learn more about laser teeth whitening here.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
What Are the Benefits of Turmeric for Your Teeth?
Does turmeric for teeth whitening actually work? Read on to learn more about turmeric, if it whitens teeth and if there are other oral health benefits.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How Your Smile Can Boost Your Self Confidence
No matter what profession you’re in, it’s important to have a confident smile. Here are some insights on how your smile can boost your self-confidence
Read More
Teeth Whitening
What Are the Different Types of Teeth Whitening Products?
Here is a quick guide to the most popular teeth whitening products, including tips on what to look for, how they work and causes of tooth stains. Dive in!
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How to Get Rid of Teeth Sensitivity After Whitening
Do sensitive teeth after whitening sound familiar? There are many ways to get rid of sensitivity caused by whitening treatment so that you can enjoy your smile.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Home Remedies for Teeth Whitening: What Works & What Doesn't
Get whiter teeth at home with these all-natural Home Remedies for Teeth Whitening. Taking just minutes, they are an easy way to get a natural smile makeover.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Teeth Whitening in the Philippines: Cost, Procedures, and What to Expect
Find out how much teeth whitening will cost, and the different options that you have at home and clinic. You'll be on your way to a brighter smile in no time!
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Tips on How to Smile for Photos
A smile can make your photos look so much better. By following these tips on how to smile for photos you will be a pro in no time with advice on brighter teeth
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Make-Up Tips For Whiter Teeth
Learn how to use make-up to enhance your teeth and make it look white
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Lipstick Color For Whiter Teeth: How Makeup Can Help Brighten Your Smile
Enhance your smile and whiten your teeth by using different shades of lipstick.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
How Does Purple Toothpaste Whiten Teeth
Dive into the innovative world of Colgate® Optic White® Purple Toothpaste and discover how it uses the principles of color theory to brighten your smile.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Will Purple Toothpaste Turn My Teeth Purple?
Dive into the innovative world of Colgate® Optic White® Purple Toothpaste and discover how it uses the principles of color theory to brighten your smile.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Debunking the Myth: Are Yellow Teeth Truly Stronger?
Discover the truth behind the belief that yellow teeth are stronger and learn how Colgate Optic White Purple Toothpaste can effectively brighten your smile without any staining.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Why Stop at Purple Shampoo? Extend Color Correction to Your Smile with Purple Toothpaste!
Fans of purple shampoo, take your color correction further! Colgate Optic White Purple Toothpaste makes your smile as radiant as your hair, effortlessly.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Transform Your Beauty Routine: The Science of Color Correction Across Hair, Skin, and Teeth
Fans of purple shampoo, take your color correction further! Colgate Optic White Purple Toothpaste makes your smile as radiant as your hair, effortlessly.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Why Teeth Turn Yellow: Causes and Preventive Strategies
Fans of purple shampoo, take your color correction further! Colgate Optic White Purple Toothpaste makes your smile as radiant as your hair, effortlessly.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Bakit Nangingilaw ang Ngipin: Mga Dahilan at Paano Ito Maiiwasan?
Fans of purple shampoo, take your color correction further! Colgate Optic White Purple Toothpaste makes your smile as radiant as your hair, effortlessly.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Teeth Whitening Serum: An Easy Path to a Brighter Smile
Discover how teeth whitening serum can brighten your smile. Learn about its benefits, usage tips, and more.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
White Spots on Teeth: What Causes Them and How to Treat It
Don't let discoloration keep you from smiling. Like most oral issues, figuring out how to get rid of white spots on teeth may be easier than you thought.
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Brighten Your Smile This Holiday Season with Everyday Foods and Colgate Fresh Confidence
Discover how to polish and brighten your smile this holiday season with Colgate Fresh Confidence and a guide to teeth-friendly festive foods. Perfect for the Filipinos looking to shine!
Read More
Teeth Whitening
Gentle on Gums: Keeping Your Holiday Smile Bright with Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal
Celebrate the holidays without worrying about your gums. Learn how the ultra-soft Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal toothbrush can be part of your festive oral care routine.
Read More



















Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
What Causes White Spots On Baby Teeth?
Although you don't want to panic, you do want to take action if you see white spots on baby teeth. Here are two reasons these blemishes may develop.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Natural Toothache Pain Relief for Your Child
Whether your bunso complains of a loose tooth after playing in playground or your older child has unexpected tooth pain in the night, you can naturally and effectively administer toothache pain relief until you can visit with a dentist.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Kids' Teeth And Cavity Protection
Even if you had cavities when you were young, your child doesn't have to develop them. Find out how to protect kids' teeth from tooth decay.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Top Teething Remedies For Babies: Helping Your Little One Overcome The Pain
When your baby's first tooth breaks through the gums, you have both reached an exciting milestone. But it's a painful one. These remedies can help.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Baby Bottle Tooth Decay
In infants, tooth decay is commonly referred to as baby bottle tooth decay. This occurs when sugars from food & liquids attach to teeth for periods of time.
Read More
Oral Care: Kids (5-12)
Toddlers and Bleeding Gums: What Should You Do?
Toddlers and bleeding gums don't have to be a cause for alarm, but they're definitely a warning sign that your little one's oral habits should be improved.
Read More



Tooth Extraction
Pain After Having A Tooth Removed: 3 Tips To Help Your Kids Keep Brushing
Read More


Tooth Extraction
Tooth Extraction: What You Need To Know
Tooth extraction, or "pag-bunot ng ipin" is the removal of a tooth from its socket in the bone. If you are facing a tooth extraction, it can seem a little daunting and nerve-wracking.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
What Products Are Available From My Dentist For Home Tooth Whitening?
Read More

















Dental Product Guidance
Mouthguards: Everything You Need To Know
Dentists might recommend mouth guards for their patients who grind their teeth at night, play contact sports, or have TMJ problems or sleep disorders.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
How to Choose Whitening Toothpaste for a Brighter Smile
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Are Electric Toothbrushes Better Than Manual Toothbrushes?
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
A Guide to Have a Beautiful Smile for Your Date Night
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Electric Toothbrush Buying Guide: Everything You Need to Know
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Electric Toothbrush for Braces: A Complete Guide
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
How Electric Toothbrushes Help Treat Receding Gums
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
How to Travel with an Electric Toothbrush: The Ultimate Guide
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More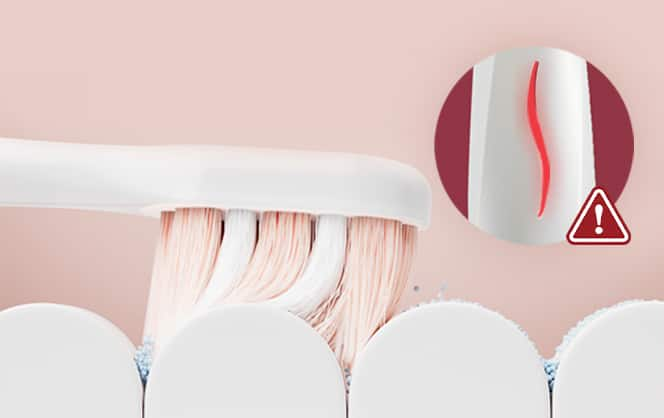
Dental Product Guidance
Electric Toothbrush with Pressure Sensor for Sensitive Teeth: Find Out if It Is Right for You
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Do electric toothbrushes whiten teeth faster than manual?
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
How to Build a Healthy Oral Care Habit With a Timed Electric Toothbrush
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
What Are Sonic Electric Toothbrushes, and Why Are They Essential?
The best toothpaste to use for fast results depends on your oral care needs. Here are four things to keep in mind when making a selection.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Should You Try Coconut Toothpaste?
Should you seek oral care products that contain coconut? Learn more about the health benefits of coconut for your oral health.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Using Tartar Control Toothpaste For Healthy Teeth And Gums
Brushing your teeth properly using tartar control toothpaste regularly is an important part of establishing and maintaining good oral health.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Should You Buy A Vibrating Toothbrush?
There are many types of electric toothbrushes, including vibrating toothbrushes. Learn what to consider when selecting a new toothbrush. Here's what to consider when selecting a new toothbrush.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Should You Consider a Water Flosser?
Traditional string floss isn't the only way you can clean the hard-to-reach areas. Water flosser can help with this task. Learn more now. If you have difficulty using string floss, talk to your dentist about alternatives, like a water flosser.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
What Is In Toothpaste? 5 Key Ingredients Explained
Discover the history and evolution of toothpaste, learn about the key ingredients, and get practical tips for selecting the right toothpaste for you.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Does Mouthwash Expire?
Does mouthwash expire? Walang forever, including that bottle of mouthwash you have stashed away. Learn more about the shelf life of mouthwash.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Should You Use Homemade Toothpaste?
Is it a good idea to make your own toothpaste? Here's what you need to know before you decide to make homemade toothpaste and how it compares.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
The Facts About Abrasive Toothpaste
Abrasive toothpaste can damage tooth enamel. Here's how you can keep your enamel safe from abrasive toothpaste ingredients.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
What is a Toothpaste Color Code?
One popular hoax in recent years had to do with a toothpaste color code on the bottom of the tubes. Find out what the toothpaste color code really means.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Teeth Whitening Pens 101
If you're looking for a last-minute touch-up to your smile, a teeth whitening pen might be just the thing. Here's what makes it work, and how to use it.
Read More
Dental Product Guidance
Bright Smiles and Style: Gifting Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal
Choose a gift that's both adorable and essential. The Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal toothbrush with its minimalist design and soft bristles fits every bathroom and every smile.
Read More


Mouth Sores and Infections
Mouth Sores and Canker Sores: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Read More











Mouth Sores and Infections
Dental Abscesses and Gum or Tooth Infections: What You Need To Know
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
What A Gum Boil (Singaw) Could Mean For Your Dental Health
If you notice anything strange in your mouth, such as a gum boil or a bump that looks like a pimple, it's a good idea to have it checked out by a dentist.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
What a Sore Throat and Tongue Can Mean
Having a sore throat is uncomfortable and inconvenient, and even more so when accompanied by a sore tongue. The combination of a sore throat and tongue isn't a rare symptom of certain conditions, but your diagnosis depends on the other signs and symptoms you experience.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
What Are Tonsil Stones?
Tonsil stones, clinically called tonsilloliths, are small, white discharges that form in the crevices of the tonsils. They are typically found on the surfaces of the pharyngeal tonsils on either side at the back of the throat. They can be as small as a grain of rice or as large as a pea. They are quite common and usually harmless, but they may spark alarm in patients when noticed for the first time.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
How Salt Water Mouth Rinse Benefits Oral Health
A salt water mouth rinse is useful for a number of different reasons. It's a great option for anyone who has a sore throat, gum sores or recently underwent dental procedures. It doesn't take the place of modern dental hygiene, but is used as a supportive measure for adults and children alike.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
Canker Sore Vs. Cold Sore: Spot The Differences
It can be hard to differentiate between a canker sore vs. cold sore. Visit Colgate Philippines now and learn the differences, prevention and treatments.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
Tooth Abscess
A tooth abscess is a bacterial infection found in the inner part of the tooth. Learn more about common causes, symptoms and how to prevent a tooth abscess.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
What Causes a Black Spot on Your Gums?
A dark spot on gums may look concerning. Fortunately, in the vast majority of cases these spots are benign and easily explainable. Let's consider some of the more common conditions that might cause gum discoloration and what can be done about them.
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
White Patches on Gums: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
White patches on gums are whitish spots that may signal thrush, leukoplakia, canker sores, or gum irritation. Learn the common causes and risks
Read More
Mouth Sores and Infections
Understanding Periodontal Abscess: Causes, Signs & Treatment
A periodontal abscess is a painful gum infection caused by bacteria in deep pockets around teeth, linked to swelling, redness, and severe discomfort.
Read More


Dental Health Threats
Dental Grills — The New Trend Affecting Dentistry And The Health Of Your Teeth
Read More


Dental Health Threats
Rotten Teeth: Symptoms And Treatment
How can you tell if you have rotten teeth? Can a dentist save them and make your mouth healthy again? Learn the signs and treatments for rotten teeth.
Read More
Dental Health Threats
Q&A ON COLGATE-PALMOLIVE LABORATORY AND CLINICAL RESULTS ON EFFECTS OF TOOTHPASTE AND MOUTHWASH ON COVID-19 VIRUS
Can toothpaste and mouthwash neutralize and reduce the virus that can cause COVID-19 in your mouth? Read more on this new Colgate-Palmolive research for toothpaste and mouthwash effects on the COVID-19 virus.
Read More
Dental Health Threats
How Mouth Spray Helps Dry Mouth
A mouth spray may be good option if you need short-term relief of dry mouth. Learn how sprays work and what you can do for longer-term solutions, here.
Read More
Dental Health Threats
Q&A ON COLGATE-PALMOLIVE LABORATORY AND CLINICAL RESULTS FOR EFFECTS OF TOOTHPASTE AND MOUTHWASH ON COVID-19 VIRUS
Can toothpaste and mouthwash neutralize and reduce the virus that can cause COVID-19 in your mouth? Read more on this new Colgate-Palmolive research for toothpaste and mouthwash effects on the COVID-19 virus.
Read More



Pain Management (Anesthesia)
Dental Anesthesia: Understanding Types, Side Effects, Risks, and Precautions
Read More







Diabetes & Other Endocrine Disorders
Prevent Diabetes Problems, Keep Your Teeth And Gums Healthy
Read More

Diabetes & Other Endocrine Disorders
Can You Get Diabetes from Eating Too Much Sugar?
Can you get diabetes from eating too much sugar? The answer is complicated, but diets and lifestyles can lead to this disease. Learn more, here.
Read More









Respiratory Conditions
Post Nasal Drip and Bad Breath
A common cause of bad breath is post-nasal drip, which involves mucous secretions from your nose and throat. Click here to learn more about the causes and ways to prevent it.
Read More









Early Orthodontics (Braces)
Braces Colors: How To Choose Your Perfect Shade
Braces colors abound! How can you pick the right color for your braces? Learn more here.
Read More
Early Orthodontics (Braces)
5 Most Common Questions Kids Have About Braces
Getting braces can be a stressful endeavor for parents and children. Take a look at some of the best ways to combat the fear.
Read More
Early Orthodontics (Braces)
Early Orthodontics
Learn more about common orthodontic issues in children and orthodontic treatments, including alignment, kids braces, and much more, from the Colgate Oral Care Center.
Read More
Early Orthodontics (Braces)
Why Does My Child Need a Palate Expander?
Is a palate expander necessary? Is it painful? What does it do? Find out more about how this treatment can help guide the growth of your child's mouth.
Read More
Dental Emergencies & Sports Safety
Dental Abscess Explained: Causes, Symptoms & How to Treat It
Read More











Dental Emergencies & Sports Safety
Can I Use Clove Oil for Toothache Pain?
Using clove oil for toothache pain can provide you with relief now, but it doesn't last as long as treatment from your dentist. Here's why.
Read More




Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
Adult Braces Before And After: What To Expect When They Come Off
Read More


Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
Benefits of Teeth Retainers: Post-Braces Essentials for a Healthy Smile
Read More



Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
How Much Braces Cost and Finding Payment Solutions
Fortunately, there are usually ways to bring down the cost or at least spread out the expense with a payment plan. Here are some ways to make paying for braces fit into the budget.
Read More
Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
What Are Lingual Braces?
Lingual braces, one of the more recent forms of orthodontic work, is proving popular for people conscious about having visible braces.
Read More
Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
Should You Use Mouthwash Before or After Brushing?
Should you use mouthwash before or after brushing? Here's the answer that will help you improve your daily oral care routine.
Read More
Adult Orthodontics (Braces)
Embrace the Holiday Season with a Braces-Friendly Feast and Colgate Fresh Confidence
Read More









Oral Care: Adults (18+)
What Is Referred Tooth Pain?
Sometimes a toothache isn't all it seems. Pain that feels as though it's coming from a tooth may be referred tooth pain. Learn more about it, here.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
What To Do About Black Teeth Stains
Learn more about the causes of your black stains on teeth and stop them at the source and bring back your shiny white smile.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Taking Care Of Swollen, Bleeding Gums
When swollen, bleeding gums cause discomfort, there may be several reasons.
Read More











Oral Care: Adults (18+)
What Causes A Swollen Gum Around One Tooth?
It's common to suddenly spot something you didn't notice before. How, for example, could a swollen gum around one tooth form? Here are three explanations.
Read More


Oral Care: Adults (18+)
New Year, New Smile: Achievable Resolutions for a Healthier Smile with Colgate
Embrace the New Year with a commitment to better oral health. Discover simple, effective resolutions with Colgate's oral care range to keep your smile bright all year long.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Fresh Start for Your Smile: Oral Care Essentials for the New Year
Kick off the New Year with achievable resolutions for better oral health. Learn how to create a dental routine you can stick to with Colgate Fresh Confidence White Blast and track the positive changes month by month.
Read More
Oral Care: Adults (18+)
Festive Cheers Without the Fears: Protect Your Smile This Holiday Season
Indulge in the holiday spirit the Filipino way, while keeping your smile bright and healthy. Learn how Colgate Fresh Confidence White Blast helps you maintain oral health during the festive season.
Read More





Oral Cancers
How Lymphoma Can Affect Your Oral Health
Lymphomas are cancers that affect the lymphatic system, an important part of the body's immune system and blood network. Learn more today.
Read More







Pregnancy Oral Care
Oral Health During Pregnancy
To avoid a toothache during pregnancy, or any other dental problem when expecting a baby, your best strategy starts with a dental visit.
Read More
Pregnancy Oral Care
7 Ideas For Healthy Pregnancy Lunches
With unexpected cravings and bouts of nausea, pregnancy can be a tough time for healthy eating. Here are some ideas for healthy pregnancy lunches.
Read More
Pregnancy Oral Care
Antibiotics During Pregnancy: Is It Safe?
If pregnant, you're likely watching your health, but do you know if you can take antibiotics during pregnancy? Learn more about antibiotics and pregnancy.
Read More
Pregnancy Oral Care
Is A Tooth Extraction During Pregnancy Safe?
Can you safely undergo a tooth extraction during pregnancy? The answer, as far as medical professionals are concerned, is yes. Learn more, here.
Read More
Pregnancy Oral Care
Swollen Gums During Pregnancy
Learn more about caring for swollen gums during pregnancy and the necessary questions to ask your dentist.
Read More
Pregnancy Oral Care
Relief For Dry Mouth During Pregnancy
What can you do about dry mouth during pregnancy? While dry mouth may not be as talked about as other common pregnancy symptoms, that dry, sticky...
Read More











Plaque & Tartar
Black Tartar On Teeth
Black tartar on teeth forms below the gum line and causes many dental issues. Though it isn't difficult to treat, only dentists can remove it.
Read More
Plaque & Tartar
Flossing: Do I Really Have To?
Maintaining proper oral hygiene requires the cultivation of several good oral care habits which, when performed together.
Read More










Digestive (Gastrointestinal) Disorders
Celiac Mouth Sores: How To Recognize And Manage Them
Read More





















Nutrition & Oral Health
Is Milk Good for Your Teeth?
Dairy products keep your teeth as healthy as your bones throughout your life. So, is milk good for your teeth? The answer is a resounding yes, and here's why.
Read More

Nutrition & Oral Health
10 Easy and Fun Filipino Media Noche Traditions for a Joyful New Year
Embrace these 10 simple and delightful Filipino traditions for Media Noche to welcome the New Year with joy and prosperity. From wearing polka dots to a symbolic door opening, celebrate with these unique customs.
Read More
Nutrition & Oral Health
Inuman Na! Understanding Alcohol's Impact on Dental Health
Find out how your favorite drinks, from tuba to gin, affect your teeth. Learn simple ways to enjoy them while taking care of your ngiti with tips and Colgate products.
Read More
Nutrition & Oral Health
Savor the Yuletide: Nutrient-Packed Filipino Christmas Foods
Revel in the rich flavors of Filipino Christmas dishes and their hidden nutritional treasures. Plus, discover a simple way to maintain a healthy smile during the feasts!
Read More




Brushing & Flossing
Oil Pulling As A Detox Mouthwash? The Effectiveness Of Natural Oral Care Remedies
Read More




Brushing & Flossing
Garlic & Tooth Pain
Garlic can be used to reduce or stop the pain from toothache because if can kill the bacteria in your mouth. Find out how to use it properly for your tooth pain.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
If Your Gums Bleed When You Floss, Should You See Your Dentist?
If you notice bleeding gums when flossing, then should you call your dentist? Gums that bleed after daily flossing can be a warning sign of gingivitis,...
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Safe Storage for Your Toothbrush: Best Practices
Safe storage for family toothbrushes isn't difficult or complex, but it can help keep extra germs and contaminants away from your toothbrushes and your mouth.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Why Daily Flossing Is Important to Your Oral Care Routine
Flossing is important in maintaining healthy gums and preventing periodontal disease, as well. Learn more here.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
All About Silicone Toothbrushes
Having the right toothbrush is just as important as the act of brushing your teeth. Learn about whether a silicone toothbrush is right for your oral health.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Can an Electric Flosser Make Flossing Easier?
Flossing is an essential part of an oral hygiene routine, but it can be difficult for some people. An electric flosser might make the task easier.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Do I Need Toothbrush Sanitizer?
Is a toothbrush sanitizer necessary to keep your oral hygiene routine clean at home and on the go? Find out more about toothbrush sanitizers here.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Flossing: How Important Is Flossing to You?
How important is flossing to you? Many people hate flossing. Why? Because for many, it may be a challenging task. Here's why you shouldn't skip this step.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Using a Floss Threader: Flossing Made Easier
Do you avoid flossing because you have braces, a dental bridge or a permanent retainer? A floss threader may be just the too.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Waxed or Unwaxed Dental Floss? Assessing Your Oral Health Needs
Waxed and unwaxed dental floss are two of the most common types, and they both have their merits. Here's how they differ and how to know which to use.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
3 Possible Causes of Tooth Pain After Brushing
Do you have pain after cleaning your teeth? Pain from brushing and flossing may be a sign that there is something wrong with your oral health or with.
Read More
Brushing & Flossing
Replace Your Toothbrush Head Already!
Find out when you need to replace your toothbrush head and the importance of a fresh brush head to your oral health.
Read More







Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Dental Scaling And Root Planing To Keep Your Teeth And Mouth Clean
Read More














Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Gum Inflammation Linked To Other Diseases
Oral and gum inflammation indicate not only decreased oral health, but also other health problems. Learn more from Colgate. Learn more.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
When Do My Teeth Need a Deep Cleaning?
Your dentist may say you need a teeth deep cleaning. But what is it and why would you need it? The process addresses gum disease in the following way:
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
What Is The Best Toothpaste For Gingivitis?
What is the best toothpaste for gingivitis? Brushing with the right toothpaste can help to protect against gingivitis and prevent the later (and more...
Read More.png)
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Gingivitis: Overview And Prevention
Gingivitis is a treatable and reversible form of gum disease. It is the first and mildest stage.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Successful Treatments For Periodontal Disease
Today, with so many successful treatment options available for advanced periodontal disease, losing teeth doesn't have to be your next step with an unhealthy gumline.
Read More.png)
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Are Your Teeth Bleeding? No, Your Gums Are
Learn about causes of teeth bleeding, ways to gently relieve the discomfort and methods to stop the bleeding.
Read More.png)
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
How To Fight Gingivitis In Three Easy Steps
Gum disease is very common. If you want to know how to fight gingivitis, it's as easy as one-two-three: brushing, flossing and professional cleanings.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Why Are My Gums Bleeding? Understanding Causes & Treatment
Bleeding gums when you brush or floss is often an early symptom of gingivitis, which can lead to advanced stages of gum disease.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Can Receding Gums Grow Back?
Gum recession happens for a number of reasons, from brushing your teeth with too much pressure to grinding your teeth. Learn more about what causes gums to recede and how to treat it here.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
How to Cure Gingivitis
People seeking a gingivitis home remedy cure have a variety of options available to alleviate their pain, or prevent the problem entirely.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Mouthrinse for Gum Disease: Another Good Tool
Although gum disease comes from bacteria living in your mouth, mouthwash for gum disease is actually the ideal complement to traditional oral care.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Sore Gums: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Worried about bleeding or sore gums? Find out what may be causing them and what you can do to prevent gum pain and damage. Learn more.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Why Do You Have Itchy Gums?
The most likely reason for your itchy gums is plaque. check-in with your dentist so they can properly examine your gums and teeth.
Read More



Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
This Year, Show Some Love to Your Gums with Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal
Dive into the unsung hero of oral health – your gums! Learn how the Colgate Cushion Clean Charcoal toothbrush can help you focus on gum care this New Year.
Read More
Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
10 Causes of Bleeding Gums You Should Know and How to Treat Them
Bleeding gums are a common sign of gum issues. Discover what causes them and how to treat each cause effectively to protect your oral health
Read More



















Tooth Sensitivity
How Does Mouthwash For Sensitive Teeth Work?
Regular rinsing with mouthwash for sensitive teeth can actually bring relief to many who suffer from tooth sensitivity or pangingilo. Here's how it kills the pain.
Read More
Tooth Sensitivity
How Tooth Nerve Pain Occurs
Here are some foods and drinks to avoid when suffering from tooth pain, and some insight into how the nerve becomes exposed in the first place.
Read More
Tooth Sensitivity
Sensitive Gums vs. Sensitive Teeth
Find out how teeth sensitivity is caused and how you can not only treat sensitivity but prevent it in the future. Visit Colgate PH and find out more now! Find out how teeth sensitivity is caused, and how you can not only treat sensitivity, but prevent it in the future. Find out more, today!
Read More
Tooth Sensitivity
The Best Toothpaste For Sensitive Teeth: What's In It?
And although many over-the-counter toothpastes contain fluoride, your dentist can prescribe high-strength fluoride toothpastes to treat tooth sensitivity in particular.
Read More























Oral Care: Babies (0-4)
Teething Gel: Cautions And Alternatives
Because it causes pain, teething can be a challenging time for both parent and child. In the past, the application of teething.
Read More











