Knowing how to treat periodontal abscess is important because quick action can prevent the infection from spreading and protect your oral health. Read on to understand what a periodontal abscess is, its symptoms, causes, and treatment methods, as well as prevention tips so that you can maintain a healthy smile.
What is a Periodontal Abscess?
A periodontal abscess occurs when a bacterial infection penetrates deep into the gum tissues, often due to untreated gum disease, injury, or poor oral hygiene. A periodontal abscess involves a localized infection within the periodontium, which includes the gums, ligaments, and supporting bone.
It causes pus in gums to accumulate, creating pressure that leads to pain and swelling. One of the common pus in gums causes is the trapping of food particles or plaque in deep gum pockets, which allows bacteria to multiply rapidly.
Unlike mild gum irritation, a periodontal abscess is an advanced condition that requires professional dental treatment. The swelling may be localized or extend to surrounding areas, and if left untreated, it can damage both soft tissue and bone. Dentists often diagnose it through clinical examination and imaging, ensuring accurate identification before beginning treatment.
Difference Between Periodontal and Periapical Abscess
Although both periodontal and periapical abscesses involve infections, they are not the same. A periodontal abscess develops in the gum tissues surrounding a tooth, typically due to gum disease. In contrast, a periapical abscess originates at the tooth root, usually as a result of deep decay or trauma, and is a type of tooth abscess or a dental abscess.
The symptoms of periodontal and periapical abscesses may overlap, but treatment varies depending on the type. For example, periodontal abscess treatment focuses on gum cleaning and infection control, while a periapical abscess might require root canal therapy. Dental professionals often rely on X-rays and a detailed oral examination to distinguish between the two.
Early Signs and Symptoms of a Periodontal Abscess
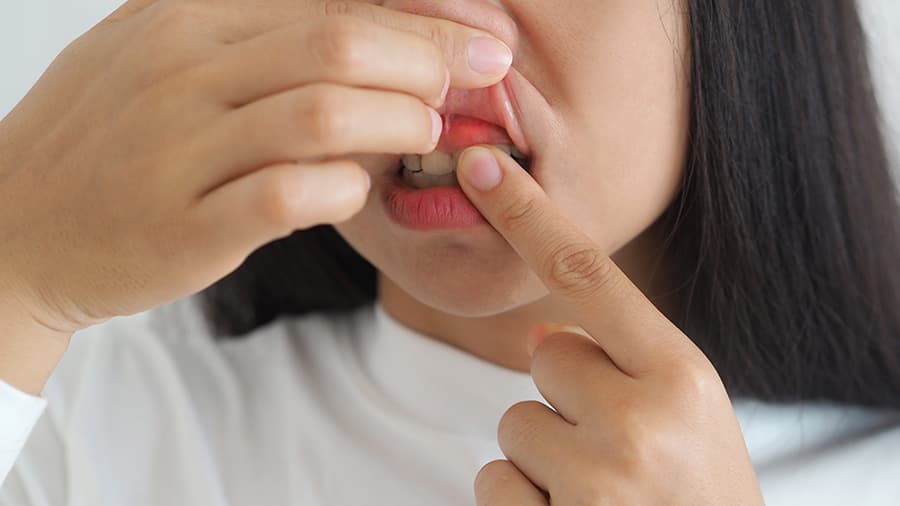
Recognizing early signs is essential for preventing complications. One noticeable symptom is visible pus in gums, often appearing as a whitish or yellowish spot on the gum surface. Other periodontal abscess symptoms include gum swelling, redness, tenderness, and pain that worsens when chewing.
Some people experience bad breath or a persistent bad taste caused by pus drainage. The gum may also feel warm to the touch and appear shiny. In advanced cases, the abscess can cause tooth mobility or swelling in the face and jaw, signaling that the infection is spreading.
Main Causes of Periodontal Abscess
Poor oral hygiene is the leading cause, allowing plaque and calculus buildup that leads to periodontal disease. Untreated gum disease progresses to deep gum pockets where bacteria thrive, resulting in infection. This is why periodontal abscess causes are often linked to neglected dental care. Another pus in gums cause is gum injury from aggressive brushing, flossing, dental procedures, or food particles lodged between teeth.
Bacteria can accumulate around the affected tooth, especially if there is deep periodontal pocketing. People with weakened immune systems or conditions like diabetes are more vulnerable. Additionally, incomplete dental treatments that fail to remove all bacteria can trigger abscess formation. Maintaining consistent oral hygiene reduces these risks significantly.
Several lifestyle and health factors can significantly increase your risk of developing a chronic periodontal abscess. Habits like smoking not only reduce blood flow to the gums but also slow the healing process. A lack of proper nutrition further limits the vitamins and minerals needed to maintain gum health.
Common risk factors include:
Smoking – Reduces blood flow to the gums, slowing healing and weakening the body’s ability to fight off infections.
Dry mouth - Conditions like dry mouth can reduce saliva’s protective effect, increasing the risk of gum infections.
Poor nutrition – Lacking essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, which is crucial for gum repair.
Medical conditions like diabetes or immune disorders – Make it harder for the body to resist bacterial infections.
Skipping regular dental visits – Allows gum disease to develop silently and progress unnoticed.
Pericoronitis - In rare cases, conditions like pericoronitis, which affect partially erupted wisdom teeth, can contribute to abscess development.
Untreated tooth decay - Untreated tooth decay can spread below the gumline, increasing the risk of an abscess.
It is important that everyone understands why oral health is important for healthy living, as it helps to take care of oral hygiene and prevents pus in gums and other infections in the mouth. Regular dental checkups are also essential to get the right treatments for dental problems at the right time.
Leaving a periodontal abscess untreated can have serious consequences. The infection may spread to adjacent teeth, the jawbone, or even the bloodstream, which raises the question: “Is pus in gums dangerous?” The answer is pus in gums can get dangerous if neglected, and can cause systemic infections and affect overall health.
In extreme cases, untreated abscesses can contribute to serious health problems such as endocarditis (a type of heart disease) or complications in people with diabetes. Early dental intervention not only preserves oral health but also prevents life-threatening situations.
How is a Periodontal Abscess Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of periodontal abscess begins with a visual examination to assess swelling, redness, and drainage. Dentists probe the gums to check pocket depth and identify infection sites. X-rays help determine bone loss and confirm the presence of an abscess, which is vital for the management of periodontal abscess.
Dentists may also review your medical history to identify underlying risk factors. Temporary relief methods or home remedies, including saltwater rinses, can be part of periodontal abscess home treatment, but these should not replace professional care.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Abscess
Usually, the first step in periodontal abscess treatment is draining the infection to relieve pressure and pain. This may be done by gently opening the gum tissue and cleaning out debris. Scaling and root planing are performed to remove plaque and tartar from beneath the gumline. If the infection has compromised the tooth pulp, which is made up of blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissues, root canal treatment may be necessary alongside gum therapy.
Since a periodontal abscess often develops as a complication of untreated periodontitis, early intervention is crucial. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed by healthcare professionals to eliminate bacteria and reduce swelling. Supportive pus in gums treatment at home includes warm saltwater rinses and avoiding hard foods. Complete recovery often requires follow-up visits to ensure the infection is gone and the gum tissue has healed properly.
How to Prevent Periodontal Abscess?
Good oral hygiene practices form the foundation of periodontal abscess cure. Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss to remove debris between teeth, and use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacterial buildup.
Prevention also includes scheduling dental check-ups every six months for professional cleaning and early detection of gum problems. These habits are also part of how to get rid of pus in gums before it becomes a major infection.
When to See a Dental Professional
You should see a dentist immediately if you experience symptoms such as persistent pain, swelling, or visible pus. This is particularly important for individuals dealing with a chronic periodontal abscess, as prompt care can prevent the condition from worsening. Those currently trying periodontal abscess home treatment with over-the-counter products for temporary relief should still seek professional help to avoid complications.
Delaying care for an infected tooth can allow the abscess to spread to surrounding tissues. Delays in taking the required treatments can worsen the conditions and may require tooth extraction. Early dental intervention can stop the infection from spreading, protect jawbone health, and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
A periodontal abscess is a dental condition that demands prompt attention. Without treatment, it can lead to significant oral and systemic health problems. Maintaining good oral hygiene, seeking early care, and following your dentist’s instructions can act as an effective pus in gums remedy. Addressing the issue quickly also reduces the risk of developing pus in mouth gum and ensures a healthier, more confident smile. Your gums are just as important as your teeth, so give them the care they deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you get rid of a periodontal abscess?
While there are several home remedies to provide temporary relief, professional treatment often involves draining the abscess, deep cleaning, and prescribing antibiotics if necessary.Is periodontal abscess life threatening?
While rare, untreated infections can spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening. It is ideal to get professional treatment to avoid the worsening of the condition.How long does a periodontal abscess take to heal?
Mild cases may improve within a few days, but full healing of the gums can take several weeks.What is the difference between a dental abscess and a periodontal abscess?
A dental abscess begins inside the tooth due to decay, while a periodontal abscess starts in the gum tissue surrounding the tooth.