What is Gingivitis?
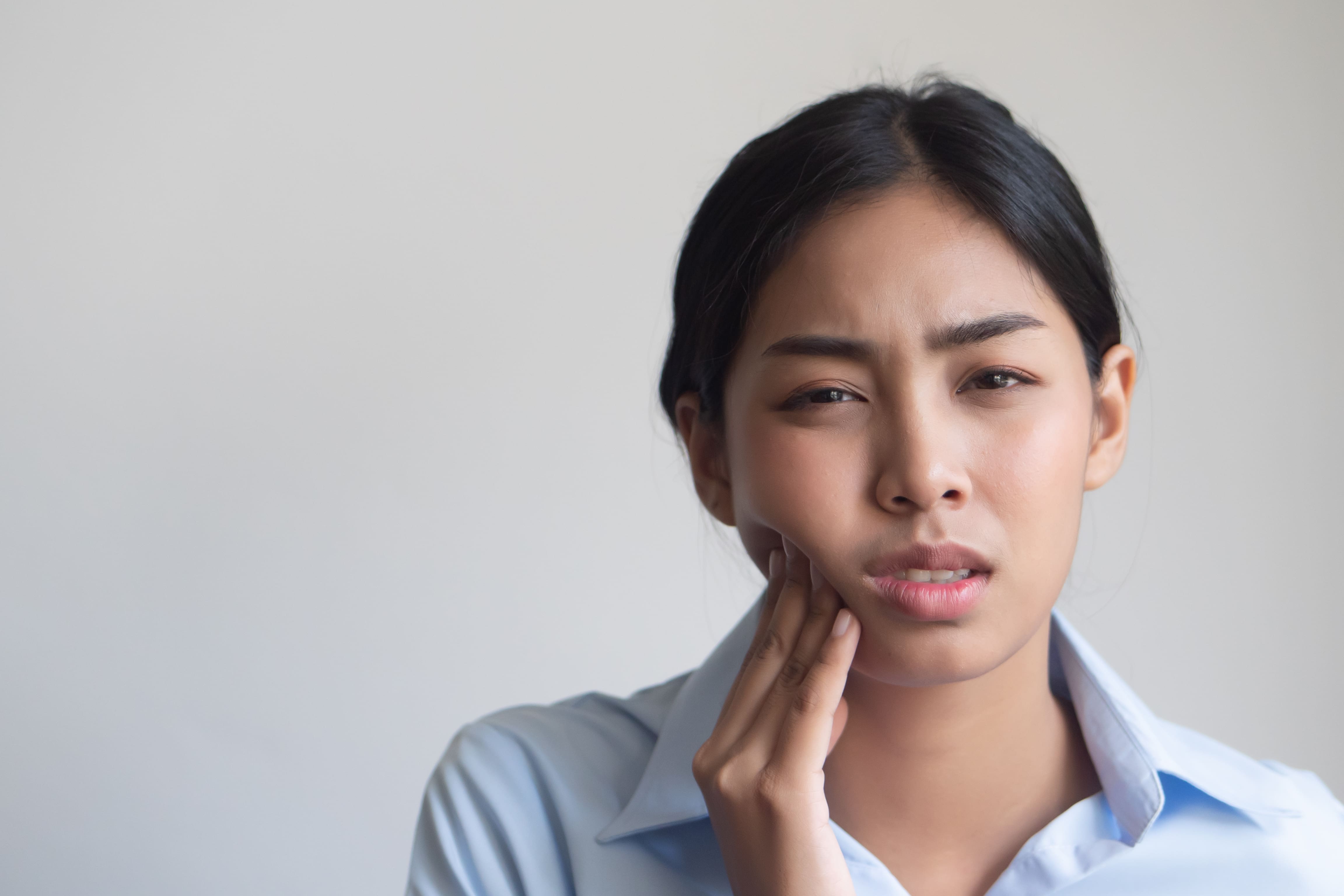
Wondering what is gingivitis? Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease characterized by inflammation of the gums. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, accumulates on the teeth and gumline. Without good oral hygiene, this plaque can harden into tartar, which worsens the plaque buildup and further irritates the gums. If not cleaned properly, this accumulation leads to irritation, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
Healthy gums should be firm, a pale pink color, and fit snugly around the teeth. In contrast, gingivitis gums look swollen, tender, and prone to bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing.
What Causes Gingivitis?
You might wonder, what causes gingivitis in the first place? The most common cause is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque to form on teeth and gums. However, several other factors contribute to gingivitis. Understanding gingivitis causes is the first step toward prevention and effective treatment. These include:
Poor oral care habits: Infrequent brushing and flossing cause plaque to harden into calculus, leading to irritation and gum inflammation.
Smoking or chewing tobacco: Tobacco use harms the gum tissue and increases the chances of infections and delayed healing.
Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make the gingiva (gums) more sensitive and prone to swelling.
Diseases: Conditions like diabetes and immune system problems lower the ability to fight germs, raising the risk of severe gum infections and painful ulcers.
Medications: Certain drugs decrease saliva, allowing plaque to build up and cause bleeding gums during brushing or flossing.
Nutritional deficiencies: Deficiency in vitamin C weakens gums, making them more vulnerable to irritation and gum disease progression.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
Recognizing gingivitis symptoms early can help you prevent the disease from advancing. The most common symptoms of gingivitis include:
Red, swollen gums
Bleeding while brushing or flossing
Persistent bad breath
Tender gums
Receding gums
Other signs of gingivitis are gum discoloration and soft gum tissues that bleed easily. Identifying these symptoms early can help you seek timely treatment and prevent further damage.
Stages of Gingivitis and Gum Disease Progression
Gum disease progresses in phases, and knowing the types of gingivitis and gingivitis stages is vital for protecting dental health. The initial stage of gingivitis features swollen gums that bleed when brushing or flossing. Poor oral hygiene and ignoring the early symptoms lets it progress into stage 2 gingivitis.
The second stage of gingivitis increases risk factors like bone loss and tooth loss as gingivitis advances to periodontitis. Timely professional cleaning can help treat gingivitis and halt disease progression. Below are the major stages of gingivitis and how it progresses.
Healthy Gums
Healthy gums are firm, pale pink, and fit snugly around the teeth without any discomfort, while gums affected by gingivitis appear red, swollen, and are often tender to the touch. The comparison of normal gum vs gingivitis is essential for recognizing early signs of gum disease and maintaining good oral health. When examining healthy gum vs gingivitis, the differences are quite clear.
One of the most noticeable signs is that gingivitis-affected gums are prone to bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing. By understanding the visual and physical differences between normal and gingivitis affected gum, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their oral health and prevent the onset of gum disease. Consistent brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups helps prevent plaque buildup that causes gingivitis.
Gingivitis
In the early stage gingivitis, irritation in the gums due to dental plaque buildup can lead to inflammation of the gum. Mild redness, swelling, or bleeding during brushing are among the early signs of gingivitis. Early stage gingivitis is typically painless, making it easily overlooked without routine dental care. However, if not addressed, it can worsen or even develop into more severe infections like trench mouth, a painful and advanced gum condition. Fortunately, early-stage gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene and professional care.
Early Periodontitis
When early-stage gingivitis is ignored, it can advance to early periodontitis, a more severe stage of periodontal disease. At this point, the cause of gingivitis, mainly plaque buildup, leads to persistent gingival bleeding and the development of a gingival abscess. This condition damages the supporting structures of teeth and often requires specialized care from a periodontist to prevent further progression.
Moderate to Severe Periodontitis
As moderate gingivitis progresses, it can lead to more advanced phases such as severe gingivitis and chronic gingivitis, both representing serious developments in the phases of periodontal disease. Persistent inflammation may severely damage the gum tissues and supporting jaw bones. If the condition is not managed, the destruction of these tissues can cause teeth to become loose, ultimately resulting in tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
When it comes to gingivitis treatment, the approach varies based on the severity of the condition. Maintaining proper dental hygiene is the first step to reversing gingivitis, especially in its early stages. If you are wondering how to cure gingivitis, addressing the bacterial infection that causes gum inflammation is crucial. Treatment options include professional dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar from the oral cavity, as well as home care routines like brushing, flossing, and using an antibacterial mouth rinse.
In-Office Treatments
Dentists provide several professional procedures to reverse gingivitis and prevent further progression of gum disease. Common in-office treatments include:
Professional cleaning: Removes plaque and tartar from the teeth and around the gingival crevice to reduce bacterial buildup.
Scaling and root planing: A deep cleaning technique that cleans below the gumline and smooths root surfaces, helping to prevent gingival recession and further infection.
Gum surgery: Surgical procedures may be recommended in severe periodontitis (an advanced form of gingivitis) where non-surgical treatments are insufficient, aiming to repair damaged tissues.
These treatments are guided by professional experts to effectively manage gingivitis and preserve oral health.
At-Home Treatments
For individuals looking for gingivitis treatment at home, there are several effective home remedies for gingivitis that support gum health:
Oil pulling, which involves swishing with coconut oil or clove oil for 10-15 minutes before spitting it out.
Applying aloe vera gel on the affected area on the gums to soothe irritation.
Using an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and control infection.
Warm saltwater rinses to soothe inflamed gums and aid healing.
It is vital to use home treatments with caution. They may improve gum condition temporarily and do not address the underlying cause. Home remedies should only complement and not replace daily oral hygiene habits and professional dental healthcare.
How to Prevent Gingivitis?
If you are wondering how to avoid gingivitis, the best approach is to adopt consistent oral care habits and address factors that affect your overall health condition. Learning how to prevent gingivitis from getting worse can protect your gums from long-term damage.
Brush your teeth twice daily using a soft toothbrush to control plaque and prevent tartar buildup.
Floss every day to clean between teeth where plaque hides.
Use antibacterial mouthwash to reduce harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Follow a balanced diet to support your immune system and gum health.
Avoid smoking and tobacco, which can increase the risk of gum disease.
Choosing the right toothpaste designed for gum care is also essential to strengthen your defenses against gingivitis.
By following these practices, you can maintain healthy gums and prevent the progression of gum disease.
When to See a Dental Professional
Swollen, bleeding gums and bad breath can be notable signs that you have gingivitis. If you experience severe gingivitis symptoms or suspect chronic gingivitis causes, it is important to visit a dental professional promptly. Conditions like dry mouth, fungal infection, or ill-fitting dentures can worsen gum problems and may require specialized care.
Factors such as high blood pressure, old fillings, crooked teeth, or misaligned dentures can also contribute to worsening gum health. Seeking early professional care helps prevent further damage and supports better oral health outcomes.
Gingivitis is a prevalent yet preventable gum disease. Knowing what to do if you have gingivitis, such as improving oral hygiene, and seeking timely treatment is key to maintaining healthy gums. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments, you can effectively manage gingivitis and avoid more serious dental issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you tell if you have gingivitis?
You can tell if you have gingivitis if your gums are red, swollen, bleed easily during brushing or flossing, and if you experience persistent bad breath.
Can I cure gingivitis on my own?
Yes, gingivitis can be cured in the early stages and can often be reversed at home with proper oral hygiene, but it is always best to consult a dentist for a personalized treatment plan.
How to tell if gingivitis is healing?
Signs of healing from gingivitis include reduced gum swelling, no bleeding during brushing, and firmer gum texture.
How long does it take to reverse gingivitis?
With proper care, gingivitis can begin to heal in as little as two weeks, though more severe cases may take longer and require professional treatment.