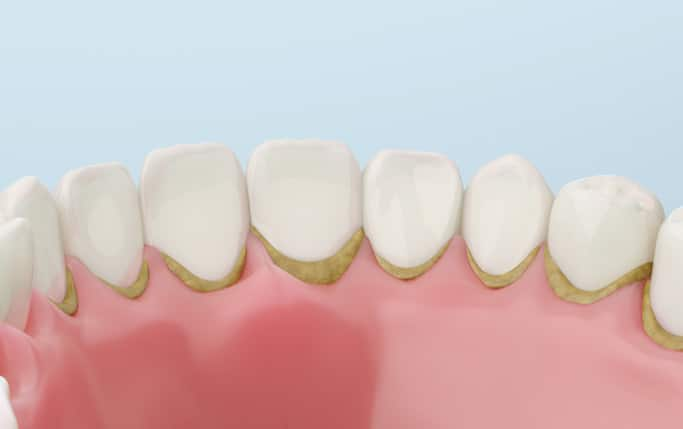
Dental Plaque Meaning
Dental plaque is the soft, sticky biofilm that develops on teeth which contains bacteria, food particles, and saliva. Plaque coats the teeth every day and needs to be removed by brushing and flossing. If plaque is not cleaned off properly, it can harden into a substance called tartar, also known as dental calculus. Proper oral hygiene is essential for maintaining good dental health by controlling plaque buildup.
Try our best oral care toothpaste range for antibacterial protection and better oral health.
Why You Should Care About It
Tooth decay and gum disease are the first two potential problems if plaque in teeth is left to build up. The waste produced by the bacteria in the plaque is acidic and wears away your tooth enamel, leading to tooth decay. If left uncleaned, plaque can continue through the dentin to the pulp of the tooth. Ignoring dental plaque can eventually lead to an abscess, bacterial infection, periodontal disease (a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth, potentially leading to tooth loss) or even loss of teeth.
Without regular brushing and flossing, tooth plaque can harden into tartar in no time. Although plaque is not usually visible on the teeth, tartar does stain the teeth and can irritate your gums, leading to gingivitis. Unlike plaque, brushing and flossing alone cannot help remove tartar. You will need to see a dentist to remove any tartar buildup.
What Are The Symptoms of Dental Plaque?
Dental plaque symptoms can include a fuzzy feeling as you run your tongue across the teeth. Bad breath may be another indicator of plaque build-up on teeth. Uncleaned plaque hardens to tartar which may stain the teeth, causing an unpleasant appearance. Plaque, if not removed, may also become the reason for cavities and various gum diseases.
What Causes Plaque on Teeth
Your mouth contains a lot of bacteria that collect on the surfaces of your teeth and create the bacterial film called plaque, which often starts at the gum line. Plaque build-up on teeth is completely normal and, according to most dentists, to be expected.
Dental plaque forms when oral bacteria combine with the sugar and carbohydrates from foods and produce acids. If you eat a lot of sugary or sweet foods or those that contain a lot of simple carbohydrates, the bacteria in your mouth feed on these sugars as you let them linger on the tooth surface.
What is The Treatment For Plaque?
Effective dental plaque treatment is necessary to maintain optimal dental health.
- Professional dental cleanings: During regular dental visits, the dentist or dental hygienist will use special instruments to remove plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) buildup from teeth surfaces.
- Scaling and root planing: For more advanced cases of plaque and gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing may be performed to remove plaque and tartar from beneath the gum line and smooth the root surfaces.
How To Prevent Plaque?
Though plaque formation is a continuous process, you can be proactive about removing it to prevent any negative effects and minimise the resulting tartar. Maintaining proper oral hygiene techniques is vital for plaque control and thereby preventing tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues.
- Brushing: Brush for two minutes, at least twice a day, using a fluoride toothpaste. You may also use an antibacterial toothpaste such as Colgate Total Advanced Health. It fights germs on teeth, tongue, cheeks, and gums, protecting your mouth for 12 hours and keeping plaque, tartar, cavities, and bad breath at bay.
- Flossing: Floss between the teeth at least once a day can help reduce the plaque build-up on teeth before it turns into tartar.
- Rinsing: Consider using a mouthwash with antimicrobial properties, but these shouldn't replace brushing and flossing.
- Dietary changes: Limiting starchy and sugary foods and drinks can be beneficial, which can contribute to plaque formation.
Dental plaque is a common oral concern that people want to get rid of while eating their favourite food. Understanding the plaque meaning and adopting measures to effectively treat plaque on teeth can save you from potential oral problems. The key is to adopt good oral hygiene, regularly visit the dentist, and be mindful of your diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What does dental plaque mean?
Dental plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on teeth. If not removed regularly by brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar and lead to tooth decay and gum disease. - What is the significance of dental plaque?
Dental plaque is significant because it is the primary cause of tooth decay and gum disease. The bacteria in plaque produce acids that lead to the oral cavity and inflame/infect the gums. Removing plaque in the mouth through oral hygiene prevents these major oral health problems. - How to remove plaque from teeth?
To remove tooth plaque, it's essential to brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, floss once a day to clean between teeth, and get regular professional dental cleanings. Brushing and flossing help remove plaque before it hardens into tartar, while dental cleanings remove hardened plaque that can't be removed at home. - Is it safe to remove tooth plaque?
Yes, dental plaque removal from your teeth is completely safe and recommended for good oral health. Brush, floss, and get regular professional cleanings to disrupt and remove plaque on teeth safely. - How do you remove hardened plaque?
Tooth plaque, if left uncleaned, hardens to form tartar. Unlike plaque, which goes off with regular brushing and flossing, tartar cannot be removed in the same manner. You will need to see a dental professional to remove any tartar buildup.
This article is intended to promote understanding of and knowledge about general oral health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine