Black gums aren't always indicative of an oral health issue. Let's understand how gum shades vary, what the dark shades or patches on the gums signify, and when to consult a dental professional for treatment.
Natural Variations in Gum Colour
Gums are most often coral-pink. If you are wondering, ‘Why are my gums black?' The most likely answer is melanin, a dark pigment produced by the body that gives colour to the skin, hair, eyes, and gums. Excess of it makes the eyes, skin, and hair darker. A person’s dark or black gums are often a result of excess melanin, also known as gingival hyperpigmentation.
As melanin pigmentation of the gums is normal, there’s no room for worry, and no treatment is required. Gum colour variation can occur on either or both sides of the mouth and be uniform or in patches. However, if your gum colour has changed recently or black patches have appeared, melanin is less likely to be the reason, and it may signal an underlying cause that requires attention.
Symptoms of Black Gums
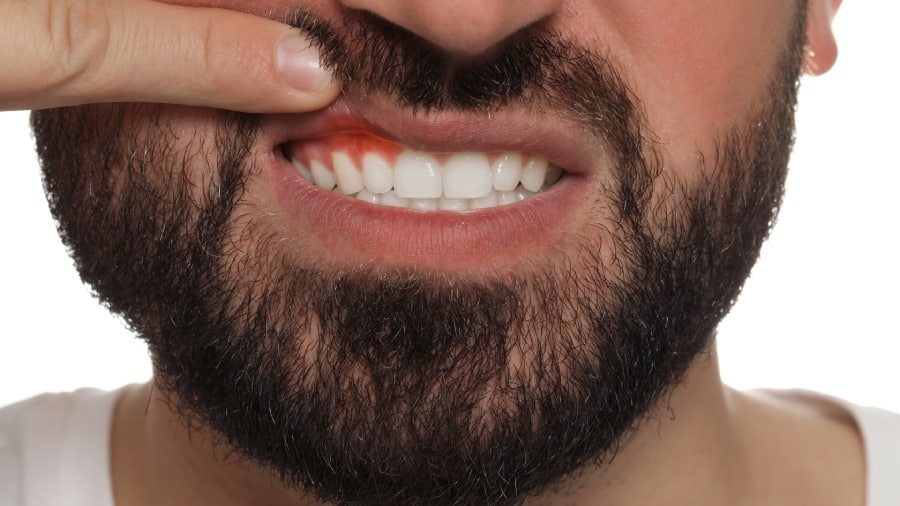
While black gums aren't always a cause for concern, it is essential to be aware of the symptoms that might accompany them and determine when to see a dentist. The most common symptoms include gums that look black or dark brown. Other colour variations in gingival pigmentation include dark blue, light brown, dark purple or red.
The entire gum area may be discoloured, or there may be patches, spots, or strands of black. Gums that have always looked dark mostly indicate a discolouration by birth. Pigmented dark spots are mostly harmless. However, some underlying health conditions can cause gradual or sudden black patches or a uniform discolouration of the gums, sometimes accompanied by symptoms that include pain, bleeding, or swelling.
Causes of Black Gums
Black gums are not always a sign of an oral health problem. Dark patches on gums may also be the result of a variety of factors, like underlying health issues, medication side effects, or tobacco use. Looking into the various black gums reasons is vital for anyone with dark gums or gum discolouration to rule out any medical conditions that need attention. Apart from natural colour variations, the other factors responsible for your gums turning black include:
Melanotic Macules: Sometimes, excess melanin production in the gums, palate, and lower lip results in small, dark patches or lesions called melanotic macules. These benign lesions usually appear gradually in brown, black, or blue.
Smoker’s Melanosis: Smoking can cause many side effects inside the mouth, including dark gums. Research shows that the nicotine in cigarettes or tobacco activates the melanin-producing cells, leading to darker gums. Quitting smoking may help reduce this pigmentation.
Medications: Studies show that blue or black pigmentation can occur in any part of the mouth, including the gingiva and tongue, as a side effect of some medications. Some antibiotics, antimalarials, antipsychotics, and cancer therapy drugs pose a greater risk of such pigmentation.
Diseases: Black gums can also be associated with some endocrine diseases. For example, Addison’s disease is caused by damage to the adrenal glands. It lowers cortisol levels and triggers the hormone that stimulates melanin production, causing the gums to darken.
Oral malignant melanoma: Sometimes, a black spot on the gums may indicate a type of oral cancer called oral malignant melanoma. The cancer starts in cells called melanocytes, which give skin its colour. Consulting a dentist is ideal for examining the presence of cancerous cells in such lesions using a biopsy.
Amalgam Tattoos: These appear as harmless blue, black, or grey patches that may appear on the gums near a tooth that recently had a silver (amalgam) dental filling. Dentists usually diagnose amalgam tattoos based on appearance and dental history or by using an X-ray.
Severe Gum Disease: A severe form of gum disease (periodontal disease), known as acute necrotising ulcerative gingivitis (trench mouth), can cause the gumline to appear black or dark grey. The colour change results from damaged gum tissue around the teeth caused by bacterial infection due to poor oral hygiene.
Treatment Options for Black Gums
Treatment is not required if your gums are naturally dark or black by default or if harmless lesions cause discolouration. However, various options are available for people with very dark gums who seek cosmetic solutions to beautify their gummy smile. Treatment is necessary if black gums cause you troubles such as pain or bleeding or indicate malignancy. Black gums treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Instead of experimenting with home remedies, it is ideal to consult a dentist to diagnose the discoloured gums. Upon examining your gums, a dentist can identify the cause and recommend appropriate treatment based on your unique oral conditions and needs. The various treatment options for darkened gums include:
Scalpel gingivectomy: This surgical method removes darkened gum tissue with a scalpel. Despite the initial results of this procedure, melanin-producing cells can sometimes migrate into the treated area, causing more pigmentation.
Cryosurgery: This method involves freezing the affected gum tissues by applying cryogenic materials, such as liquid nitrogen, at very low temperatures. A study published in the International Journal of Health Sciences reports that the rate of recurrence of pigmentation after cryosurgery is low.
Gingival grafts: Gingival grafting is another technique that is used. This treatment involves harvesting unpigmented tissue from the roof of the mouth and applying it to the gums. This conceals the dark gum tissue instead of eliminating it.
Besides, you can enhance oral care with regular brushing, flossing, and mouthwash to avoid gum discolouration due to gum disease. You may also consider including an antibacterial toothpaste, such as Colgate Total Advanced Health, to curb infection-causing bacteria. Its unique Dual Zinc and Arginine formula protects your gums, teeth, cheeks, and tongue from germs for 12 hours.
When to See a Dental Professional?
Regular dental checkups are important for good oral hygiene as they help you rule out potential dental problems. Should you be worried if your gums are black? Gums that have always looked dark pose no threat. If you cannot spot black gums reason other than natural variations, treatment is not needed unless you require a cosmetic solution to enhance your smile.
However, if the gums turning black or gaining patches is a sudden or recent symptom, it is worth getting checked by a dentist. As darkening of the gums may also result from a severe form of gum disease (gingivitis), it is likely to be accompanied by various other signs. A dental checkup should not be delayed in case you experience any of the following:
Bleeding gums
Swollen or inflamed gums
Loose teeth
Pain in gums or teeth
Changing spots on the gums
Halitosis (bad breath)
The above-mentioned signs are often a consequence of poor dental hygiene, which leads to the buildup of plaque and tartar, harbouring bacteria and causing gum infection. Improving daily oral care with brushing, flossing, and routine dental visits helps you keep these in check, thereby preventing gum diseases that damage the gum tissues.
Gum colour varies among individuals. Black gums are often a natural colour variation and not necessarily a medical concern. However, sudden changes in gum colour, the emergence of black patches, and symptoms like bleeding or swelling may require a dental check-up. Early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause can help prevent complications. Regular dental visits are vital for maintaining good oral health and catching potential issues early on.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to get rid of black gums?
If your gums are not naturally black, the best way to eliminate the discolouration is to identify and tackle the underlying black gums reason with the help of a dentist. It may be a severe gum disease, a side effect of medication or disease, or a habit such as smoking.
Why my gums are black?
The most common cause of black gums is natural colour variation due to melanin. Other black gum causes include harmless lesions, side effects of medication, smoking or tobacco use, underlying disease, severe gum disease, or malignant lesions.
How to remove black gums naturally?
One may look for black gums treatment at home; however, consulting a dentist is ideal to diagnose the underlying cause and get recommendations on the best treatment. Ensuring dental hygiene helps prevent severe gum diseases and the resultant darkening of gums.
Does everyone have black gums?
While most people have coral-pink gums, gum shades vary depending on the amount of melanin produced by the body. Dark or black gums are common in people with excess melanin production, which also causes their skin, hair, and eyes to look darker.
This article is intended to promote understanding of and knowledge about general oral health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine