-
-

FLUORIDE
What Is Stannous Fluoride Toothpaste?Stannous fluoride toothpaste helps prevent cavities, reduce sensitivity, fight plaque, and support daily gum and enamel health.

TEETH WHITENING
Why Should I Whiten My Teeth?Maybe you've always wanted a beautiful white smile. Or your teeth have yellowed over time...
-
Science & Innovation
- ORAL HEALTH CHECK
- PRODUCT MATCH


What is the Right Way to Floss?
Proper flossing removes plaque and food particles in places where a toothbrush cannot easily reach - under the gumline and between your teeth. Because plaque build-up can lead to tooth decay and gum disease, daily flossing is highly recommended.
To receive maximum benefits from flossing, use the following technique:
- Starting with about 18 inches of floss, wind most of the floss around each middle finger, leaving an inch or two of floss to work with
- Holding the floss tautly between your thumbs and index fingers, slide it gently past the tight contact point between the teeth
- Gently curve the floss around the base of each tooth, making sure you go beneath the gumline. Never snap or force the floss, as this may cut or bruise delicate gum tissue
- Use clean sections of floss as you move from tooth to tooth
- To remove the floss, use the same back-and-forth motion to bring the floss up and away from the teeth
What Type of Floss Should I Use?
There are two types of floss from which to choose:
- Nylon (or multifilament) floss
- PTFE (monofilament) floss
Nylon floss is available waxed and unwaxed, and in a variety of flavors. Because this type of floss is composed of many strands of nylon, it may sometimes tear or shred, especially between teeth with tight contact points. While more expensive, single filament (PTFE) floss slides easily between teeth, even those with tight spaces between teeth, and is virtually shred-resistant. When used properly, both types of floss are excellent at removing plaque and debris.
 | 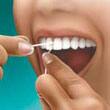 | 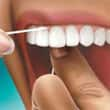 |
Use about 18" of floss, leaving an inch or two to work with. | Gently follow the curves of your teeth. | Be sure to clean beneath the gumline, but avoid snapping the floss on the gums. |
11/15/2010
This article is intended to promote understanding of and knowledge about general oral health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Related Articles

Selecting dental products
Choosing the Right ToothbrushChoosing the right toothbrush is very important. Learn how to choose the right toothbrush, when you should replace your toothbrush and more at Colgate.com

Selecting dental products
Choosing The Best Toothbrush For YouThe best toothbrush for the job depends on a variety of things that are unique to you. Here are three things to look for in a product that does this.

Selecting dental products
Antiseptic Vs Antibacterial Mouthwash: What's the Difference?Mouthwash can freshen your breath and protect against cavities. When it comes to antiseptic vs antibacterial mouthwash, is one better than the other?
Related Products

Helping dental professionals
More professionals across the world trust Colgate. Find resources, products, and information to give your patients a healthier future







