บทความเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพช่องปากทั้งหมด
450 results

ฟลูออไรด์
ทำความรู้จักฟลูออไรด์: แร่ธาตุธรรมชาติที่ช่วยเสริมสุขภาพฟัน
ฟลูออไรด์เป็นแร่ธาตุจากธรรมชาติที่ช่วยต่อสู้กับฟันผุ คอลเกตจะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจสิ่งที่ทำให้เกิดฟันตกกระ (Fluorosis) และตัวเลือกในการรักษาและเสริมฟลูออไรด์
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
น้ำดื่มบรรจุขวด กับ ฟลูออไรด์
ถ้าคุณดื่มน้ำบรรจุขวดเป็นประจำในชีวิตประจำวัน อาจจะเป็นสาเหตุของการขาดฟลูออไรด์ได้ มาดูว่าสาเหตุ และต้องทำอย่างไรเพื่อให้ได้รับฟลลูออไรด์อย่างเหมาะสม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ฟลูออไรด์จะช่วยผู้ใหญ่ ได้หรือไม่
ทุกคนควรใช้ฟลูออไรด์ทุกวัน ผู้ใหญ่บางคนก็มีความเสี่ยงในระดับสูงในการใช้ฟลูออไรด์ และอาจต้องการอาหารเสริมที่มีความเข้มข้นมากกว่า ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
เคลือบฟลูออไรด์ช่วยอะไร? ป้องกันฟันผุและเสริมความแข็งแรงให้ฟันได้อย่างไร
ทำความรู้จักฟลูออไรด์ และฟลูออไรด์เสริม พร้อมขั้นตอนการปฏิบัติตัวก่อนและหลังการเคลือบฟลูออไรด์ เพื่อช่วยเสริมความแข็งแรงให้กับฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ทำไมเราถึงควรใช้ยาสีฟันฟลูออไรด์
คุณรู้ไหมว่าฟลูออไรด์ในยาสีฟันมีบทบาทสำคัญในการลดปัญหาฟันผุ มาดูกันว่าฟลูออไรด์มีบทบาทอย่างไร และทำไมเราจึงต้องใช้ยาสีฟันที่มีฟลูออไรด์
อ่านเพิ่มเติม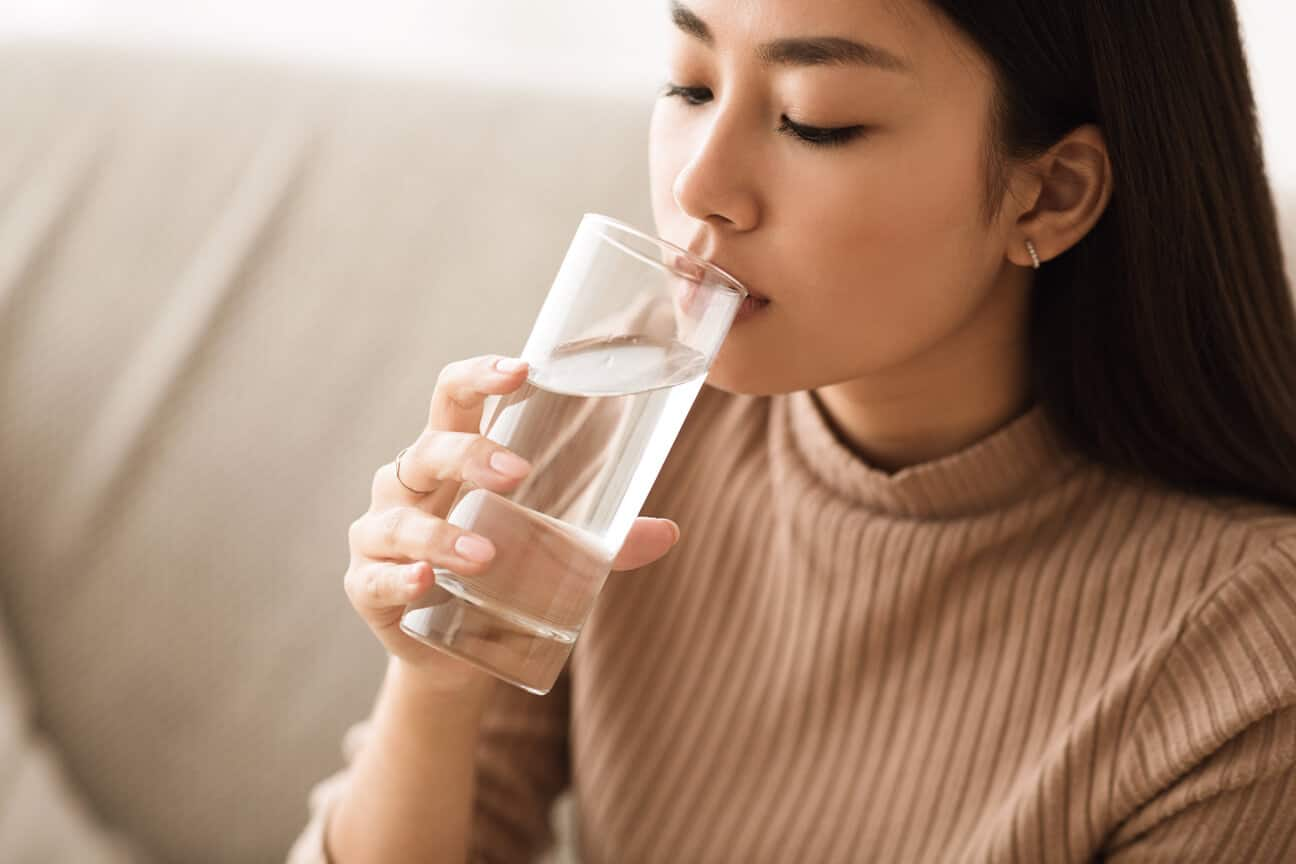
ฟลูออไรด์
ฟลูออไรด์ในน้ำดื่มส่งผลต่อฟันผุในผู้ใหญ่อย่างไร
ฟลูออไรด์ในน้ำดื่มช่วยป้องกันฟันผุได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพได้อย่างไร มาเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์ในน้ำดื่มกัน อ่านข้อมูลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
อะไรคือยาสีฟันผสมสแตนนัสฟลูออไรด์
ยาสีฟันผสมสแตนนัสฟลูออไรด์ช่วยดูแลช่องปากที่ดีเมื่อใช้เป็นประจำทุกวันเพื่อสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ฟลูออไรด์ช่วยป้องกันฟันผุในผู้ใหญ่ได้หรือไม่?
ฟลูออไรด์ไม่ได้มีประโยชน์แค่สำหรับเด็ก! คอตเกตรวบรวมข้อมูลและคำตอบที่น่าสนใจเกี่ยวกับประโยชน์ของฟลูออไรด์สำหรับผู้ใหญ่มาฝาก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
อันตรายของฟลูออไรด์: แค่ไหนคือมากเกินไป?
เพราะอะไรที่มากเกินไปก็อาจให้โทษได้ อย่างเช่นฟลูออไรด์ก็มีปริมาณที่เหมาะสมเช่นกัน แล้วแค่ไหนถึงจะเรียกว่าพอดี แค่ไหนถึงเรียกว่ามากเกินไป มาดูกันเลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ฟลูออไรด์สำหรับเด็กน้อย: ปลอดภัยหรือไม่?
ฟลูออไรด์นั้นปลอดภัยและแนะนำให้ใช้กับเด็กทารกและเด็กเล็ก เพียงแค่ต้องทำตามข้อปฏิบัติ และใช้ในปริมาณที่เหมาะสม เรียนรู้สิ่งที่คุณควรทราบได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ข้อเท็จจริงเกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์
ไขข้อสงสัยเกี่ยวกับข้อเท็จจริงของฟลูออไรด์... แหล่งที่มาของฟลูออไรด์มีที่ไหนบ้าง? ฟลูออไรด์ 1450 ppm เพียงพอต่อการป้องกันฟันผุหรือไม่?
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ฟลูออไรด์ทำอะไรได้บ้าง?
ฟลูออไรด์สามารถปกป้องรอยยิ้มของคุณให้แข็งแรง สวยสดใสไปนาน ๆ ได้ หากคุณสงสัยว่าฟลูออไรด์ช่วยปกป้องสุขภาพในช่องปากได้อย่างไร พบคำตอบได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ใครควรใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากฟลูออไรด์บ้าง และเพราะเหตุใด?
ผู้ใหญ่ก็อาจมีความเสี่ยงสูงที่จะเกิดอาการฟันผุได้ น้ำยาบ้วนปากฟลูออไรด์เป็นอีกหนึ่งตัวช่วยที่เหมาะสม นอกเหนือจากการทำความสะอาดช่องปากตามปกติ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
คำถามที่พบบ่อยเกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์
มีคำถามที่ถูกถามเข้ามาบ่อย ๆ เกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์ และผลิตภัณฑ์ของคอลเกต ลองเข้ามาหาคำตอบดูเพื่อความเข้าใจที่มากขึ้นในเรื่องของฟลูออไรด์และสุขภาพฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม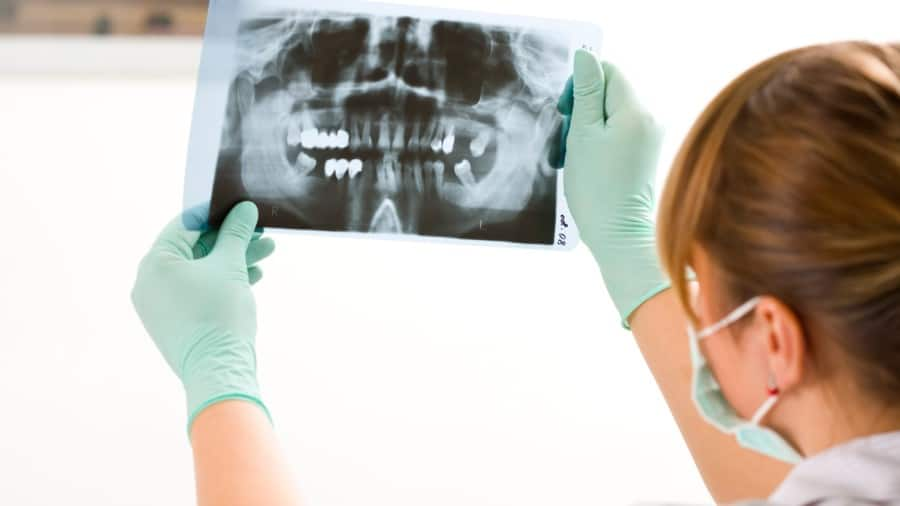
ฟลูออไรด์
การขาดฟลูออไรด์และสัญญาณ
ช่องปากของคุณอาจไม่ได้มีสุขภาพดีอย่างที่คุณคิด คุณอาจกำลังประสบปัญหาจากภาวะการขาดฟลูออไรด์ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้ถึงอาการหรือสัญญาณเตือนของภาวะนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
ยาสีฟันที่มีฟลูออไรด์ควรเลือกใช้แบบไหน? สามารถป้องกันฟันผุได้หรือไม่?
คุณควรใช้ยาสีฟันปราศจากฟลูออไรด์หรือไม่? คำตอบนั้นขึ้นอยู่กับอายุของคุณ เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์และหาคำตอบว่าควรใช้หรือไม่ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟลูออไรด์
อะไรคือยาสีฟันผสมสแตนนัสฟลูออไรด์
คุณควรใช้ยาสีฟันปราศจากฟลูออไรด์หรือไม่? คำตอบนั้นขึ้นอยู่กับอายุของคุณ เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับฟลูออไรด์และหาคำตอบว่าควรใช้หรือไม่ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
สิ่งสำคัญในการควบคุมกลิ่นปาก
กลิ่นปากอาจมีผลมาจากสาเหตุต่างๆ อาหารบางอย่าง รวมถึง โรคเหงือก ปากแห้ง เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับสาเหตุและการแก้ปัญหาภาวะที่มีกลิ่นปาก ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
สาเหตุห้าประการของกลิ่นปากในเด็กที่คุณต้องประหลาดใจ
ลูกมีกลิ่นปาก? ปัญหานี้เกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไร ลองมาดู 5 สาเหตุของกลิ่นปากในเด็ก และวิธีการแก้ไขที่นอกเหนือจากการแปรงฟันเป็นประจำทุกเช้าเย็น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
กลิ่นปากและความสัมพันธ์ที่มีต่อปัญหาทางช่อง ปากและปัญหาที่มีความเกี่ยวข้องกับระบบการ ทำงานของร่างกาย
75% ของกลิ่นปาก มีสาเหตุมาจากปัญหาภายในช่องปาก และสาเหตุอื่น ๆ อย่างปัญหาทางกระเพาะอาหาร การติดเชื้อที่ไซนัส ดูวิธีการดูแลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
5 เคล็ดลับกำจัดกลิ่นปาก
ปัญหาปากเหม็นหรือมีกลิ่นปาก อาจจะทำให้คุณขาดความมั่นใจได้ สำหรับใครที่กำลังสงสัยว่าปากเหม็นแก้ยังไง? คอลเกตรวบรวม 5 เทคนิคดีๆ ทำได้ง่ายๆ มาฝากกันแล้ว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
กลิ่นปาก - วิธีรักษาปัญหากลิ่นปาก
กลิ่นปากหรือภาวะปากเหม็นนั้นเป็นปัญหาด้านสุขอนามัยในช่องปากที่ก่อให้เกิดความรู้สึกไม่สบายใจ อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
กลิ่นปาก - สาเหตุของกลิ่นปาก
การทราบถึงสาเหตุของกลิ่นปากเป็นเรื่องสำคัญ เพราะอาจเป็นสัญญาณเตือนถึงปัญหาในช่องปากหรือปัญหาสุขภาพ อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก: ปากเหม็นเกิดจากอะไร
รู้หรือไม่ว่าสาเหตุของการมีกลิ่นปากอาจเกิดจากกิจวัตรประจำวันของคุณ เชิ่นอาหารกินหรือการแปรงฟัน คอลเกต ให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม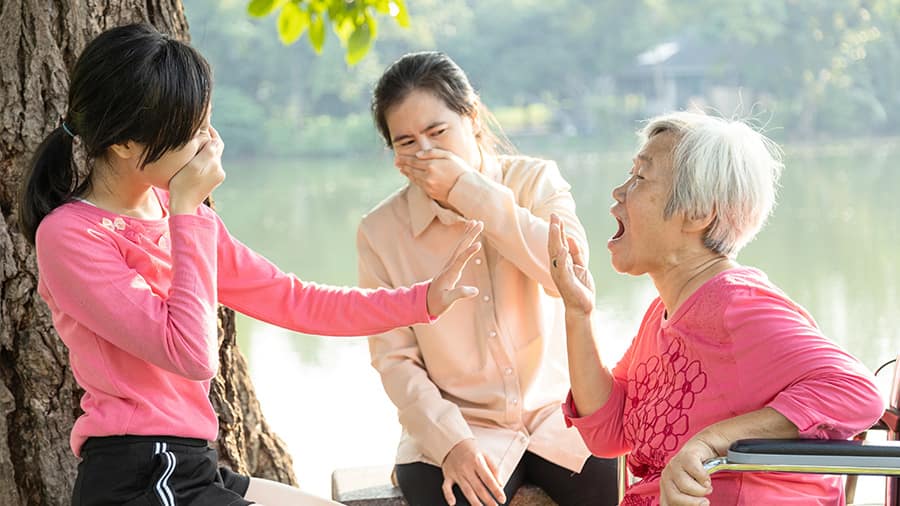
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
กลิ่นปาก - วิธีแก้กลิ่นปากส่วนผู้สูงอายุ
กลิ่นปากเป็นปัญหาที่ทุกคนพบได้ อย่างไรก็ตามผู้สูงอายุจะมีกลิ่นปากมากกว่าเนื่องจากปัญหาช่องปากที่มากขึ้น คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม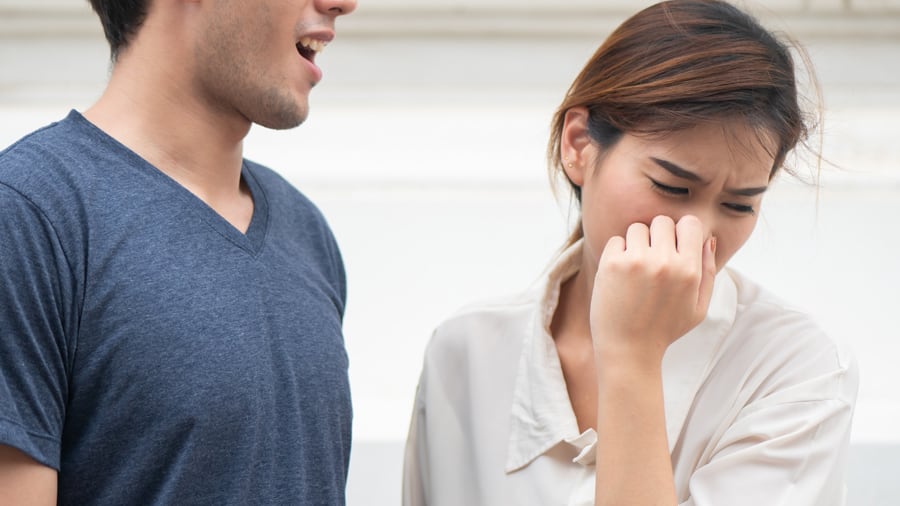
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ข้อมุลเกี่ยวกับเด็กฟันผุ
มีปากเหม็นหรอ ไม่ต้องเป็นห่วง วิธีแก้ปัญหากลิ่นปากที่ดีที่สุดคือการแปรงฟันและการใช้ไหมขัดฟัน คอลเกต ให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
เคล็ดลับดับและลดกลิ่นปากเมื่ออยู่นอกสถานที่
อาจเป็นเรื่องยุ่งยากมากหากมีปากเหม็นเมื่อที่คุณไมีอยู่ที่บ้าน คอลเกต เล่าให้เคล็ดลับช่วยดับกลิ่นปากในช่วงเวลาที่คุณอยู่นอกสถานที่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
โพรไบโอติกช่วยแก้ปัญหากลิ่นปากได้อย่างไร?
มีการวิจัยใหม่ที่แสดงว่า โพรไบโอติกสามารถช่วยดับกลิ่นปากได้ คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้เกี่ยวกับความเป็นไปได้ในการนำจุลินทรีย์ตัวดีมาใช้ประโยชน์
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
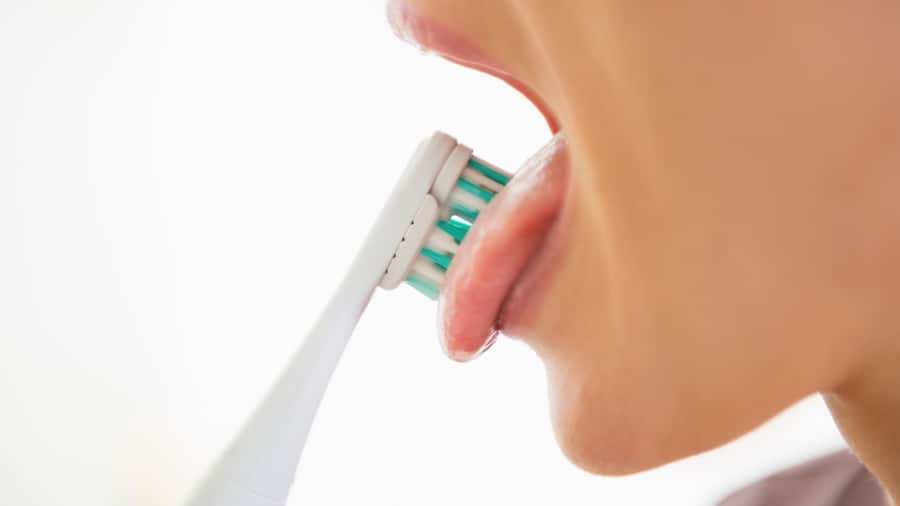
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
การใช้แปรงลิ้นเพื่อช่องปากที่สะอาดยิ่งขึ้น
การแปรงฟันเพียงอย่างเดียวไม่สามารถกำจัดแบคทีเรียได้หมด คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้ว่าทำไมการใช้แปรงลิ้นสามารถเพิ่มความสดชื่นให้กับช่องปากได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
วิธีดับกลิ่นปากอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
รู้ไหมว่าคุณไม่จำเป็นต้องมีอุปกรณ์มากมายเพื่อใช้ระงับกลิ่นปาก เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต เกี่ยวกับการระงับกลิ่นปากได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม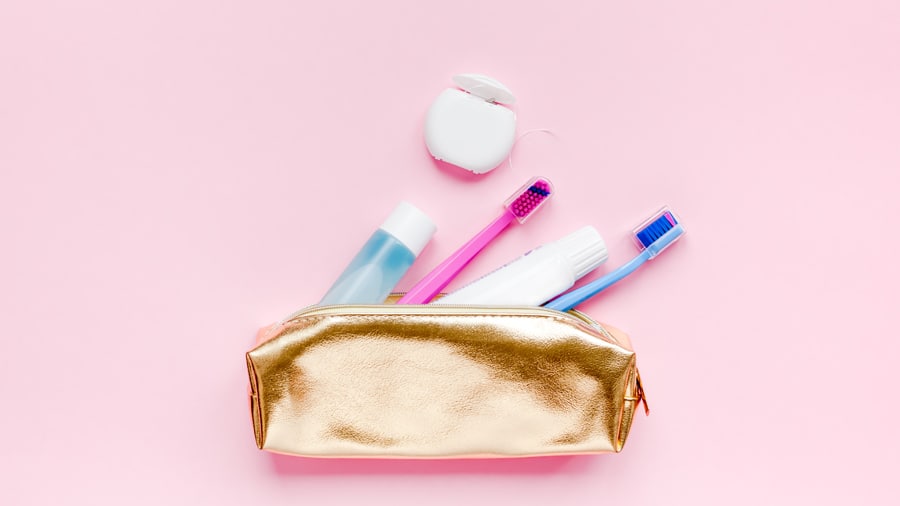
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
เคล็ดลับเพื่อลมหายใจหอมสดชื่น: 10 วิธีลดกลิ่นปาก
เคล็ดลับเพื่อลมหายใจหอมสดชื่น 10 ประการต่อไปนี้จะช่วยให้ปากคุณมีกลิ่นหอมคู่กับรอยยิ้มที่สดใส อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเต็มจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ความเชื่อมโยงระหว่างปริทันต์อักเสบและกลิ่นปาก
ในบางกรณี กลิ่นปากนั้นมีสาเหตุมาจากปัญหาพื้นฐานด้านทันตกรรม คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับปัญหากลิ่นปากที่เกิดจากเหงือกอักเสบ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม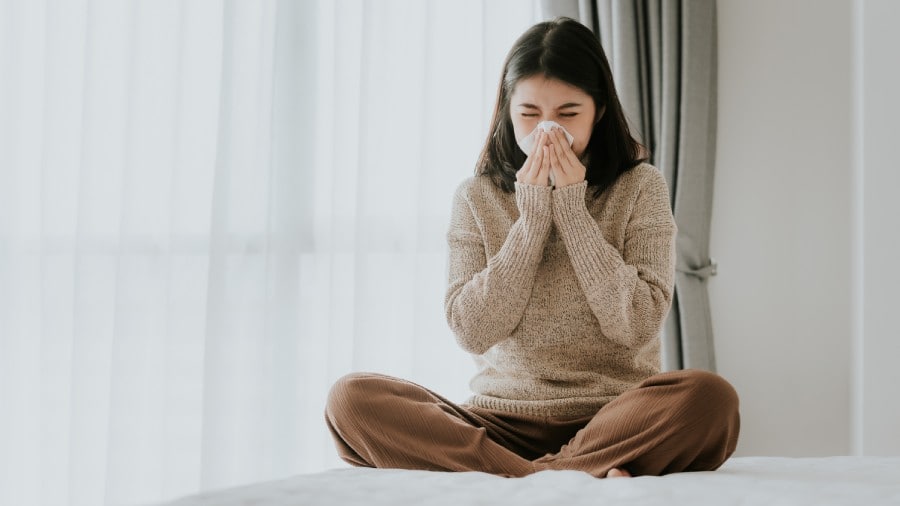
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ไซนัสอักเสบสามารถทำให้เกิดกลิ่นเหม็นในคอและปากหรือไม่
น้ำมูกที่เกิดจากการเป็นไซนัสนั้นอาจมีกลิ่นที่ไม่พึงประสงค์ที่ทำให้ลมหายใจนั้นมีกลิ่นได้ เรียนรู้ว่าไซนัสและกลิ่นลมหายใจมีความเกี่ยวข้องกันอย่างไร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
น้ำยาบ้วนปากดีที่สุดเพื่อลดกลิ่นปาก
ประสิทธิภาพของน้ำยาบ้วนปากเพื่อลดกลิ่นปากขึ้นอยู่กับส่วนประกอบในน้ำยาบ้วนปาก คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้สิ่งที่ควรมองหาในน้ำยาบ้วนปากได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม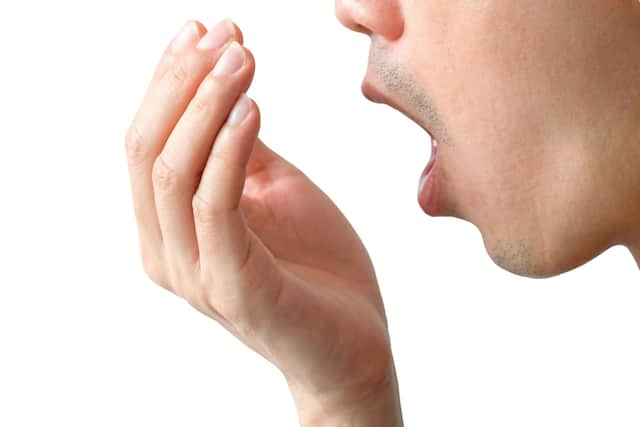
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
กลิ่นปากตอนเช้า: เคล็ดลับการป้องกันและการรักษา
กลิ่นปากตอนเช้าอาจต้องระวังและเป็นเรื่องน่าอายได้ ปัญหานี้เกิดขึ้นได้กับทุกคนและนี่คือเคล็ดลับในการป้องกันดูแลกลิ่นปากตอนเช้า อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ลิ้นเป็นฝ้าขาวและมีกลิ่นปากเกิดจากอะไร? พร้อมวิธีดูแลและป้องกัน
หากมีอาการลิ้นเป็นฝ้าขาว คุณอาจมีกลิ่นปากร่วมด้วย มาดูกันว่าสาเหตุที่ทำให้ลิ้นของเป็นฝ้าขาวเกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม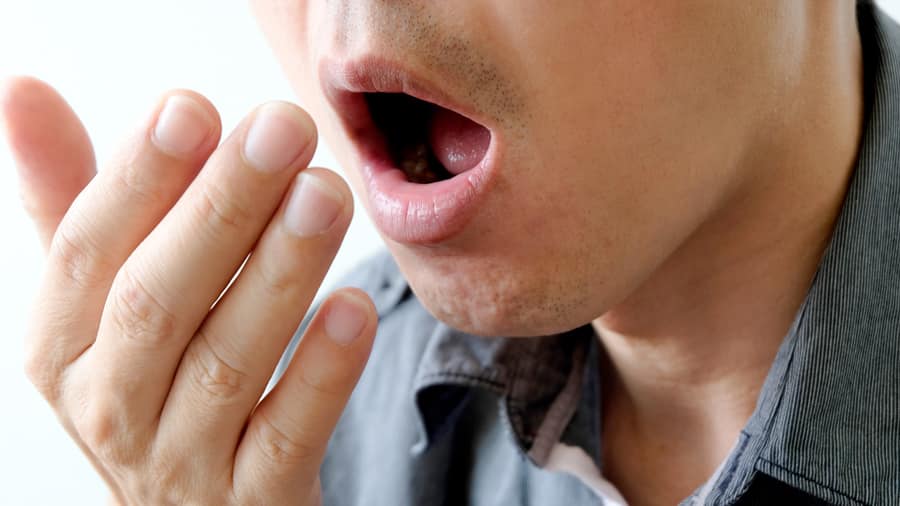
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ลมหายใจมีกลิ่นคาว? เรียนรู้สาเหตุและวิธีการรักษาภาวะกลิ่นตัวเหม็น
กลิ่นลมหายใจเหม็นอาจเกิดจากภาวะทางพันธุกรรมที่เรียกว่า Trimethylaminuria หรือภาวะกลิ่นตัวเหม็น ค้นหาสาเหตุและข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
วิธีแก้ปัญหากลิ่นปาก
วิธีแก้ปัญหากลิ่นปากหรือภาวะปากเหม็นอาจเป็นขั้นตอนที่ซับซ้อน หากคุณไม่ทราบถึงสาเหตุที่แท้จริงตั้งแต่แรก ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ปัญหากลิ่นปากที่มีสาเหตุจากกระเพาะอาหาร หมายถึงอะไรและควรรับมืออย่างไร
กลิ่นปากที่เกิดขึ้นอาจไม่ได้เกิดจากสภาพช่องปากแต่เกิดขึ้นจากกระเพาะอาหารของคุณ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสาเหตุของกลิ่นปากมาจากกระเพาะอาหาร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
ฟันผุทำให้เกิดกลิ่นปากหรือไม่
พวกเราทุกมีกลิ่นปากที่อาจเป็นเรื่องน่าอาย แล้วอะไรคือสาเหตุของกลิ่นอันไม่พึงประสงค์นั้น ฟันผุสามารถเป็นต้นเหตุของการมีกลิ่นปากได้หรือไม่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
จัดการกับกลิ่นปากเรื้อรังอย่างไรดี
หากคุณมีกลิ่นปากอันไม่พึงประสงค์มาอย่างยาวนานจะทราบดีว่าปัญหานี้เป็นเรื่องที่น่าอายอย่างไร เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตในตอนนี้และเรียนรู้สาเหตุและวิธีการรักษาที่เห็นผล
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลิ่นปาก (ภาวะมีกลิ่นปาก)
วิธีดับกลิ่นกระเทียมในปาก
จะมีวิธีกำจัดลมหายใจกลิ่นกระเทียมจากอาหารมื้อโปรดของคุณที่ยากจะดับกลิ่นได้อย่างไร เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้วิธีที่จะจัดการกับลมหายใจของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ฟันผุคืออะไร
ฟันเป็นโพรง หรือฟันผุ สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ทั้งในเด็กและผู้ใหญ่ ซึ่งฟันผุมีอยู่หลายชนิด มาดูรายละเอียดของฟันผุ พร้อมการป้องกันรักษาที่ถูกต้องกัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
น้ำลายและการเคี้ยวหมากฝรั่ง — ประโยชน์ต่อสุขภาพปาก
น้ำลายช่วยรักษาความชุ่มชื้นของปาก น้ำลายจะเพิ่มขึ้นขณะที่เราทานอาหารหรือเคี้ยวหมากฝรั่ง ช่วยให้เราเคี้ยวหรือกลืนอาหารได้ง่าย ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
หากคุณขาดของหวานไม่ได้ แล้วจะป้องกันฟันผุได้อย่างไร
ทำตามเคล็ดลับเหล่านี้เพื่อช่วยป้องกันฟันผุสำหรับคนรักน้ำตาลลองทำตามเคล็ดลับสำหรับคนขาดหวานไม่ได้เหล่านี้เพื่อป้องกันฟันผุสิ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ฟันผุควรทำอย่างไร สามารถบรรเทาอาการเองที่บ้านได้หรือไม่?
คุณรู้สึกปวดฟันในขณะที่รับประทานอาหารรึเปล่า? หากคุณสงสัยว่าฟันกำลังผุ เราขอแนะนำวิธีรักษาและวิธีการป้องกันฟันผุเป็นรู เพื่อสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันที่ดีของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
เด็กและฟันผุ: 3 ลักษณะนิสัยที่อาจทำลายฟัน
สิ่งหนึ่งที่คุณควรเอาใจใส่เช่นเดียวกับสุขภาพส่วนอื่นๆของลูกคือสุขภาพช่องปาก มารู้จักลักษณะนิสัยที่อาจทำให้เด็กฟันผุและวิธีป้องกันเพื่อสุขภาพฟันที่แข็งแรง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ฟันผุ - วิธีรักษาและป้องกันฟันผุ
ปัญหาฟันผุสามารถลุกลามได้อย่างรวดเร็วหากละเลย คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ขั้นตอนการป้องกันที่ดีที่สุดและตัวเลือกในการรักษาหากคุณมีฟันผุ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
วิธีป้องกันฟันผุอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
วิธีป้องกันฟันผุอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ อาจเป็นเรื่องที่คุณเคยได้ยินได้ฟังมาตลอดระยะเวลาที่ผ่านมา แต่ลองมาดูให้แน่ใจกันอีกทีว่าคุณตกหล่นข้อไหนไปหรือเปล่า
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
วิธีรักษาฟันผุภายใน 2 วัน
จากวิจัยที่ผ่านมา ฟันผุเป็นอาการที่สามารถรักษาได้โดยทันตแพทย์เท่านั้น คอลเกตเล่าให้ฟังว่าทำไม "รักษาฟันผุในสองวัน" ไม่เป็นความจริง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
สาเหตุและการป้องกันการเกิดฟันผุ
ฟันผุ คือผิวเคลือบฟันที่อยู่ชั้นนอกและแข็งที่สุดถูกทำลาย คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้สาเหตุเกิดฟันผุและวิธีป้องกันการเกิดฟันผุได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
แมงกินฟันมีจริงหรือไม่
บางคนเชื่อจริงๆ ว่า "แมงกินฟัน" กัดกินเนื้อฟันจากด้านในทำให้ปวดฟัน แม้ว่าท่อเนื้อฟันในฟันที่มีเนื้อเยื่อในอักเสบ ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ปัญหาเคลือบฟันผุ: สาเหตุและการแก้ไข
ฟันผุที่ผิวเคลือบฟันจะเริ่มกลายเป็น ปัญหาเมื่อเริ่มปรากฏเป็นรูขึ้นที่ฟัน ดังนั้นการรักษาแต่เนิ่นๆ จะสามารถป้องกันไม่ให้ฟันผุลุกลามได้ อ่านข้อมูลได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
วิธีป้องกันฟันผุ
กรดคือสาเหตุหลักที่ทำให้เกิดฟันผุ เมื่อมีเศษอาหารตกค้างสะสมในฟันบ่อยๆ แบคทีเรียในช่องปากจะเจริญเติบโต วิธีป้องกันฟันผุ อ่านข้อมูลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม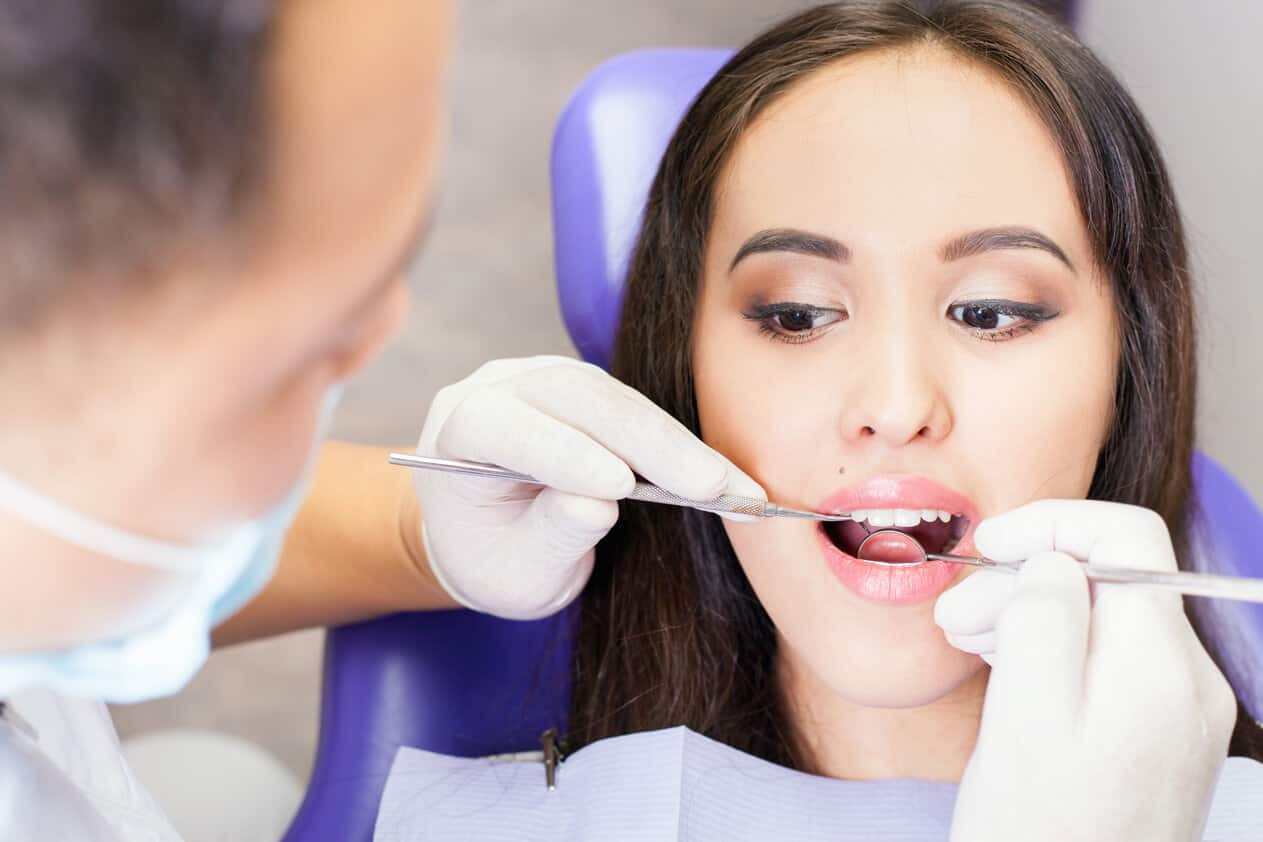
ฟันผุ
คู่มือสำหรับโรคฟันผุระยะต่างๆ
อาการฟันผุจะแย่ลงเมื่อเวลาผ่านไปและโรคฟันผุในระยะลุกลามจำเป็นต้องได้รับการรักษาที่ครอบคลุมมากขึ้น หากตรวจพบตั้งแต่เนิ่นๆ อ่านข้อมูลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม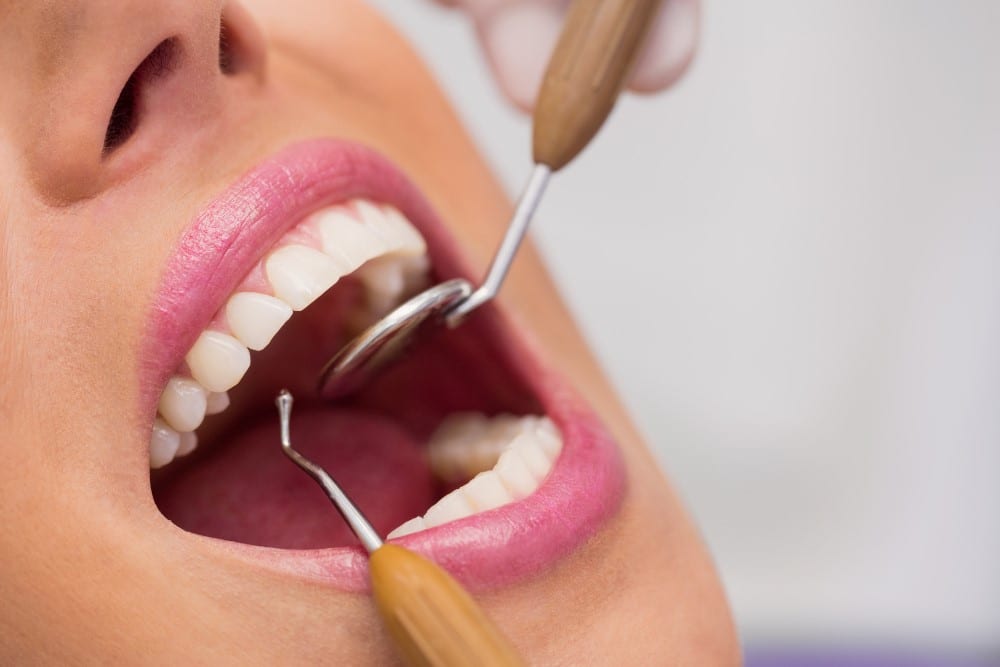
ฟันผุ
อาการฟันผุเป็นอย่างไร? มาทำความเข้าใจสาเหตุและวิธีดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากให้ดีขึ้น
ฟันผุทำให้คุณอาจรู้สึกถึงอาการเสียวฟันและรู้สึกปวดฟัน โดยเฉพาะหลังจากรับประทานอาหาร หรือขนมหวาน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม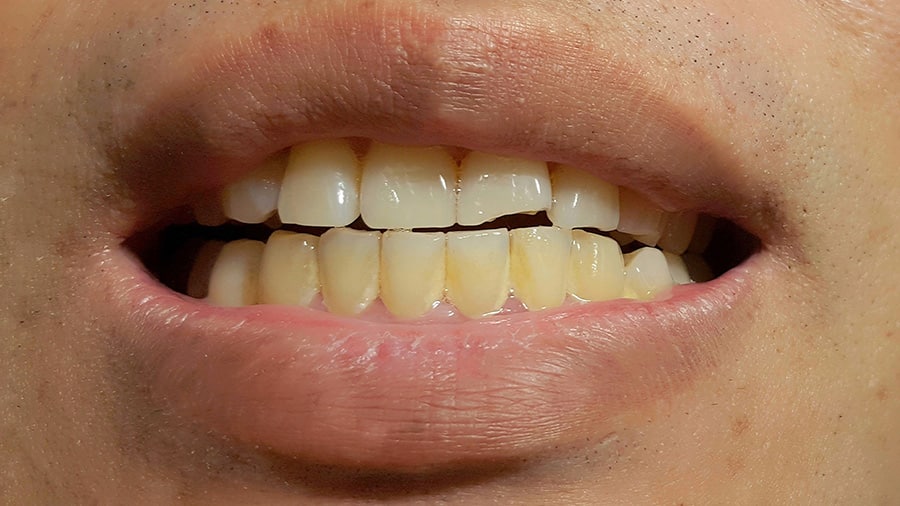
ฟันผุ
สาเหตุที่ทำให้ฟันหน้าผุคืออะไร
หากลูกของคุณมีฟันหน้าผุหรือคุณเองที่มี คุณอาจสงสัยว่าเกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไรและทันตแพทย์จะรักษาอย่างไร ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม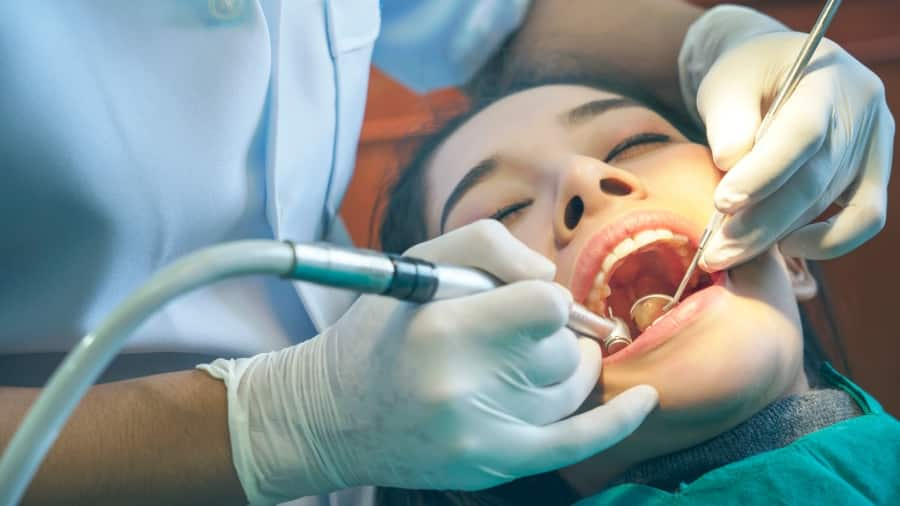
ฟันผุ
อุดฟันเจ็บไหม?
หากคุณต้องได้รับการอุดฟันและกำลังกังวลว่าการอุดฟันจะเจ็บไหม เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการอุดฟัน ขั้นตอนการอุดฟันก่อน และหลัง รวมถึงวิธีการป้องกันการฟันผุ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
คอยสังเกตอาการของฟันผุ
หากคุณรู้สึกถึงอาการเสียวฟันขณะที่สบฟัน นั่นอาจเป็นสัญญาณของฟันผุหรือการเกิดโพรงที่ตัวฟันซึ่งต้องได้รับการรักษา เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ฟันคุดผุควรทำอย่างไร
คุณอาจสงสัยว่าหากฟันคุดของคุณมีการผุเกิดขึ้น คุณควรที่จะได้รับการถอนฟัน หรือการอุดฟัน เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับฟันผุที่ฟันคุดที่คอลเกตได้ในตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ประเภทของฟันผุมีอะไรบ้าง
การมีความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับประเภทของฟันผุและ วิธีการป้องกันการเกิดฟันผุนั้นถือว่ามีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่ง เยี่มชมคอลเกตและ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ 6 ระยะของฟันผุ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
รากฟันผุคืออะไรแล้วจะป้องกันได้อย่างไรบ้าง
รากฟันผุเกิดขึ้นที่บริเวณรากของฟันมากกว่าที่ชั้นเคลือบฟัน เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้เพื่อเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีการป้องกันและรักษาฟันผุประเภทนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันผุ
ยาปฏิชีวนะ เมื่อมีการติดเชื้อที่ฟันและมีอาการปวดฟัน
การได้รับการรักษาขณะมีอาการปวดฟันเป็นเรื่องที่สำคัญ และคุณอาจต้องใช้ยาแก้อักเสบเพื่อใช้บรรเทาอาการนี้ในบางครั้ง เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตเพิ่มเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
อาการปากแห้งคืออะไร
อาการปากแห้ง เป็นความผิดปกติอย่างหนึ่ง ที่รบกวนการใช้ชีวิตของคุณแล้ว โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งถ้าปากแห้งรุนแรง ควรป้องกันเอาไว้ก่อน ด้วยวิธีง่าย ๆ มาดูเลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
ข้อเท็จจริงเกี่ยวกับอาการปากแห้ง
อาการปากแห้งเกิดขึ้นจากการที่ไม่มีน้ำลายเพียงพอ เนื่องจากการทานยาต่าง ๆ จนเกิดปัญหาช่องปากขึ้น ควรปรึกษาแพทย์ของคุณเพื่อรักษาอาการ ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
การใช้ยาบางชนิดมีผลต่อสุขภาพปากและฟันหรือไม่
การใช้ยาบางชนิด อาจส่งผลกระทบต่อสุขภาพช่องปากได้ เช่น ทำให้ปากแห้ง ปรึกษากับทันตแพทย์ของคุณเพื่่อการแก้ไขอาการได้ ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
ยาตามใบสั่งแพทย์กับอาการปากแห้ง
ยาตามใบสั่งแพทย์กว่า 500 ประเภทสามารถทำให้เกิดอาการปากแห้งได้ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งเมื่อมีการทานยาหลายประเภทร่วมกัน มียาอะไรบ้างที่สำคัญ ดูได้ที่นี่ คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
อาการปากแห้งและเบาหวาน: เคล็ดลับ 4 ข้อในการป้องกัน
คุณอาจสงสัยว่า "จะทำอย่างไรถึงจะหายจากภาวะปากแห้งในโรคเบาหวาน?" เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้ถึงสาเหตุของการปากแห้งและความเกี่ยวข้องกับโรคเบาหวาน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะปากแห้ง
วิธีแก้ปากแห้ง
การจะตัดสินใจเลือกวิธีการรักษาอาการปากแห้งนั้นขึ้นอยู่กับต้นตอสาเหตุที่แท้จริง ซึ่งมีแต่ละสาเหตุมีวิธีการรักษาที่แตกต่างกันไป เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันคุด
คุณควรถอนฟันคุดไหม
มาทำความเข้าใจกับฟันคุด ว่าฟันคุดจะงอกเมื่อไร มีอาการอย่างไร มีวิธีที่จะป้องกันไหม และ เมื่อไรที่คุณควรพบหมอฟันเพื่อปรึกษาเรื่องฟันคุด คลิกดูเลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันคุด
ฟันกราม
การถอนฟันกราม หรือฟันบดเคี้ยวซี่ที่สามเป็นเรื่องจำเป็นสำหรับบางคน โดยเฉพาะผู้ที่มีอายุช่วงยี่สิบต้น ๆ โดยทันตแพทย์จะเป็นผู้วินิจฉัย ดูเพิ่มเติมที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันคุด
การถอนฟันและกระดูกเบ้าฟันอักเสบ
5 วันแรกของการถอนฟันคุดสำคัญมาก เพราะอาจเกิดอาการข้างเคียงขึ้นได้ มาดูสาเหตุและลักษณะอาการ เพื่อการดูแลที่ถูกต้อง ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันคุด
พักฟื้นหลังผ่าฟันคุดใช้เวลานานเท่าไหร่?
ผ่าฟันคุดกี่วันหาย อาการหลังผ่าฟันคุดเป็นอย่างไร ควรหลีกเลี่ยงอาหารประเภทใด พร้อมเคล็ดลับและวิธีดูแลที่เหมาะสม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันคุด
ฟันคุดงอกไม่สมบูรณ์
มาทำความรู้จักว่า ฟันคุดคืออะไร อาการข้างเคียงของการมีฟันคุดเป็นอย่างไร การถอนฟันคุด และเมื่อไรต้องไปพบทันตแพทย์ ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกตได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม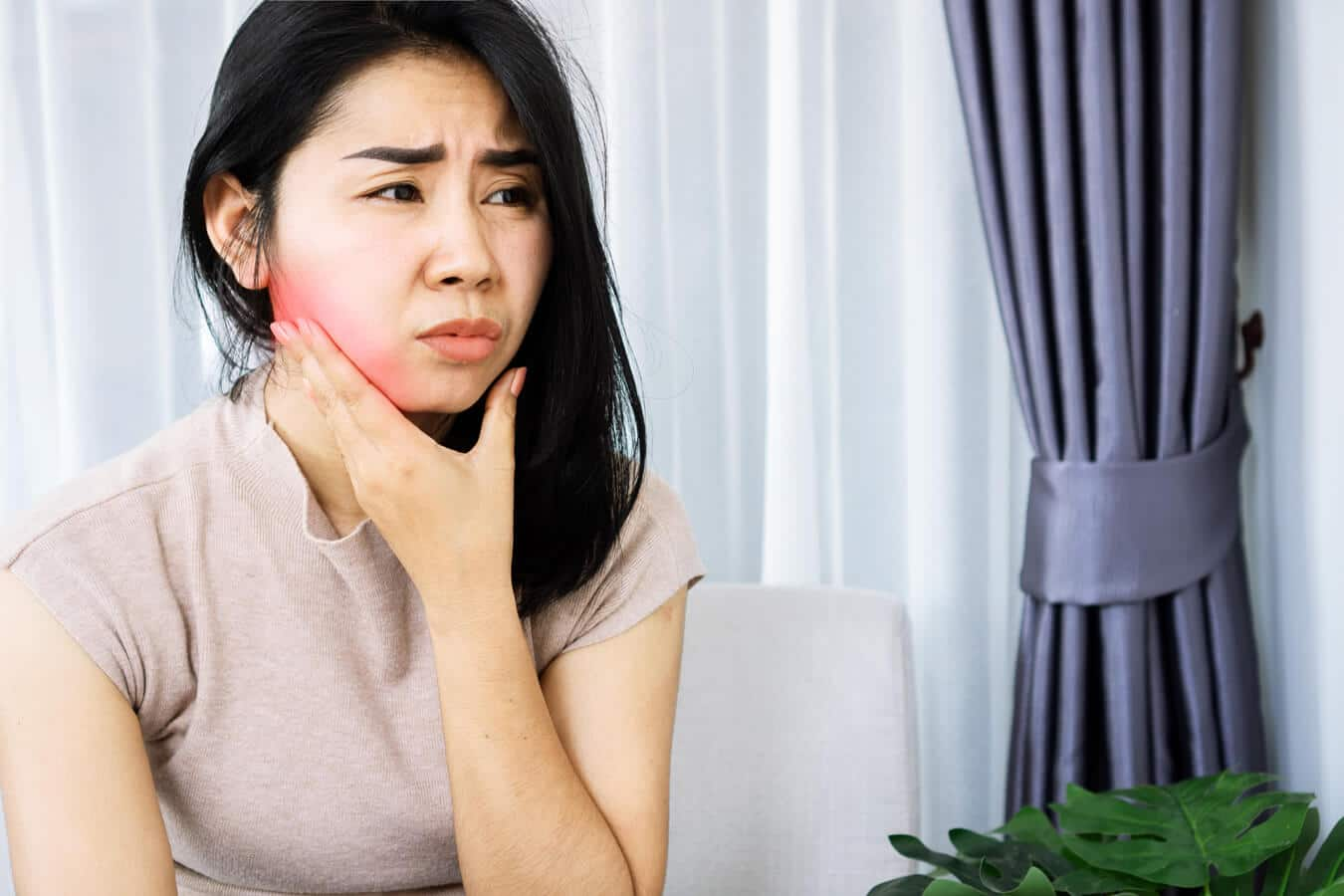
ฟันคุด
เหงือกบวม: สาเหตุและวิธีบรรเทาอาการ
เหงือกบวมเกิดจากหลายสาเหตุ แต่ไม่ว่าจะเกิดขึ้นจากสาเหตุใดก็อาจกลายเป็นปัญหาใหญ่ในภายหลังได้ มาดูวิธีการบรรเทาเหงือกบวมอย่างได้ผล ที่นี่เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม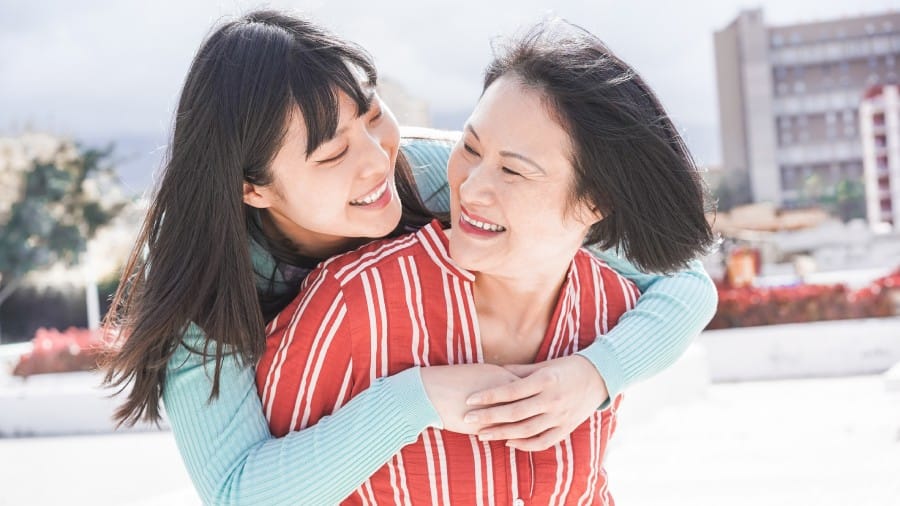
ฟันคุด
การถอนฟันคุด
การถอนฟันคุดคือการผ่าตัดเพื่อนำฟันคุดออกจากช่องปาก เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับขั้นตอนการผ่าตัดฟันคุดทั้งหมดที่อาจเกิดขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
เรามีฟันทั้งหมดกี่ซี่
เคยสงสัยไหมว่า เรามีฟันทั้งหมดกี่ซี่ ฟันน้ำนมมีกี่ซี่ ฟันแท้มีกี่ซี่ ฟันสองชุดนี้ดูแลต่างกันอย่างไร? คอลเกตมีเคล็ดลับน่ารู้ให้คุณดูแลฟันและสุขอนามัยในช่องปากอย่างถูกวิธี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
ต่อมทอนซิลและต่อมอดีนอยด์ต่างกันอย่างไร
รู้จักความต่างระหว่าง ต่อมทอนซิลและต่อมอดีนอยด์ ด่านแรกที่คอยสกัดกั้นสิ่งแปลกปลอมเมื่อเข้าสู่ร่างกาย พร้อมวิธีดูแลรักษาต่อมทั้งสอง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
ทำความเข้าใจโครงสร้างฟัน
ฟันของเราประกอบด้วยฟันหน้า ฟันเขี้ยว ฟันกราม รวมไปถึงฟันคุด การเรียนรู้และทำความเข้าใจโครงสร้างฟันเป็นส่วนสำคัญในการดูแลช่องปากให้มีสุขอนามัยที่ดีอยู่เสมอ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
ฟันไหนเป็นฟันน้ำนมบ้าง?
หลายคนคงสงสัยว่าฟันน้ำนมมีกี่ซี่ ฟันซี่ไหนเป็นฟันน้ำนมซี่ไหนเป็นฟันแท้ มารู้จักกับหน้าที่ของฟันน้ำนม พร้อมวิธีการดูแลเพื่อสุขภาพฟันของลูกน้อยที่แข็งแรง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
หน้าที่ของส่วนประกอบในช่องปาก
ช่องปากประกอบด้วยหลายส่วนที่ทำหน้าที่ร่วมกันเพื่อให้คุณสามารถหายใจ พูดคุย และรับประทานอาหารได้ อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โครงสร้างปากและฟัน
โพรงฟันคืออะไร
โพรงประสาทฟันเป็นโครงสร้างที่อยู่ตรงกลางของฟัน ช่วยปกป้องหลอดเลือดและเส้นประสาท เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโพรงประสาทฟันได้ที่คอลเกตตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม


การฟอกฟันขาว
วิธีรักษารอยยิ้มที่ขาวสะอาดสดใสทำอย่างไร?
ใครๆ ก็อยากมีฟันขาว เพื่อเผยรอยยิ้มสดใสและที่มั่นใจ แต่จะทำอย่างไรให้มีฟันขาวกระจ่างใส ดูสุขภาพฟันแข็งแรง คอลเกตรวบรวมข้อมูลมาฝากกันแล้ว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม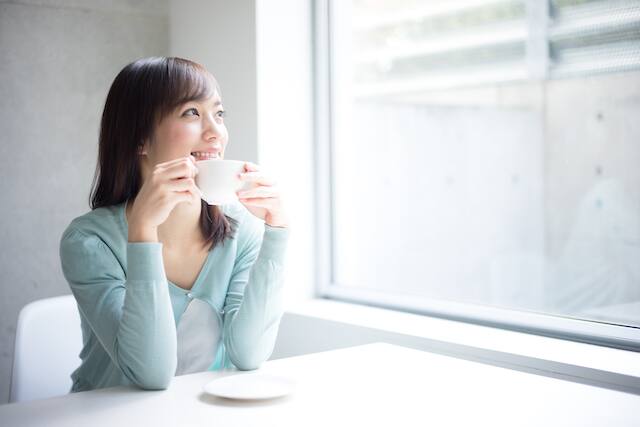
การฟอกฟันขาว
ทางลัดในการฟอกฟันขาวที่บ้าน
คุณมีงานสำคัญใกล้เข้ามาและคุณอยากดูดีที่สุดเมื่อถ่ายรูป อะไรคือทางลัดที่ทำให้ฟันขาวขึ้นซึ่งทำเองได้ที่บ้าน อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม


การฟอกฟันขาว
การเลือกระบบฟอกสีฟัน
หลายคนอยากมีรอยยิ้มที่ขาวขึ้น ดังนั้นคุณจะเลือกระบบฟอกสีฟันที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับคุณได้อย่างไร ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับระบบฟอกสีฟันได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม


การฟอกฟันขาว
เราจะรู้ได้อย่างไรว่าฟันของเรามีเฉดสีอะไร??
รู้หรือไม่ ฟันของเรามีเฉดสีระดับความขาวด้วยนะ แล้วคุณอยากรู้ไหมว่าคุณมีฟันขาวระดับไหน ลองมาดูคู่มือเฉดสีฟันที่นี่ คลิกดูได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
เคล็ดลับจัดการฟันเหลืองให้กลับมาขาวขึ้น
พบสาเหตุของฟันเหลืองว่าเกิดจากอะไร พร้อมเคล็ดลับและวิธีการแก้ปัญหาเมื่อเกิดฟันเหลืองให้กลับมาดูขาวขึ้นอีกครั้ง เพื่อรอยยิ้มที่ดูสดใสของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

การฟอกฟันขาว
วิธีทําให้ฟันขาว
ฟันที่ขาวสดใสทำให้เรารู้สึกมั่นใจมากขึ้น เรามีคำแนะนำในการช่วยให้ฟันของคุณขาวขึ้นได้ง่ายๆด้วยตัวเอง เพื่อสร้างความมั่นใจและคืนรอยยิ้มที่สดใสให้กับคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

การฟอกฟันขาว
ยาสีฟันเพื่อฟันขาวทำงานอย่างไร
การเข้าใจถึงยาสีฟันเพื่อฟันขาวแต่ละประเภทจะช่วยให้ทราบว่าผลิตภัณฑ์ชนิดใดที่เหมาะสมกับคุณมากที่สุด คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ชุดฟอกฟันขาวเพื่อรอยยิ้มที่สดใสกว่าที่เคย
ชุดฟอกฟันขาวสามารถช่วยให้คุณมีฟันขาวสะอาดได้ไม่ว่าจะที่คลินิคทันตแพทย์หรือทำเองได้ที่บ้าน คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
แผ่นฟอกฟันขาวเป็นทางเลือกที่ดีที่สุดของคุณหรือไม่?
ทุกคนต้องการที่จะยิ้มกว้างได้อย่างมั่นใจ และด้วยผลิตภัณฑ์ฟอกสีฟันใหม่ๆ ที่เปิดตัวในตลาดทุกปี บริษัทต่างๆ จึง...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
น้ำยาบ้วนปากฟันขาวที่ดีที่สุด: ควรดูจากอะไร
น้ำยาบ้วนปากฟันขาวที่ดีที่สุดคืออะไร และช่วยให้คุณมีรอยยิ้มที่สดใสขึ้นหรือไม่? หาคำตอบได้ที่นี่!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
รายละเอียดค่าใช้จ่ายในการทำเลเซอร์ฟันขาว
การทำเลเซอร์ฟันขาวเป็นวิธีที่มีประสิทธิภาพสูงในการทำให้ฟันของคุณขาวขึ้น ซึ่งกำลังเป็นที่นิยมมากขึ้นในกลุ่มคนทั่วไป
อ่านเพิ่มเติม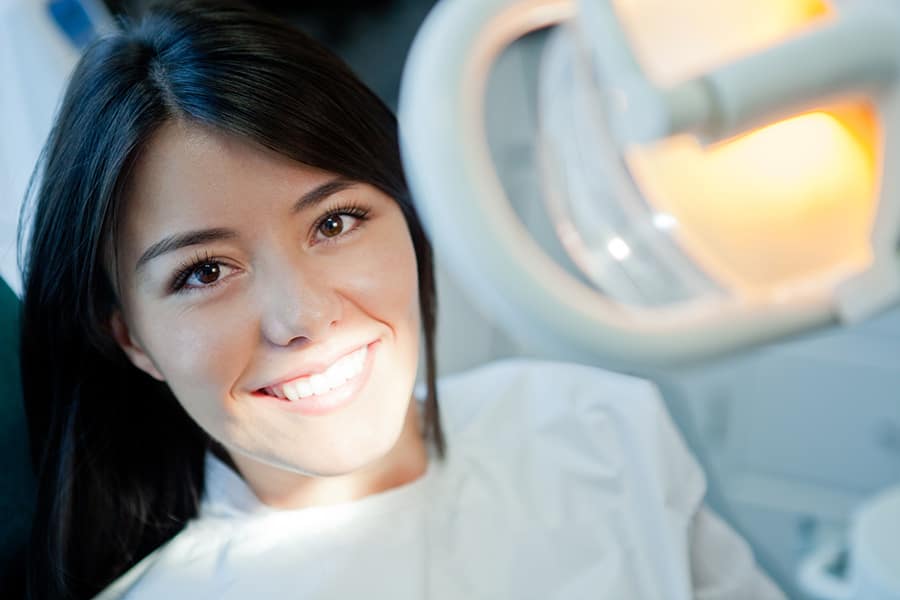
การฟอกฟันขาว
ชุดฟอกสีฟันที่บ้าน
คุณสามารถทำชุดฟอกสีฟันได้ที่บ้านจากผลิตภัณฑ์ที่หาซื้อได้ทั่วไป ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการทำชุดฟอกสีฟันที่บ้านได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
์การฟอกสีฟันด้วยเลเซอร์
การฟอกสีฟันด้วยเลเซอร์เป็นทางเลือกที่มีให้บริการที่คลินิกทันตกรรม แต่อาจไม่เหมาะสมในบางกรณี เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการฟอกสีฟันด้วยเลเซอร์
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ฟอกสีฟันแบบไหนดีที่สุดสำหรับคุณ
ถ้าชอบจิบกาแฟร้อนๆ ในตอนเช้า ฟันก็จะมีคราบสีเหลืองหรือน้ำตาล และคิดอยากฟอกสีฟันเองที่บ้าน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
3 เคล็ดลับการฟอกสีฟันราคาประหยัด
การฟอกสีฟันในราคาประหยัดนั้นง่ายกว่าที่คุณคิด ขอเสนอ 3 ขั้นตอนง่ายๆ เพื่อการมีรอยยิ้มที่สดใส
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
เบกกิ้งโซดาทำให้ฟันขาวจริงหรือ
เบกกิ้งโซดาเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ในครัวเรือนทั่วไปที่มีประโยชน์ใช้สอยมากมายในบ้าน ตั้งแต่การกำจัดกลิ่นไปจนถึงการทำความสะอาดพรม อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ชาทำให้เกิดคราบบนฟันหรือไม่
เราทราบดีว่ากาแฟทำให้เกิดคราบบนฟันได้ แล้วชาทำให้เกิดคราบบนฟันหรือไม่ คำตอบก็คือ ใช่ ในความเป็นจริง ชาอาจทำมากกว่า…
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ผลิตภัณฑ์ฟอกฟันขาว 4 ประเภท
ปัจจัยหลักที่ใช้พิจารณาในการฟอกสีฟัน คือ ความสะดวกในการใช้งาน ประสิทธิผล และราคาที่จ่ายได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
อาหาร 5 ชนิดที่ทำให้เกิดคราบสี และทำให้สีฟันเปลี่ยน
เบื่อไหมที่ฟันของคุณดูเหลืองและหมองคล้ำแต่ไม่แน่ใจว่าเพราะอะไรทำให้ฟันเป็นแบบนั้น เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับอาหาร 5 ชนิดที่ทำให้ฟันเปลี่ยนสี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
คราบกาแฟติดฟันได้อย่างไร?
คนส่วนใหญ่รู้สึกเหมือนขาดอะไรไปหากไม่ได้ดื่มกาแฟก่อนเริ่มงานในแต่ละวัน แต่เครื่องดื่มที่ทำให้คุณยิ้มได้นี้... อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
การรับประทานอาหารที่เหมาะสมช่วยให้ฟันขาวขึ้นได้อย่างไร
วิธีทำให้ฟันขาวขึ้นจากผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ช่วยให้ฟันขาว รวมถึงอาหารที่รับประทานอาจช่วยคุณได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ทำอย่างไรให้ฟันคงความขาว
คุณอาจมีฟันขาวอยู่แล้วหรือเพิ่งฟอกฟันขาวมา จำไว้ว่าคุณมีสิ่งที่ต้องปฏิบัติ...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
การฟอกฟันขาวโดยผู้เชี่ยวชาญเป็นวิธีที่เหมาะกับคุณหรือไม่
การฟอกฟันขาวโดยผู้เชี่ยวชาญเหมือนเป็นทางออกอันน่าอัศจรรย์สำหรับคราบที่ติดแน่นและฟันสีออกเหลือง แต่เป็นทางเลือกที่ดีที่สุดหรือไม่...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ใช้ถาดฟอกสีฟันเพื่อรอยยิ้มที่สดใสขึ้น
ไม่ว่าคุณจะสูบบุหรี่จัด ดื่มกาแฟวันละสามแก้ว หรือแค่สังเกตเห็นว่าฟันหมอง มีสีเหลืองเมื่ออายุมากขึ้น...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม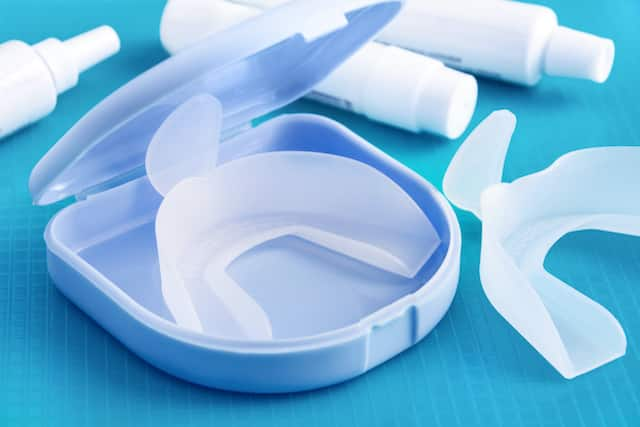
การฟอกฟันขาว
การฟอกสีฟันแบบใดเหมาะกับคุณที่สุด
ในขณะที่ฟันธรรมชาติไม่ได้ขาวปิ๊งไร้ที่ติ คนส่วนใหญ่จึงอยากให้ฟันขาวขึ้น สดใสขึ้น… อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม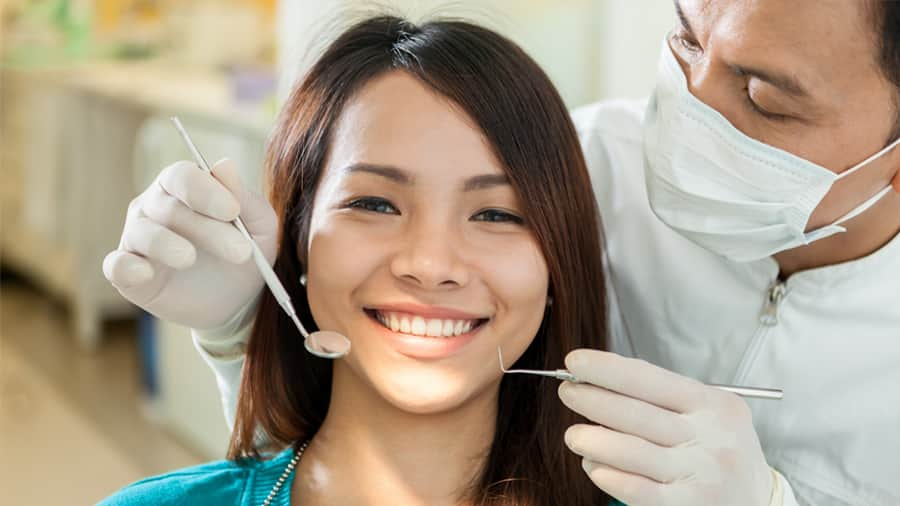
การฟอกฟันขาว
การฟอกฟันขาวโดยผู้เชี่ยวชาญคุ้มค่าหรือไม่
หากคิดจะฟอกฟันขาว คงทราบว่าราคาฟอกฟันขาวโดยผู้เชี่ยวชาญค่อนข้างสูงและแพงกว่าการทำเองที่บ้านมาก เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
ยาสีฟันช่วยให้ฟันขาว - ไฮโดรเจนเปอร์ออกไซด์เปรียบเทียบกับ คาร์บาไมด์เปอร์ออกไซด์
การใช้ยาสีฟันที่มีส่วนประกอบไฮโดรเจนเปอร์ออกไซด์เป็นวิธีทำให้ฟันขาวขึ้นทุกวัน แล้วจะเป็นประโยชน์กับคุณหรือไม่ ต่อไปนี้คือ 4 ข้อที่คนมักสงสัย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม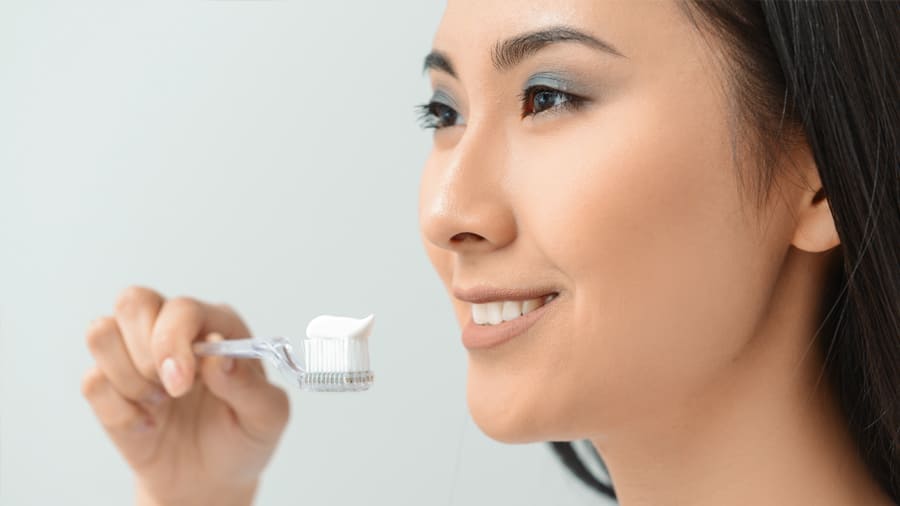
การฟอกฟันขาว
ออยล์พูลลิ่งคืออะไร สิ่งที่คุณจำเป็นต้องรู้
ออยล์พูลลิ่งเป็นที่รู้จักกันมานานแล้วว่าช่วยส่งเสริมสุขภาพช่องปาก ถึงแม้จะไม่ใช่สิ่งที่ดีที่สุดก็ตาม ออยล์พูลลิ่งคืออะไร เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
การเลือกวิธีฟอกสีฟันที่ดีที่สุด (เหมาะสำหรับทุกคน)
ไม่ว่าคุณจะมีงบจำกัดหรือต้องการผลลัพธ์สำหรับออกงาน นี่คือทางเลือกการฟอกฟันขาวดีที่สุดสำหรับทุกคน เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
วิธีฟอกฟันขาวเองที่บ้านสำหรับผู้ที่ชอบดื่มกาแฟ
หากคุณชอบจิบกาแฟหรือชาในตอนเช้า คุณอาจมีคราบสีเหลืองหรือน้ำตาลบนฟัน มันคืออะไร...
อ่านเพิ่มเติม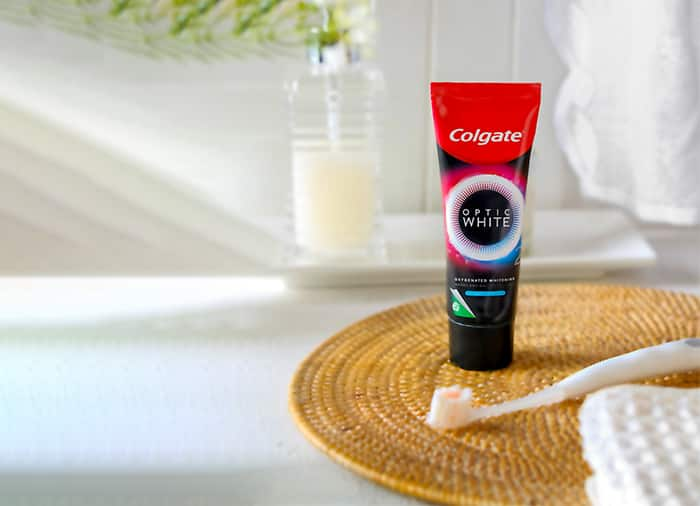
การฟอกฟันขาว
เคลือบฟันขาวราคาเท่าไร? เปรียบเทียบวิธีทำเองที่บ้านและกับผู้เชี่ยวชาญ
มาดูกันว่า การฟอกฟันขาวมีค่าใช้จ่ายเท่าไหร่ รวมทั้งความแตกต่างของตัวเลือกระหว่างการทำเองที่บ้าน และการรับบริการจากคลินิก เพื่ือให้คุณได้มีฟันขาวสดใสได้อย่างรวดเร็ว!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

การฟอกฟันขาว
ทำความรู้จักผลิตภัณฑ์ฟอกฟันขาวชนิดต่างๆ เพื่อฟันขาวสุขภาพดี
คำแนะนำแบบรวบรัดที่จะช่วยให้คุณรู้จักผลิตภัณฑ์ฟอกฟันขาว รวมถึงเคล็ดลับในการมองหา วิธีการใช้งาน และสาเหตุของคราบฟัน ฟันเหลือง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
เคล็ดลับวิธีการยิ้มเวลาถ่ายภาพด้วยรอยยิ้มอย่างมั่นใจ
รอยยิ้มสามารถทำให้ภาพถ่ายของคุณดูดีขึ้นได้ มาทำตามวิธีการยิ้มเวลาถ่ายภาพ ซึ่งมาพร้อมคำแนะนำเรื่องฟันขาวสดใส ที่จะทำให้คุณโพสต์ท่าถ่ายรูปได้แบบมือโปรฯ ในเวลาไม่นาน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
สร้างความมั่นใจให้ตัวเอง ด้วยฟันขาว
ไม่ว่าคุณจะทำอาชีพไหน แต่ความมั่นใจในตัวเองก็สำคัญ สร้างความมั่นใจในตัวเองง่าย ๆ ด้วยรอยยิ้มของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
วิธีรักษาอาการเสียวฟันหลังจากการฟอกฟันขาว
อาการเสียวฟันหลังจากการฟอกฟันขาว ฟังดูคุ้นหรือไม่? มีหลายวิธีในการรักษาอาการเสียวฟันที่เกิดจากการฟอกฟันขาว เพื่อให้คุณได้กลับมายิ้มได้อย่างมั่นใจอีกครั้ง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
อะไรเป็นสาเหตุของฟันสีเขียวและการเปลี่ยนสีฟันอื่นๆ
การเปลี่ยนสีฟันอย่างฟันสีเขียวสามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ในหลายสถานการณ์ ซึ่งคราบสีเหล่านี้อาจเกิดจากปัจจัยภายนอกหรือภายในก็ได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
วิธีทำให้ฟันขาวสําหรับคนจัดฟัน
การฟอกฟันขาวขณะจัดฟันนั้นไม่ใช่สิ่งที่เป็นไปไม่ได้ เพียงแต่ต้องมีการดูแลเป็นพิเศษเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าการรักษานั้นประสบความสำเร็จ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การฟอกฟันขาว
เคล็ดลับรอยยิ้มสวยสไตล์เกาหลี: Morning Routine ฟันขาวใสที่คุณทำได้เองที่บ้าน
เผยเคล็ดลับรอยยิ้มสวยแบบสาวเกาหลี! เรียนรู้ Morning Routine ดูแลฟันขาวใส ที่ทำได้ง่ายๆที่บ้าน เพื่อฟันสวยสะอาด มั่นใจได้ทุกวัน อ่านเพิ่มเติมที่นี่ คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การนอนกัดฟัน (Bruxism)
การนอนกัดฟัน – สัญญาณและอาการ
ถ้าคุณตื่นขึ้นมาพร้อมกับอาการปวดขากรรไกรหรือปวดศีรษะ นั่นแสดงว่าคุณนอนกัดฟัน ซึ่งอาจทำให้เกิดการปวดฟัน ฟันโยก และส่งผลกระทบอื่น ๆ ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การนอนกัดฟัน (Bruxism)
คุณกำลังประสบปัญหาเรื่องการนอนกัดฟันอยู่หรือไม่?
การนอนกัดฟัน มีสาเหตุได้จากหลายปัจจัยทั้งจากปัจจัยภายใน และภายนอก ซึ่งทันตแพทย์สามารถวินิจฉัยและรักษาด้วยวิธีที่เหมาะสมได้ ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ฟันผุในเด็กเล็ก
ทารกและเด็กเล็กมักจะมีปัญหาฟันผุ ซึ่งบางครั้งมีสาเหตุจากการดูดขวดที่เรียกว่า ฟันผุจากขวดนม ซึ่งสามารถป้องกันได้ คลิกดูวิธีการได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
สุขภาพฟันที่ดีของลูก: ข้อเท็จจริงอันน่าประหลาดใจที่ผู้ปกครองควรรู้
ความลับในการดูแลสุขภาพฟันของเด็กให้ดีคืออะไร คอลเกตขอแนะนำข้อเท็จจริงเกี่ยวกับการดูแลช่องปาก 2-3 ข้อที่สามารถปกป้องเด็กจากฟันผุ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ฟันน้ำนมและฟันแท้แตกต่างกันอย่างไร
สุขภาพฟันแท้ในอนาคตของลูกจะดีหรือไม่ ส่วนหนึ่งขึ้นอยู่กับการดูแลฟันน้ำนมด้วย มาเรียนรู้ความแตกต่าง พร้อมวิธีการดูแลอย่างถูกต้องจาก คอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
เราจะดูแลฟันของเด็กเล็กอย่างไร
การดูแลฟันเด็กวัยหัดเดิน ควรใช้แรงจูงใจในการรักษาสุขอนามัยช่องปากและฟัน เพื่อปลูกฝังนิสัยการดูแลสุขภาพปากและฟันให้กับเด็ก มาดูวิธีการได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ทำอย่างไรดีเมื่อลูกน้อยไม่อยากแปรงฟัน
เด็กส่วนใหญ่มักคิดว่าการไม่แปรงฟันนั้นไม่ได้ส่งผลกระทบอะไรมากมาย แต่คุณต้องให้กำลังใจลูกแปรงฟันเพื่อป้องกันฟันผุและปัญหาเหงือกในอนาคต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
สาเหตุของเด็กฟันไม่ขึ้น เรียนรู้ฟันเด็กควรขึ้นตอนกี่เดือนและปัจจัยที่ทำให้ฟันงอกช้า
เมื่อเด็กฟันไม่งอกหรืองอกช้า พ่อแม่ส่วนใหญ่มักจะสงสัยว่ามีอะไรผิดปกติหรือไม่ คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ทำไมนั่นไม่ใช่เรื่องน่ากังวล
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
สุขภาพปากและฟันสำหรับเด็ก
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันให้ดี ควรเริ่มต้นปลูกฝังตั้งแต่เด็ก คุณพ่อคุณแม่จะสามารถดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากเด็กได้อย่างไรบ้าง มาดูวิธีการได้ที่นี่เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ฟันกรามน้ำนมขึ้นทำให้เด็กปวดฟัน ผู้ปกครองควรรับมือย่างไร?
คู่มือการดูแลฟันกรามน้ำนมที่กำลังขึ้นของลูกน้อยและวิธีลดอาการปวดเมื่อฟันขึ้น พร้อมเคล็ดลับการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากเมื่อฟันกรามแท้ขึ้นแล้ว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
เมื่อเจ้าตัวเล็กฟันหลุด: หกไอเดียดี ๆ ฉลองลาก่อนฟันจ๋า
เมื่อลูกน้อยฟันหลุด จะเตรียมฉลองเต็มที่หรือเรียบง่ายดีนะ และไม่ว่าจะเลือกแบบไหน สิ่งสำคัญก็คือทำให้เด็ก ๆ รู้สึกว่านี่เป็นโอกาสพิเศษของเขา
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ฟันน้ำนมมีกี่ซี่? ประโยชน์ของตารางลำดับการขึ้นของฟันแท้สำหรับคุณพ่อคุณแม่
แม้การขึ้นของฟันแท้อาจเริ่มในวัยที่แตกต่างกัน แต่ลำดับการขึ้นของฟันแท้ในแต่ละตำแหน่งเหมือนกัน ตารางลำดับการขึ้นของฟันแท้จะช่วยให้รู้ว่าฟันซี่ไหนจะขึ้นเป็นซี่ต่อไป
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ทำไมลูกน้อยของคุณจึง ต้องใช้เครื่องมือกันช่องว่างที่ฟัน
เมื่อฟันน้ำนมหลุด เด็กบางรายอาจต้องใช้เครื่องมือกันช่องว่างที่ฟัน เพื่อดูแลช่องปากของเด็กให้มีสุขภาพดี ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม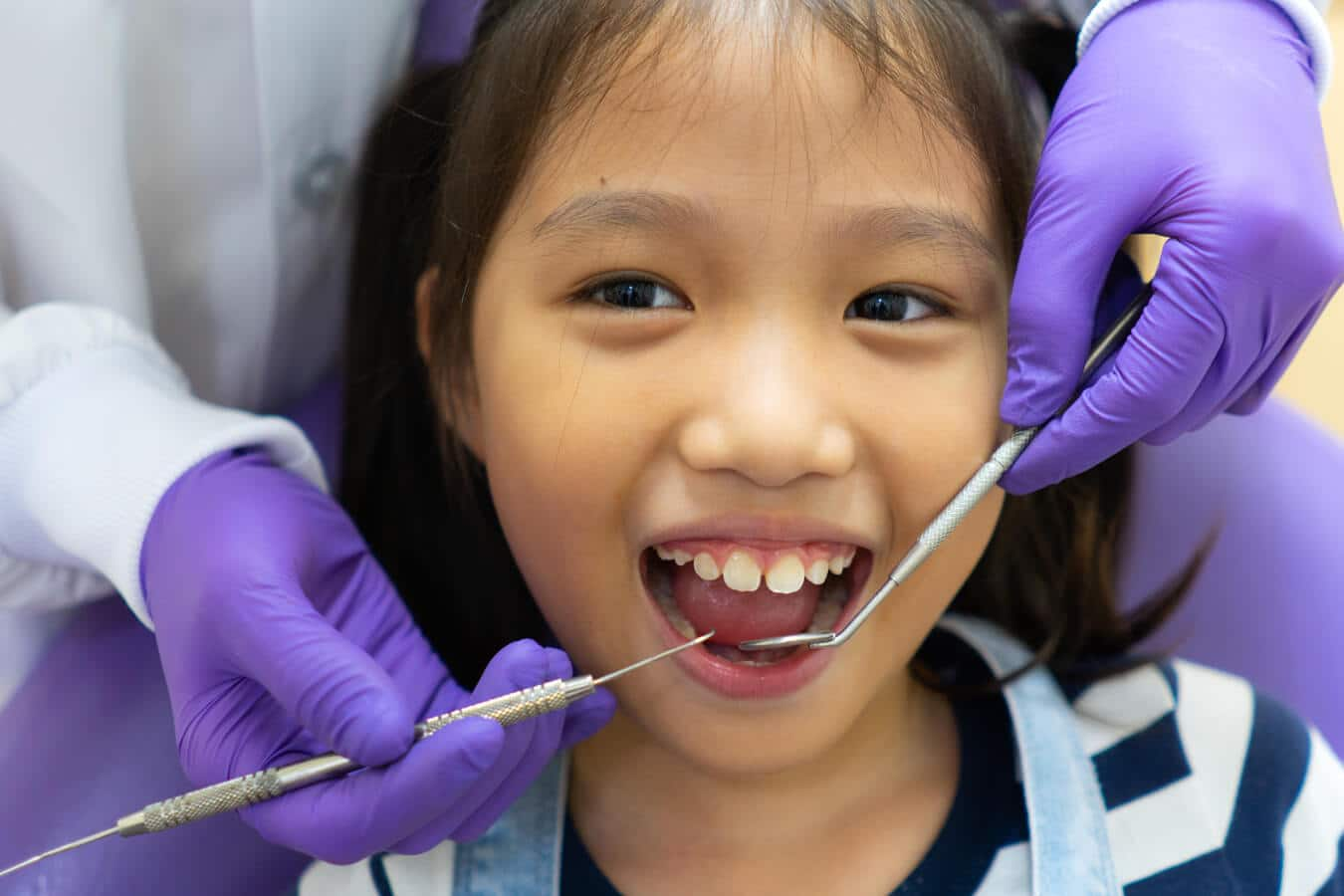
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
จัดการปัญหาเด็กฟันผุ: สัญญาณและวิธีการรักษาที่มีประสิทธิภาพ
ฟันผุในเด็กเป็นปัญหาที่พบได้บ่อยมากกว่าที่คุณคิด เด็กก่อนวัยเรียนมากกว่า 1 ใน 4 คนในสหรัฐอเมริกามีปัญหาฟันผุ อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
การรักษาเหงือกอักเสบในเด็ก
การรักษาเหงือกอักเสบในเด็กเป็นขั้นตอนที่ไม่มีอะไรซับซ้อนยุ่งยากและเป็นโอกาสอันดีที่คุณจะได้ปลูกฝังบุตรหลานของคุณเกี่ยวกับกิจวัตรเพื่อสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
น้ำยาบ้วนปากเด็ก คำแนะนำการเลือกน้ำยาบ้วนปากและการใช้อย่างถูกต้อง
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากรวมถึงการใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากช่วยส่งเสริมให้ฟันและเหงือกแข็งแรง สิ่งสำคัญคือต้องใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากเด็กอย่างปลอดภัย เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: เด็ก (5-12 ปี)
ทราบได้อย่างไรว่าฟันลูกน้อยกำลังขึ้น?
จะรู้ได้อย่างไรเมื่อฟันน้ำนมของลูกกำลังจะงอก ช่วงอายุที่ฟันจะเริ่มงอก อาการของเด็กทารกอันเป็นสัญญาณของฟันงอก และการดูแลทารกในวัยนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การถอนฟัน
การถอนฟัน
การถอนฟันไม่น่ากลัวอย่างที่หลายคนคิด ลองมาทำความเข้าใจขั้นตอนการถอนฟันจากทันตแพทย์ รวมถึงวิธีการดูแลช่องปากหลังการถอนฟัน เพื่อจะดูแลได้อย่างถูกต้อง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การถอนฟัน
อาการปวดหลังถอนฟัน: เคล็ดลับ 3 ข้อที่จะช่วยให้เด็ก ๆ แปรงฟันต่อไป
บางครั้งเด็กจะต้องมีการถอนฟันน้ำนมบ้าง ถ้ามันไม่ยอมหลุดเอง จึงจำเป็นที่จะต้องถอนออก อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ www.colgate.co.th
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ประโยชน์ของแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า
จะเลือกแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าอย่างไรให้เหมาะสมกับคุณที่สุด? คอลเกตจะพาไปรู้จักกับคุณสมบัติและข้อดีของแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อการเลือกใช้ที่เหมาะที่สุด
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ผลิตภัณฑ์ตามคลินิคทันตแพทย์อะไรบ้างที่สามารถนำมาใช้ฟอกฟันขาวได้เองที่บ้าน?
ผลิตภัณฑ์ฟอกฟันขาวที่ใช้ตามคลินิคทันตแพทย์ ที่คุณสามารถนำมาฟอกฟันขาวได้เองที่บ้านอย่างปลอดภัยและได้ผลมีอะไรบ้าง ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
น้ำยาบ้วนปากป้องกันโรคเหงือกอักเสบแบบไหนดีที่สุด
การแปรงฟัน การใช้ไหมขัดฟันและการฟันสม่ำเสมอเป็นสิ่งสำคัญในการดูแลช่องปากเพื่อป้องกันโรคเหงือก นอกจากนี้น้ำยาบ้วนปากยังสามารถช่วยป้องกันโรคเห…
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันที่เหมาะกับคุณ
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันมีความสำคัญมากกว่าที่คนส่วนใหญ่คิด เรียนรู้ชนิดของแปรงสีฟันที่คุณควรใช้ เมื่อไรคุณควรเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟันและอื่น ๆ ที่ Colgate.co.th
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
บรรเทาอาการปวดฟันด้วยวิธีธรรมชาติ
อาการปวดฟันสามารถทำให้ทุเลาลงได้หลากหลายวิธี มารู้จักวิธีแก้ปวดฟัน ด้วยวิธีธรรมชาติที่ได้ผลดีเช่นการใช้สมุนไพรและการรักษาด้วยวัตถุดิบจากธรรมชาติต่างๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
แพ้ยาสีฟัน จะทำอย่างไรดี?
อาการแพ้ยาสีฟันนั้นอาจเกิดขึ้นได้กับบางคน ด้วยการแพ้ส่วนผสมในยาสีฟัน อาจทำให้ริมฝีปากแตก บวม หรือแสบปาก แก้ไขได้ด้วยการเปลี่ยนยาสีฟัน ดูเพิ่มเติมที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ข้อเท็จจริงเกี่ยวกับยาสีฟันที่มีผงขัดe
คุณทราบว่ายาสีฟันของคุณมีปริมาณฟลูออไรด์เท่าไร และทราบว่ายาสีฟันฟลูออไรด์จะทำให้เคลือบฟันสึกกร่อนหรือไม่ อ่านข้อมูลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ยาสีฟันเกลือคืออะไร
คุณอาจสงสัยว่าการยาสีฟันเกลือมีสูตรอะไรบ้าง และใช้ยาสีฟันที่มีเกลือผสมจะช่วยให้ฟันสะอาดและสุขภาพช่องปากดีได้จริงหรือ อ่านข้อมูลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ยาสีฟันดีที่สุดสำหรับเหงือก: ควรดูจากอะไร
เหงือกอักเสบ ปัญหาปริทันต์ แผลในปาก และการติดเชื้อแบคทีเรีย จะส่งผลให้เหงือกไวต่อความรู้สึก ในช่วงนี้เป็นเรื่องสำคัญที่คุณจะหายาสีฟันที่ไวต่อความรู้สึก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
น้ำยาบ้วนปากชนิดไหนดีที่สุดสำหรับเหงือกอักเสบ
การใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากหลังจะช่วยฆ่าเชื้อ ลดปริมาณแบคทีเรียในช่องปาก รวมถึงดูแลอาการเหงือกอักเสบที่เป็นสภาวะเริ่มแรกของปัญหาเหงือกได้ ดูเพิ่มเติมได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ยาสีฟันถ่านชาร์โคล: คืออะไร
หลายคนเชื่อว่ายาสีฟันถ่านชาร์โคลมีคุณสมบัติดีพอที่จะลองใช้ดู และคอลเกตจะเล่าให้ฟังว่ายาสีฟันถ่านชาร์โคลเหมาะกับคุณหรือไม่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
การแพ้ยาสีฟัน
เป็นไปได้นะ ที่คุณจะแพ้ยาสีฟัน คอลเกตเล่าให้ฟังสัญญาณต่างๆ ที่อาจจะบ่งบอกว่าคุณแพ้ยาสีฟัน และคุณควณทำอะไรตอนประสบสัญญาณนั้นๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
เคล็ดลับการเลือกใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากเพื่อผลลัพธ์ที่ดีขึ้น
ผู้คนส่วนใหญ่อาจรู้เพียงว่าใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากแล้วสุขภาพช่องปากจะดี แต่ไม่รู้ประโยชน์ที่แท้จริง คอลเกตบอกให้รู้ว่าน้ำยาบ้วนปากทำงานอย่างไร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันให้เด็กทารก
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันที่เหมาะสมสำหรับเด็กทารกจะช่วยให้มีการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดีตั้งแต่แรกของการเติบโต คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม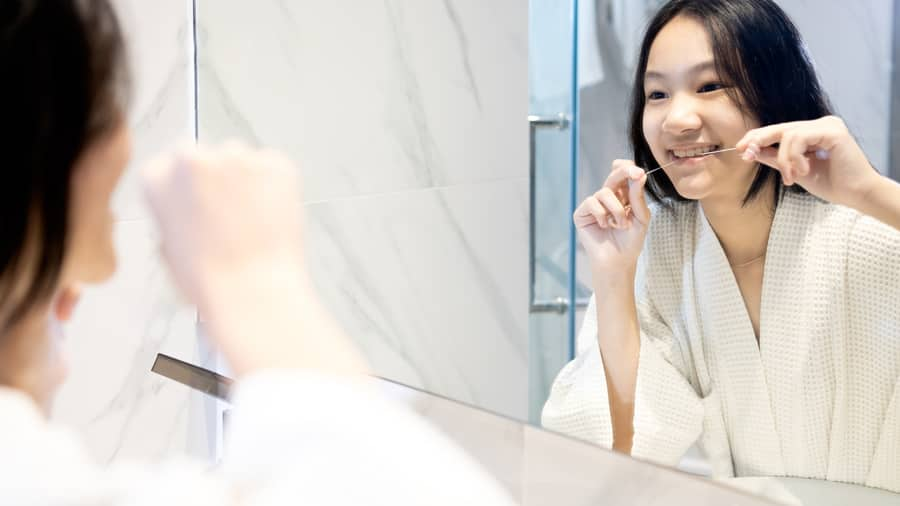
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ไม่ชอบใช้ไหมขัดฟัน? แปรงซอกฟันอาจเป็นตัวช่วยที่เหมาะสำหรับคุณ
การทำความสะอาดซอกฟันและรอบๆ เหงือกเป็นสิ่งสำคัญหากคุณต้องการรักษาสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี หลายคนใช้ไหมขัดฟันในการทำความสะอาด อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
แปรงสีฟันสำหรับคนจัดฟัน
คนที่ใส่เครื่องมือจัดฟันมักมีอาหารเกาะติดที่ฟันหรือซอกฟัน คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้เกี่ยวกับแปรงสีฟันสำหรับคนจัดฟันเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม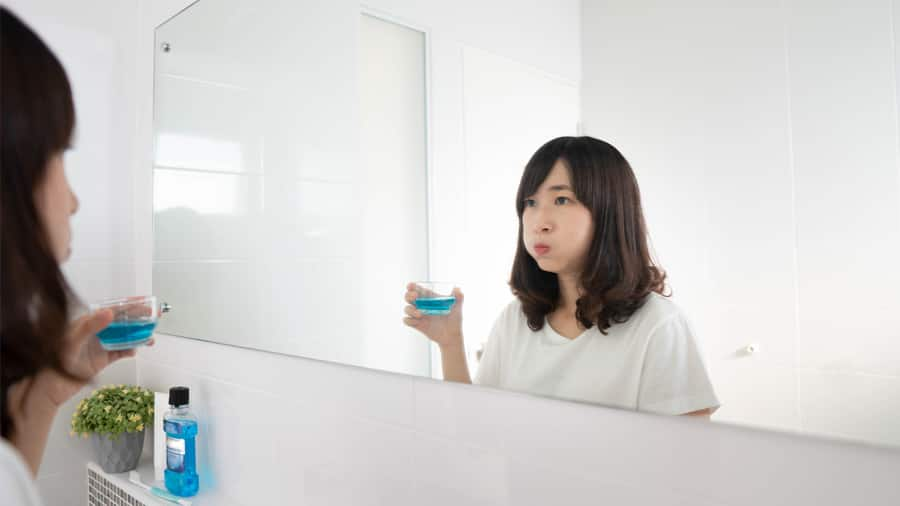
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
น้ำยาบ้วนปากจำเป็นไหมสำหรับแบคทีเรียในช่องปาก
นอกจากการแปรงฟันและขัดฟันแล้ว การใช้น้ำยาบ้วนปากเป็นอีกวิธีที่ช่วยดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากให้ปราศจากแบค คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม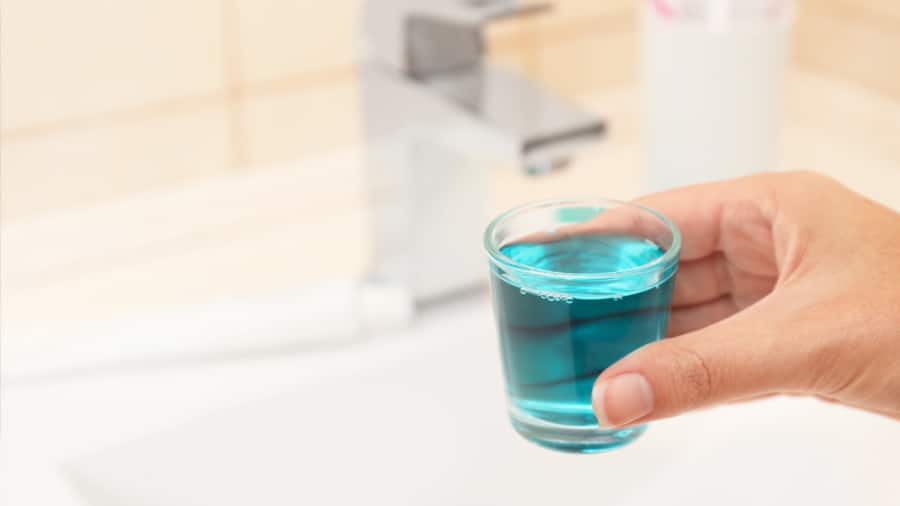
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
น้ำยาบ้วนปากที่ลดกลิ่นปากได้ดีที่สุด
อยากเลือกซื้อน้ำยาบ้วนปากสำหรับลดกลิ่นปาก คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมถึงปัญหากลิ่นปากและวิธีเลือกน้ำยาบ้วนปากดีที่สุดเพื่อลดกลิ่นปาก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าช่วยส่งเสริมสุขอนามัยในช่องปากที่ดีได้ยังไร
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าช่วยส่งเสริมสุขอนามัยในช่องปากที่ดีได้ยังไร ต้องพิจารณาอะไรตอนที่เลือกซื้อแปรงสีฟัน คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ประเภทขนแปรงสีฟัน
แปรงสีฟันขนแปรงนุ่ม และแปรงสีฟันขนแข็ง แต่ละแบบมีประโยชน์อย่างไร และต้องพิจารณาอะไรบ้างในการเลือกแปรงสีฟันที่เหมาะกับคุณ มาดูวิธีการเลือกได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
เรียนรู้วิธีเลือกแปรงสีฟันสำเด็ก
แปรงสีฟันเด็กมีขนาดและรูปร่างแตกต่าง แบบที่เหมาะสำหรับลูกขึ้นอยู่กับความต้องการและความสามารถของลูก คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
การแปรงฟันขั้นพื้นฐานสำหรับเด็ก และยาสีฟันประเภทไหนที่เหมาะสำหรับลูกน้อยของคุณ
ลูกน้อยของคุณควรแปรงฟันด้วยยาสีฟันที่มีส่วนผสมของฟลูออไรด์แล้วหรือยัง แล้วจะเริ่มใช้ฟลูออไรด์เพื่อปกป้องฟันเมื่อไร ดูคำตอบจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม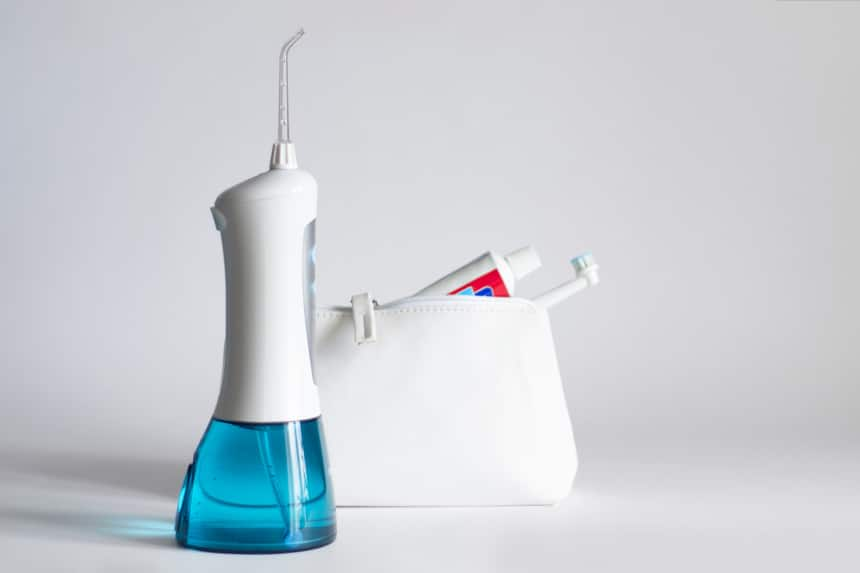
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ลองใช้ไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำดีมั๊ย?
การใช้ไหมขัดฟันเป็นส่วนสำคัญต่อการมีสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี หากคุณมีปัญหาในการใช้ไหมขัดฟัน อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับคุณ
แปรงสีฟันที่เหมาะสมกับคุณที่สุดขึ้นอยู่กับคุณสมบัติเฉพาะที่คุณต้องการ นี่คือสามสิ่งที่ควรพิจารณาในแปรงสีฟัน อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ควรใช้ฝาครอบแปรงสีฟันหรือไม่?
การใช้ที่ครอบแปรงสีฟันเพื่อป้องกันเชื้อโรคเข้าสู่แปรงจากภายนอกนั้นได้ผลหรือไม่ เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการดูแลแปรงสีฟันเพื่อรักษาความสะอาดได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ผงขัดฟันหรือ ยาสีฟัน: อะไรที่เหมาะสำหรับคุณ
เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตประเทศไทยตอนนี้และเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการใช้งานและข้อดีของการใช้ยาสีฟันที่มีขายโดยทั่วไป เมื่อทำการเปรียบเทียบการใช้ผงขัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
เหล็กครอบฟัน — แฟชั่นใหม่ที่ส่งผลต่อทันตกรรมและสุขภาพฟันของคุณ
การใส่เหล็กครอบฟันแฟชั่น ที่ไม่ได้อยู่ใต้การดูแลของทันตแพทย์ สามารถสร้างความเสียหายให้กับช่องปากของคุณได้อย่างไรบ้าง ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม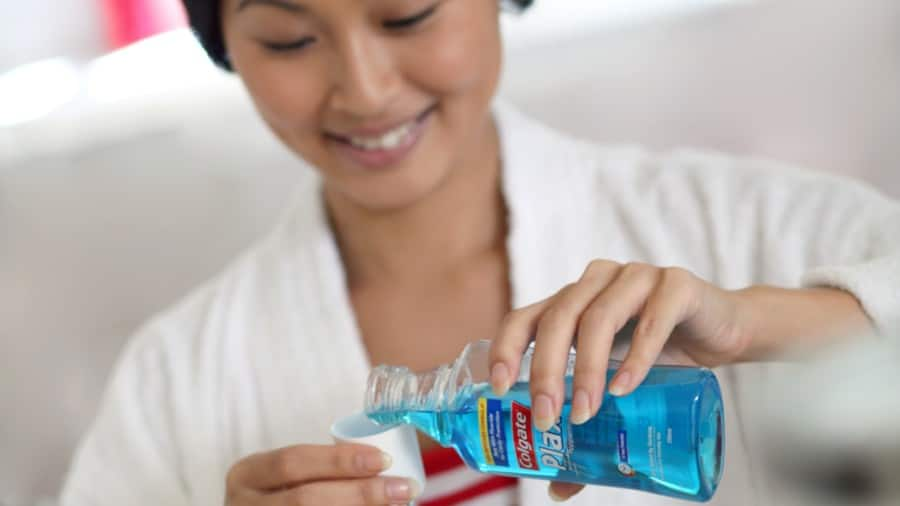
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ประโยชน์ของน้ำยาบ้วนปากสูตรไม่มีแอลกอฮอล์
น้ำยาบ้วนปากที่ปราศจากแอลกอฮอล์มีคุณค่าความสำคัญที่แตกต่างกันออกไปขึ้นอยู่กับแต่ละชนิด เรียนรู้น้ำยาบ้วนปากที่ไม่มีแอลกอฮอล์ประเภทต่างๆได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คำแนะนำด้านผลิตภัณฑ์ในการดูแลฟัน
ทำความรู้จักปากกาฟอกฟันขาว
หากต้องการมีรอยยิ้มที่น่าประทับใจ ปากกาฟอกฟันน่าจะช่วยได้ วิธีการทำงานและวิธีใช้ปากกาฟอกฟันขาว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม




แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
บ้วนปากด้วยน้ำเกลือดีต่อสุขภาพช่องปากอย่างไร?
อยากมีสุขภาพช่องปากดีต้องอ่าน! ชวนรู้จักคุณสมบัติของน้ำเกลือบ้วนปาก พร้อมขั้นตอนการเตรียมน้ำเกลือเพื่อบ้วนปาก เพื่อสุขภาพเหงือกและฟันที่แข็งแรง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
5 ปัญหาในช่องปากที่พบได้บ่อยและวิธีการรักษา
การดูแลช่องปากไม่ใช่แค่การช่วยรักษาให้ฟันแข็งแรง แต่ยังส่งผลต่อสุขภาพร่างกายโดยรวมด้วย รู้จักโรคในช่องปากที่พบได้บ่อยและแนวทางวิธึการรักษาได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
ตุ่มใสที่ปากคืออะไร?
ตุ่มใสในปากนั้นอาจเกิดขึ้นได้จากหลายสาเหตุ มาเรียนรู้สาเหตุของการเกิดตุ่มใส การรักษา และการป้องกันจากทันตแพทย์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญเพื่อสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดีของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
สาเหตุของอาการเจ็บเพดานปาก เพดานปากบวม มีวิธีรับมืออย่างไรบ้าง
อาการเจ็บเพดานปาก หรือเพดานปากบวม มาดูสาเหตุและอาการของเพดานปากบวม เพื่อบรรเทาอาการได้อย่างถูกวิธี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
วิธีรักษาเริมให้หายอย่างรวดเร็ว
แผลที่เกิดขึ้นเหล่านี้สามารถเกิดขึ้นและหายได้เองตามธรรมชาติ แต่คุณอาจสงสัยว่าจะทำอย่างไรให้เริมที่ปากนั้นหายไปได้อย่างรวดเร็วยิ่งขึ้น เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
วิธีฆ่าเชื้อแบคทีเรียในช่องปากและการยับยั้ง
แบคทีเรียบางชนิดมีประโยชน์ แต่บางชนิดอาจทำให้ฟันผุและก่อให้เกิดกลิ่นปาก เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้วิธีกำจัดแบคทีเรียที่เป็นอันตรายต่อช่องปากได้ในตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
อาการเจ็บคอและลิ้นบ่งบอกถึงอะไรได้บ้าง
การเจ็บลิ้นประกอบกับการเจ็บคอสามารถก่อให้เกิดความไม่สบายใจ และทำให้การใช้ชีวิตประจำวันเช่น การพูด หรือการรับประทานอาหารนั้นมีความยากลำบากมากขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
ฝีในฟัน
ฟันเป็นหนองเกิดจากการติดเชื้อจากแบทีเรียที่บริเวณฟันด้านใน เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ สาเหตุ อาการ และวิธีการป้องกัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
นิ่วทอนซิลคืออะไร
นิ่วทอนซิลนั้นสามารถเกิดขึ้นได้และไม่มีอันตราย แต่อาจเป็นสัญญาณตือนแก่ผู้ป่วยได้ถ้าหากตรวจพบเจอในครั้งแรก เรียนรู้ในตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
จุดสีขาวบนลิ้น: เป็นอันตรายไหม
หากคุณสังเกตได้ว่ามีจุดสีขาวเกิดขึ้นบนลิ้นของคุณ คุณอาจมีข้อสงสัยเกิดขึ้นกับสิ่งนั้นว่ามันคืออะไร เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ในตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม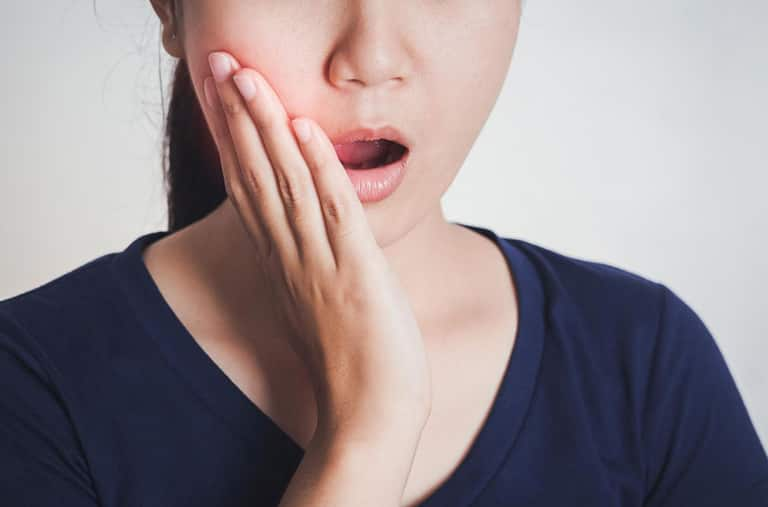

แผลร้อนในและการติดเชื้อในปาก
เหงือกมีสีขาว: สาเหตุและอาการ
ผู้คนรู้ว่าอาการปวดฟันหรือมีเลือดออกตามไรฟันคือสาเหตุที่ควรดูแลช่องปาก แล้วถ้าเหงือกเป็นสีขาวล่ะ อ่านต่อไปเพื่อเรียนรู้ความหมายและสิ่งที่คุณควรทำหากเหงือกของคุณมีสีขาว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
การเจาะภายในช่องปาก
แฟชั่นการเจาะปาก เจาะลิ้น แม้ว่าจะไม่มีอันตราย แต่รู้ไหมว่าถ้าทำไม่สะอาดหรือถูกวิธีก็อาจจะทำให้เกิดโรคอื่น ๆ ได้ แล้วต้องทำอย่างไรมาดูได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
สัญญาณบ่งชี้ว่าคุณกำลังมีปัญหาฟันสึก
คอฟันสึก ไม่ควรปล่อยปละละเลย เพราะอาจทำความสูญเสียให้กับคุณได้ มาดู 3 สัญญาณที่บ่งชี้ว่าคุณกำลังมีปัญหาคอฟันสึก เพื่อจะได้สังเกตและแก้ไขได้ทันท่วงที
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
ขจัดคราบหินปูนด้วยตัวเองได้หรือไม่?
คราบหินปูนหรือคราบพลัคเป็นต้นเหตุของปัญหาปัญหาเหงือกและฟัน ซึ่งหลายๆคนอาจสงสัยว่าเรามีวิธีการขูดหินปูนด้วยตัวเองหรือไม่ ทำได้อย่างไร ติดตามอ่านได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
งานวิจัยใหม่เกี่ยวกับยาสีฟันและน้ำยาบ้วนปากที่มีผลต่อไวรัสโควิด -19
ยาสีฟันและน้ำยาบ้วนปากสามารถปรับสมดุลและลดการเกิดไวรัสที่เป็นสาเหตุของโควิด -19 ในช่องปากของคุณได้หรือไม่? อ่านเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับงานวิจัยใหม่ของคอลเกต-ปาล์มโอลีฟ สำหรับยาสีฟันและน้ำยาบ้วนปากที่ส่งผลต่อไวรัสโควิด -19
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
ไวรัสโคโรนาและ สุขภาพช่องปาก ฉันควรดูแลรักษาสุขภาพฟันอย่างไร?
ในช่วงการระบาดของโควิด-19 ทำให้ผู้คนมีคำถามมากมายเกี่ยวกับปัญหาสุขภาพช่องปาก เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการดูแลรักษาช่องปากที่ทำได้เองที่บ้านและเวลาที่เหมาะสมในการเข้าพบทันตแพทย์ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
การเจาะลิ้นเป็นอันตรายต่อฟันหรือไม่?
ห่วงเจาะลิ้นและเครื่องประดับร่างกายที่คล้ายกันอาจส่งผลกระทบต่อสุขภาพช่องปากของคุณได้ ขึ้นอยู่กับตำแหน่งของการเจาะ อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม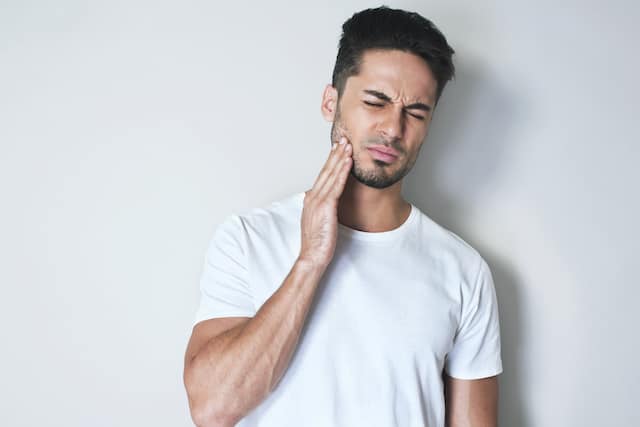
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
แก้มบวมเกิดจากอะไร?
การสังเกตเห็นว่าแก้มของคุณบวม อาจเป็นเรื่องที่น่าวิตก มีสาเหตุหลายประการที่ทำให้แก้มบวม อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
อาการเบ้าฟันแห้งหลังถอนฟัน: ทำความเข้าใจและป้องกัน
ผู้ป่วยควรระวังปัญหาบางอย่างเกิดขึ้นหลังจากการถอนฟัน ซึ่งรวมไปถึงอาการเบ้าฟันแห้ง เรียนรู้สาเหตุและวิธีการป้องกันการเกิดเบ้าฟันแห้ง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม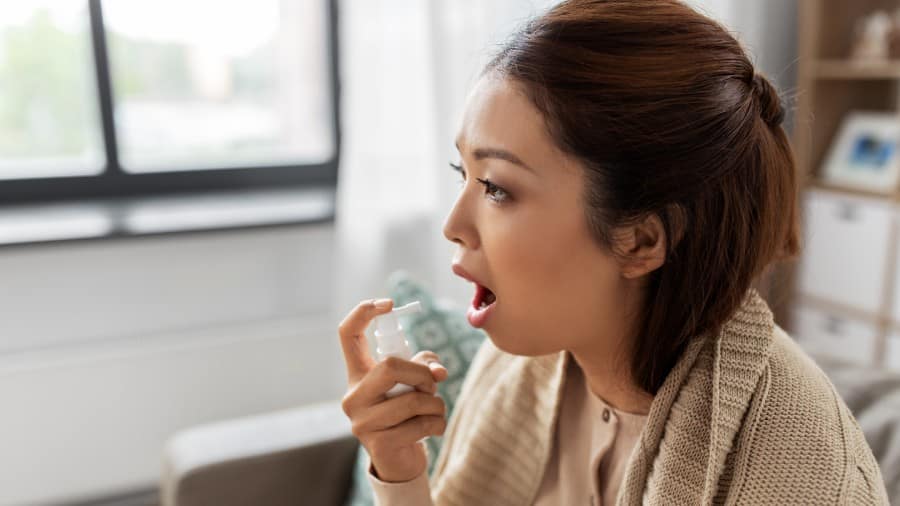
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
สเปรย์ฉีดปากช่วยอาการปากแห้งได้อย่างไร
สเปรย์ฉีดปากสำหรับผู้ที่มีความปากแห้งอาจเป็นหนึ่งในตัวช่วยที่ทำให้คุณหายจากอาการนี้ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้ว่าทำไมมันถึงใช้ได้ผลและวิธีการรักษาในระยะยาว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณอันตรายต่อสุขภาพฟัน
สาเหตุของเหงือกซีดคืออะไร สิ่งที่เป็นไปได้ 3 อย่างเพื่อนำไปปรึกษากับทันตแพทย์ของคุณ
หากเหงือกของคุณดูซีดกว่าปกติ แสดงว่าคุณอาจมีปัญหาสุขภาพได้ นี่คือสิ่งที่เป็นไปได้ 3 อย่างเพื่อนำไปปรึกษากับแพทย์หรือทันตแพทย์ของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเข้าพบทันตแพทย์
พาลูกไปหาหมอฟันครั้งแรก: สิ่งที่คุณพ่อคุณแม่ควรรู้
เมื่อฟันน้ำนมขึ้น เป็นช่วงเวลาสำคัญสำหรับลูกน้อย เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับนัดแรกกับหมอฟันของลูก และสิ่งที่คุณพ่อคุณแม่ต้องรู้และเตรียมตัว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม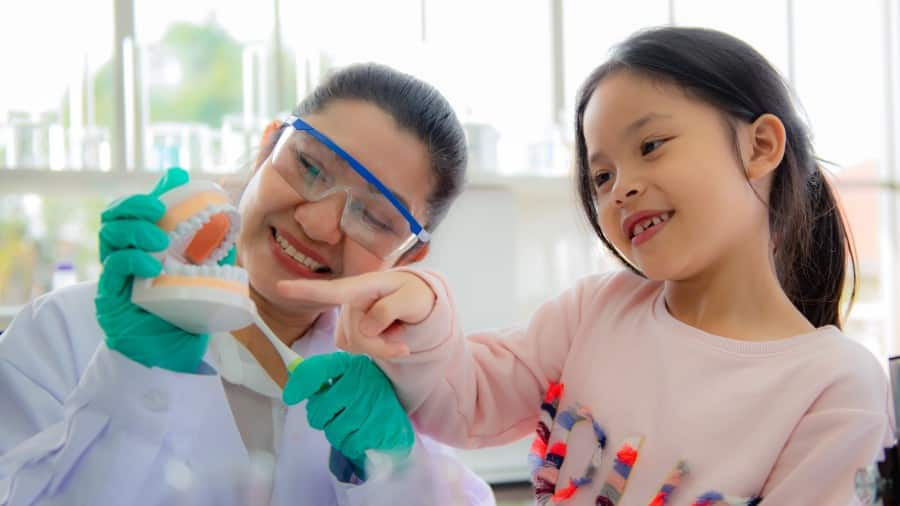
การเข้าพบทันตแพทย์
ทันตแพทย์เด็กคือใคร?
เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับความแต่งต่างระหว่างหมอฟันเด็ก และหมอฟันทั่วไป ทำไมหมอฟันเด็กถึงมีความสำคัญ และเด็กอายุเท่าไหร่ที่เข้ารับการรักษากับหมอฟันเฉพาะทางด้าน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม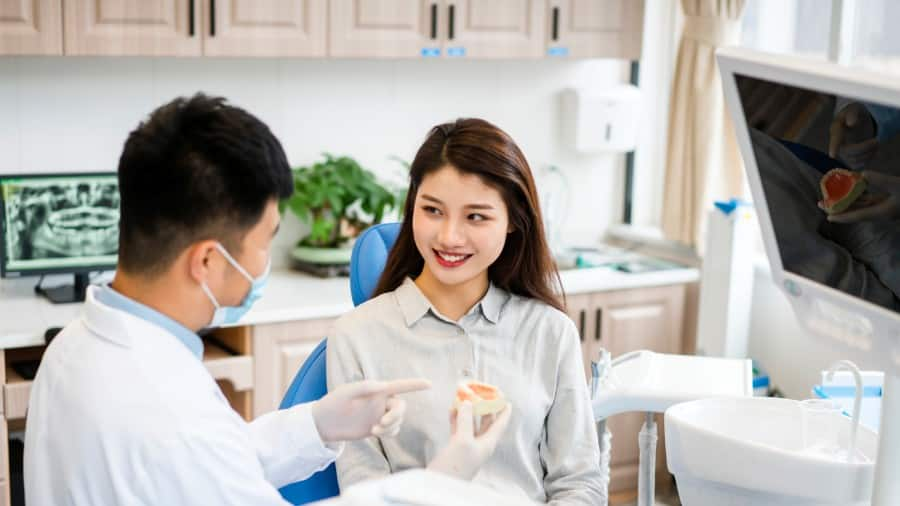
การเข้าพบทันตแพทย์
คุณควรไปพบทันตแพทย์บ่อยแค่ไหน
จริงๆ แล้วเราควรไปหาหมอฟันบ่อยแค่ไหน เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับความสำคัญ ความถี่ในการพบ และวิธีรักษาช่องปากที่จะช่วยลดความถี่ในการหาหมอฟันลงได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เคลือบฟันเทียม
เคลือบฟันเทียมกระเบื้องนำรอยยิ้มของคุณกลับคืนมาได้อย่างไร
ถ้าฟันไม่สวยทำให้คุณซ่อนรอยยิ้มของคุณ ก็อาจจะถึงเวลาสำหรับการแปลงโฉมในช่องปากแล้ว วิธีการเคลือบฟันเทียมแบบกระเบื้องอาจช่วยคุณได
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เคลือบฟันเทียม
เคลือบฟันเทียมคืออะไรและคุณควรจะดูแลรักษาอย่างไร
เคลือบฟันเทียมคืออะไรและทำไมคุณควรเลือกวิธีการนี้ การเคลือบฟันเทียมเป็นเหมือนเปลือกเคลือบสีที่เหมาะสมกับฟันที่มีคราบหรือบิ่น - และมันก็อาจเหมาะกับคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เคลือบฟันเทียม
การเคลือบผิวฟัน - เติมความสวยให้ฟันของคุณ
การเคลือบผิวฟัน เป็นการติดแผ่นพอร์เซเลนที่มีความบางบนผิวหน้าของฟัน เพื่อความสวยงามอย่างเป็นธรรมชาติของช่องปาก ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เคลือบฟันเทียม
เคลือบฟันเทียมวีเนียร์มีข้อดีข้อเสียอะไรบ้าง?
หากพูดถึงการทำฟันให้สวยและขาวสะอาดแล้ว การเคลือบฟันเทียมด้วยวีเนียร์คงเป็นอีกหนึ่งวิธีที่หลายๆคนนึกถึง วิธีนี้มีข้อดีข้อเสียอย่างไรบ้าง มาหาคำตอบได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
ไอเดียดี ๆ เกี่ยวกับเทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
ลูกของคุณเชื่อในเรื่องเทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนมไหม? เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ที่ดีในการสูญเสียฟันน้ำนมของเด็ก ลองมาดูไอเดียสร้างสรรค์ให้กับลูก ๆ ของคุณกัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
วิธีเตรียมกล่องเครื่องมือของเทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนมของลูก ไม่ใช่ใครที่ไหน แต่ก็คือพ่อแม่นี่เอง ที่จะต้องเตรียมพร้อมเพื่อดูแลฟันน้ำนมของลูก มีวิธีการอย่างไรดูได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
ลาก่อนฟันน้ำนม: ฉลองการมาเยือนครั้งสุดท้ายของเทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม จะเป็นความทรงจำที่ดีของลูกคุณหรือไม่ ก่อนที่ฟันน้ำนมซี่สุดท้ายจะหลุด มาทำความทรงจำที่ดี ๆ ในเรื่องนี้ให้เขากันเถอะ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนม
ตอบคำถามเรื่อง 'นางฟ้าฟันน้ำนมมีจริงไหม?'
ลูกน้อยของคุณเคยตั้งคำถามกับคุณไหมว่า "เทพพิทักษ์ฟันน้ำนมมีจริงไหม" แล้วคุณจะรับมือกับคำถามนี้อย่างไรดี คอลเกตมีเคล็ดลับคำตอบมาแนะนำคุณ ที่นี่เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ช่องฟันห่าง (Diastemas) กับทางเลือกในการรักษา
ปัญหาช่องฟันห่าง สามารถแก้ไขได้ ด้วยความก้าวหน้าของเทคโนโลยีการจัดฟันทำให้เครื่องมือต่างๆ เช่น เหล็กจัดฟัน เครื่องยึด ทำงานได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลมากขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
เคล็ดลับ 3 ข้อที่จะช่วยให้คุณขัดฟัน ได้ง่ายขึ้นขณะใส่เหล็ก จัดฟัน
การส่งเสริมให้ลูกให้เด็ก ๆ ในการใช้ไหมขัดฟันแม้ถือเป็นความท้าทายสำหรับผู้ปกครองส่วนใหญ่ แต่มันจะกลายเป็นความท้าทายมากขึ้นเมื่อเด็กๆ มีการจัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ฟันล่างคร่อมฟันบนและวิธีการรักษา
ปัญหาฟันล่างคร่อมฟันและฟันซ้อนหรือเกอาจทำให้คุณขาดความมั่นใจ เรียนรู้สาเหตุ อาการ และวิธีการรักษาโดยทันตแพทย์เพื่อฟันที่สวยงามที่เรียกความมั่นใจกลับคืนมา
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ฟันห่าง
ฟันห่าง โดยเฉพาะฟันคู่หน้าเป็นความผิดปกติที่เกิดขึ้นได้กับหลาย ๆ คน โดยเกิดได้จากหลายปัจจัย หากฟันห่างรบกวนการใช้ชีวิตของคุณ ดูวิธีการแก้ปัญหาได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
วิธีแปรงฟันสําหรับคนจัดฟัน
การจัดฟันทำให้แปรงฟันได้ยากขึ้น เพราะเศษอาหารและคราบจุลินทรีย์อาจเกาะติดกับเครื่องมือจัดฟันและตัวฟัน อ่านข้อมุลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
อาหารที่คุณรับประทานได้ขณะจัดฟัน
เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับอาหารประเภทไหนที่สามารถทานได้ และประเภทไหนที่ควรหลีกเลี่ยงเนื่องจากสามารถทำลายเหล็กจัดฟันและอาจก่อให้เกิดฟันผุได้ถ้าหากดูแลไม่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ฟันสบเปิดคืออะไร
ลักษณะฟันไม่สบกันคือมีช่องว่างระหว่างฟันเกิดขึ้นขณะสบฟันทำให้เกิดปัญหาเกี่ยวกับการเคี้ยวอาหาร และอื่นๆ เรียนรู้ถึงสาเหตุ และวิธีการรักษา
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในเด็ก (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ควรจัดฟันตอนอายุเท่าไหร่?
กังวลกับสภาวะฟันล่างคร่อมฟันบน (Underbite) ของลูกคุณอยู่หรือไม่ เราสามารถจัดฟันได้เมื่อไหร่บ้าง เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะฉุกเฉินทางทันตกรรมและความปลอดภัยในการเล่นกีฬา
ความปลอดภัยของสุขภาพฟันของคุณ
สุขภาพฟันของเด็กวัยหัดเดินต้องได้รับการดูแลให้ดี คอลเกตมีตารางการดูแลฟันมาบอก เพื่อช่วยแนะนำพ่อแม่ว่าควรจะดูแลเรื่องใดเป็นพิเศษ เพื่อสุขภาพฟันของลูก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะฉุกเฉินทางทันตกรรมและความปลอดภัยในการเล่นกีฬา
ฉันสามารถใช้น้ำมันกานพลูแก้อาการปวดฟันได้หรือไม่?
การใช้น้ำมันกานพลูเพื่อแก้อาการปวดฟันอาจช่วยบรรเทาอาการปวดฟันของคุณได้ในขณะนั้น แต่จะอยู่ไม่ได้นาน ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะฉุกเฉินทางทันตกรรมและความปลอดภัยในการเล่นกีฬา
ริมฝีปากบวมเกิดจากอะไร? มาดูสาเหตุและวิธีรับมือกับอาการปากบวม
การที่ริมฝีปากมีอาการปวมนั้นมักเกิดจากอาการแพ้ หรือจากสาเหตุที่รุนแรงกว่านั้น มาเรียนรู้วิธีจัดการกับอาการดังกล่าว
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะฉุกเฉินทางทันตกรรมและความปลอดภัยในการเล่นกีฬา
ลิ้นบวม: สาเหตุและการรักษา
อาการลิ้นบวมอาจเกิดจากการบาดเจ็บ การติดเชื้อ หรือการระคายเคือง แต่สาเหตุที่พบได้บ่อยคือการแพ้อาหาร อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ภาวะฉุกเฉินทางทันตกรรมและความปลอดภัยในการเล่นกีฬา
4 วิธีรักษาอาการปวดฟันฉุกเฉิน บรรเทาอาการปวดฟันฉบับเร่งด่วน
อาการปวดฟันอาจเกิดขึ้นได้แบบที่คุณไม่ได้ตั้งตัว เรียนรู้วิธีการแก้ปวดฟันฉุกเฉินด้วยตัวเอง พร้อมวิธีการรักษาอย่างถูกต้องจากคำแนะนำจากทันตแพทย์
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
วิธีเสริมสร้างความแข็งแรงของฟัน: สามวิธีที่ผ่านการพิสูจน์แล้ว
นอกจากรอยยิ้มสวยแล้ว การมีฟันแข็งแรง ก็ช่วยเพิ่มความมั่นใจได้ มาดูเคล็ด(ไม่) ลับ ช่วยให้ฟันของคุณเรียงตัวสวยงามและแข็งแรงกัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
การใส่ และการดูแลรักษาที่ครอบฟัน
หลายคนเจอปัญหารีเทนเนอร์หายบ่อย เพราะต้องถอนเวลากินข้าว แปรงฟัน หรือใช้ไหมขัดฟันแล้วลืมทิ้งไว้ มาดูเทคนิคสำหรับการใส่และการดูแลรีเทนเนอร์ ให้ใช้ได้นานๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ผู้ใหญ่กับการจัดฟัน
เนื่องจากปัจจุบันการจัดฟันไม่ดูเทอะทะ และเห็นได้ชัดเหมือนเมื่อก่อน ผู้ใหญ่จำนวนมากขึ้นจึงเข้ารับการจัดฟันจากหลายสาเหตุ ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
การจัดฟัน มีกี่แบบ? แบบไหนเหมาะกับคุณที่สุด?
ถ้าอยากมีฟันเรียงตัวสวยงาม อาจจะต้องใช้ตัวช่วยอย่าง "การจัดฟัน" แต่การจัดฟันมีกี่แบบ? แบบไหนที่จะเหมาะกับคุณมากที่สุด? คอลเกตรวบรวมข้อมูลมาให้แล้ว!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
เหงือกบวมเมื่อใส่เหล็กจัดฟัน สัญญาณบอกอะไร?
เมื่อคุณเริ่มจัดฟัน สิ่งที่อาจเกิดขึ้นตามมาคือปัญหาเหงือกบวม เรียนรู้ถึงสาเหตุของเหงือกบวมหลังจัดฟันและวิธีการดูแลรักษาเพื่อสุขภาพเหงือกและฟันที่แข็งแรง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ฟันเรียงตัวสวยด้วยการจัดฟันแบบเร่งด่วน
ขั้นตอนการจัดฟันแบบปกติทั่วไปอาจใช้เวลาหลายปีและมีค่าใช้จ่ายค่อนข้างสูง เราลองมาดูทางเลือกอื่นๆที่สามารถเร่งการจัดฟันได้อย่างรวดเร็วและมีประสิทธิภาพกัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ฟันเรียงตัวสวยได้โดยไม่ต้องจัดฟัน
การมีรอยยิ้มสวยสดใสทำให้มีบุคลิกที่ดี แต่วิธีการจัดฟันอาจรักษาไม่ได้ทุกกรณี มาพบกับคำแนะนำจากทันตแพทย์และทางเลือกแทนการใส่เหล็กจัดฟันเพื่อฟันที่สวยงาม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ทำไมต้องใช้ยางดึงฟันในการจัดฟัน?
ส่วนประกอบที่สำคัญของการจัดฟันก็คือยางดึงฟัน ซึ่งมีหลายแบบและหลายขนาด หลายๆคนคงอยากทราบว่ายางดึงฟันนั้นมีประโยชน์ต่อการจัดฟันอย่างไร ติดตามอ่านได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
ข้อดีของการจัดฟันดามอน
การจัดฟันดาม่อนเป็นวิธีจัดฟันแบบใหม่ที่หลายๆคนเลือกแทนการใส่เหล็กจัดฟัน การจัดฟันดาม่อนมีด้วยกันกี่แบบ ต้องถอนฟันไหม มีข้อดีอะไรบ้าง ติดตามอ่านได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
การดูแลรักษาสุขภาพฟันที่ดีขณะใส่อุปกรณ์จัดฟันการดูแลรักษาสุขภาพฟันที่ดีขณะใส่อุปกรณ์จัดฟัน
ขณะที่ใส่อุปกรณ์จัดฟันอยู่ คุณควรต้องดูแลรักษาความสะอาดของช่องปากให้ดีขึ้นกว่าปกติ รวมทั้งอาจต้องใช้อุปกรณ์ทำความสะอาดแบบเฉพาะ มาดูวิธีการได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
จัดฟันแบบไหนดี? การจัดฟันแบบเซรามิคเหมาะกับคุณหรือไม่
เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตเพื่อเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการจัดฟันแบบเซรามิค เช่นความแต่งต่างเมื่อเทียบกับการจัดฟันโดยทั่วไป ข้อดีข้อเสีย การดูแลรักษาช่องปากขณะจัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
จัดฟันเจ็บไหม
คุณกำลังกังวลกับการที่จะต้องจัดฟันใช่หรือไม่ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้ทุกขั้นตอนของการจัดฟันและวิธีจัดการกับอาการปวดที่เกิดขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม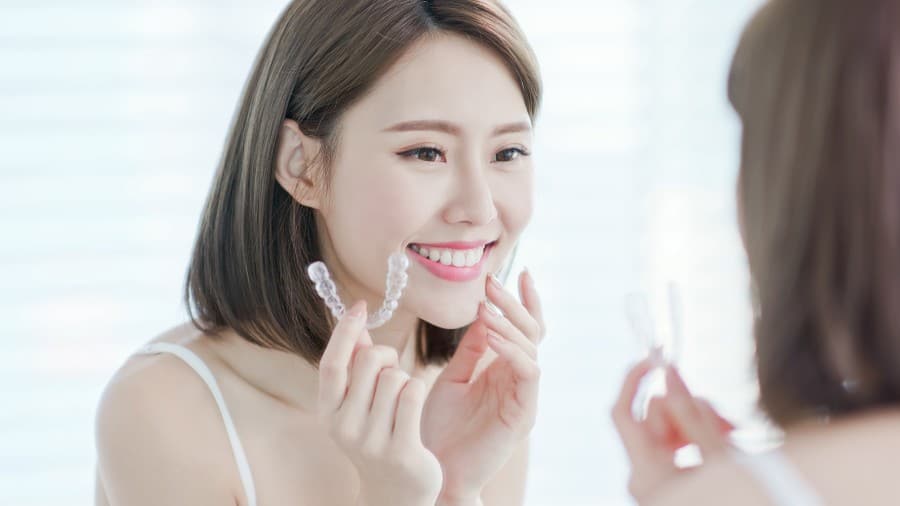
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
วิธีการทำความสะอาดรีเทนเนอร์
การดูแลรักษารีเทรนเนอร์ที่ไม่ดีอาจก่อนให้เกิดการสะสมของแบคทีเรีย คราบพลัค และหินปูนได้ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้เกี่ยวกับกับการทำความสะอาดรีเทรนเนอร์ได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม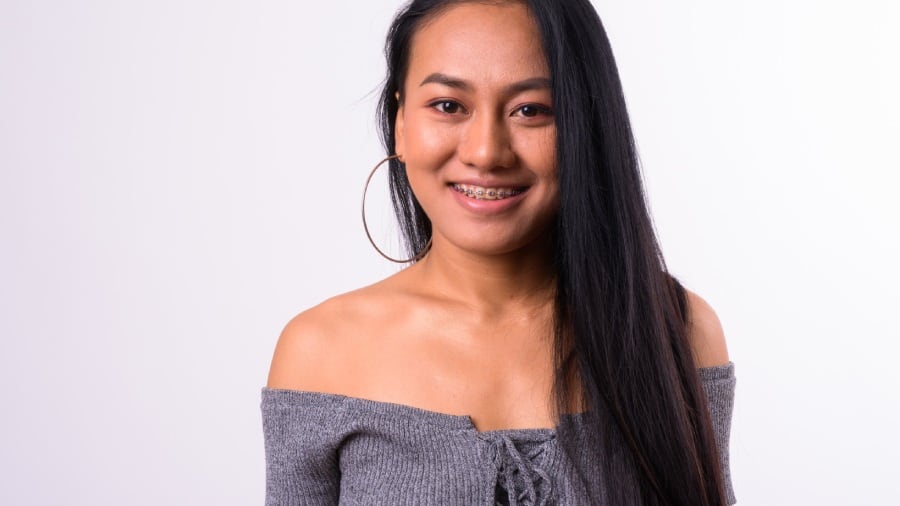
การจัดฟันในวัยผู้ใหญ่ (ลวดดัดฟัน)
สิ่งที่ควรทราบเกี่ยวกับการจัดฟันแบบเหล็ก
ในปัจจุบันมีตัวเลือกการจัดฟันที่หลากหลาย อาจเป็นเรื่องยากที่จะตัดสินใจเลือกแบบที่เหมาะกับความต้องการของคุณ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตเพื่อเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการจัดฟันแบบเหล็ก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเคลือบหลุมร่องฟัน
การอุดหลุมร่องฟัน: สิ่งที่คุณควรทราบ
หนึ่งในวิธีการดูแลฟันแท้ให้อยู่กับเราไปตลอดชีวิต ก็คือการเคลือบหลุมร่องฟัน เป็นการช่วยป้องกันฟันจากแบคทีเรียที่อาจนำไปสู่ฟันผุได้ มาดูวิธีการกันเลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม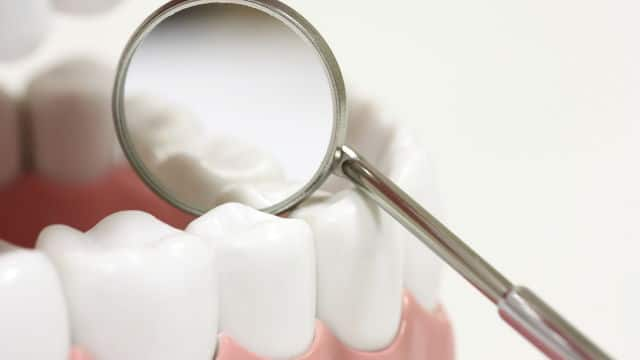
การเคลือบหลุมร่องฟัน
การอุดหลุมร่องฟัน
การเคลือบหลุมร่องฟันคือการเคลือบพลาสติกที่ด้านบดเคี้ยวของฟัน การเคลือบหลุมร่องฟันฟันจะช่วยป้องกันฟันผุได้ ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม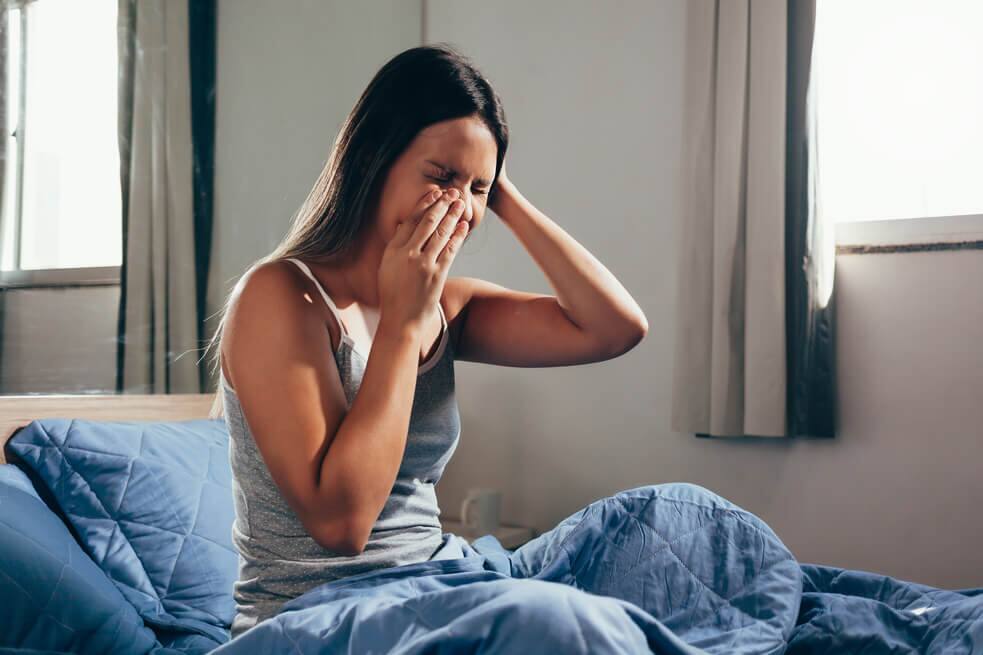
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ทำไมจึงเกิดอาการไซนัสอักเสบปวดฟัน
มีหลายสาเหตุที่ทำให้คุณปวดฟัน ทั้งฟันผุ ฟันร้าว หรือเสียวฟัน แต่สาเหตุของอาการปวดฟันที่ไม่ค่อยเป็นที่รู้จักคือ ปวดฟันจากไซนัสอักเสบ ค้นพบคำตอบจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ในฐานะผู้ใหญ่ เราจะดูแลฟันของเราอย่างดีที่สุดอย่างไร
กุญแจสำคัญของสุขภาพช่องปากสำหรับผู้ใหญ่ สู่การมีรอยยิ้มที่สดใสและแข็งแรงตลอด คือการรักษาสุขอนามัยของปากและฟันอย่างเหมาะสม ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
สุขภาพปากและฟันที่ดี คืออะไร
สุขอนามัยในช่องปากคืออะไร? เรียนรู้วิธีการที่คุณสามารถประเมินฟันและเหงือกของคุณเอง เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าคุณมีสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
เสียวฟันเวลากินหรือดื่ม ของร้อนหรือเย็น สาเหตุ และวิธีแก้ไข
หากคุณดื่มน้ำเย็นหรือกินของร้อนๆแล้วมีอาการปวดฟันหรือเสียวฟันแล้วล่ะก็ มาพบกับสาเหตุ วิธีดูแลรักษาโดยทันตแพทย์ เพื่อให้คุณรับประทานอาหารได้อย่างมีความสุข.
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
เหงือกเป็นหนอง ควรเข้ารับการรักษาเมื่อไหร่?
ฝีที่เหงือกหรือ 'เหงือกเป็นหนอง' มักเกิดขึ้นแบบเฉียบพลันและสร้างความเจ็บปวดให้ผู้ป่วย อาการฝีที่เหงือกเกิดจากสาเหตุใด เมื่อไหร่ควรพบทันตแพทย์ คอลเกตมีคำตอบ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ฟันเหลืองเกิดจากอะไร? 10 สาเหตุและวิธีแก้ไขคราบเหลืองที่ฟันที่คุณควรรู้
ปัญหาที่พบบ่อยในเรื่องสุขภาพช่องปาก คือการเกิดคราบเหลืองที่ฟัน หรือ "ฟันเหลือง" มีวิธีป้องกันฟันเหลืองอย่างไรบ้าง?
อ่านเพิ่มเติม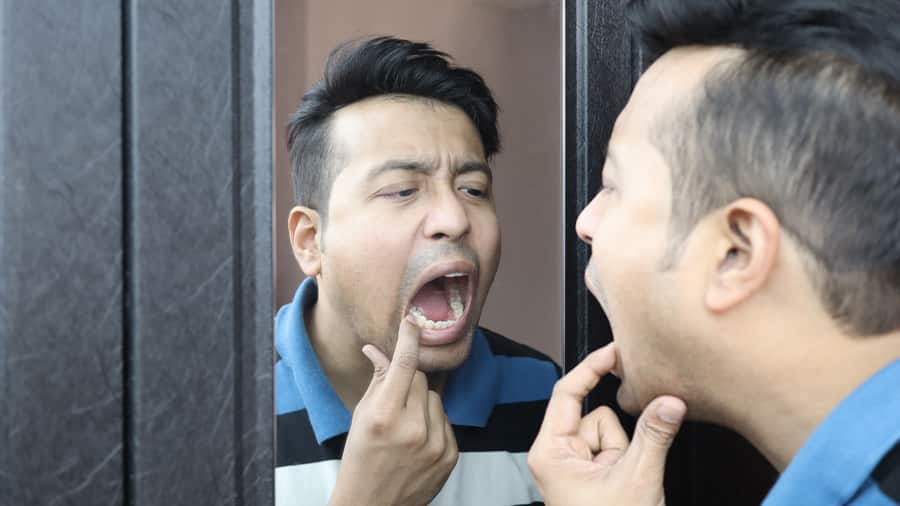
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
เหงือกบวมเกิดจากอะไร
มี 3 สาเหตุที่ทำให้เกิดเหงือกบวม ได้แก่ ฟันเป็นฝี ปัญหาเหงือกและการแปรงฟันหรือใช้ไหมขัดฟันที่ไม่เหมาะสม คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม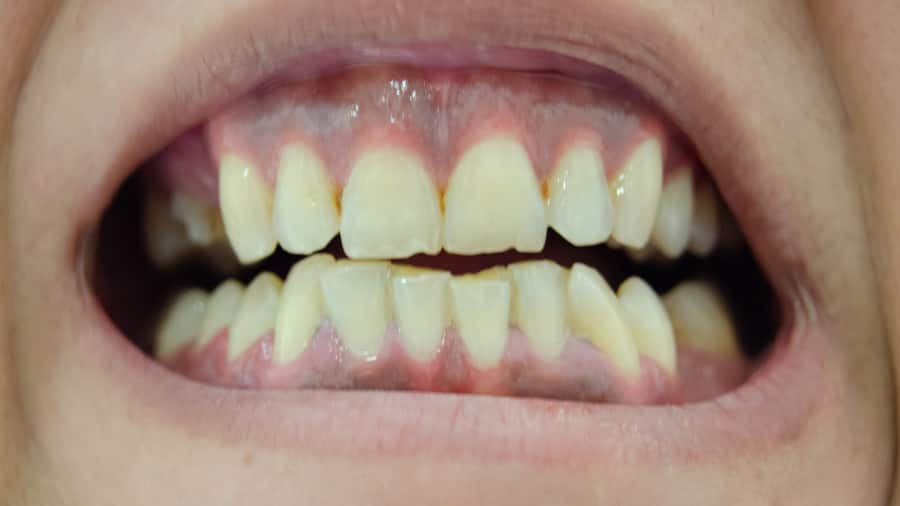
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
เหงือกดำเกิดจากอะไรและวิธีแก้เหงือกดํา
บางคนมีเหงือกดำที่ไม่ได้เกิดจากปัญหาสุขภาพ แต่เหงือกดำก็อาจได้จากผลข้างเคียงของยา การสูบบุหรี่เป็นต้น คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม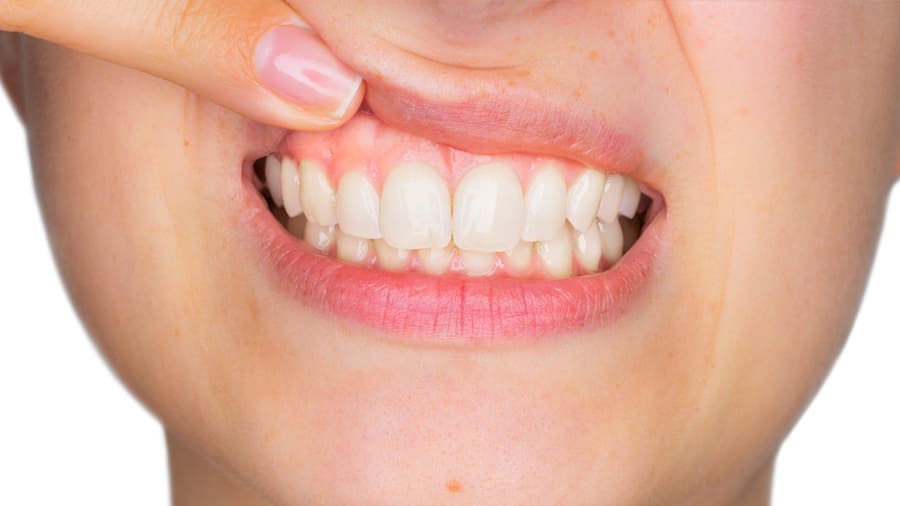
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
วิธีรักษาเหงือกบวมและมีเลือดออก
การมีสุขอนามัยในช่องปากที่ดีจะช่วยป้องกันปัญหาเหงือกบวมและมีเลือดออกได้ คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้วิธีรักษาเหงือกบวมและมีเลือดออกได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ดูแลสุขภาพเหงือกให้แข็งแรงยิ่งขึ้นในเวลาน้อยกว่า 5 นาที
หากเหงือกไม่ได้รับการดูแลอย่างเหมาะสมอาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาหลายอย่าง ที่ส่งผลต่อรูปลักษณ์และสุขภาพช่องปากของคุณได้ อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม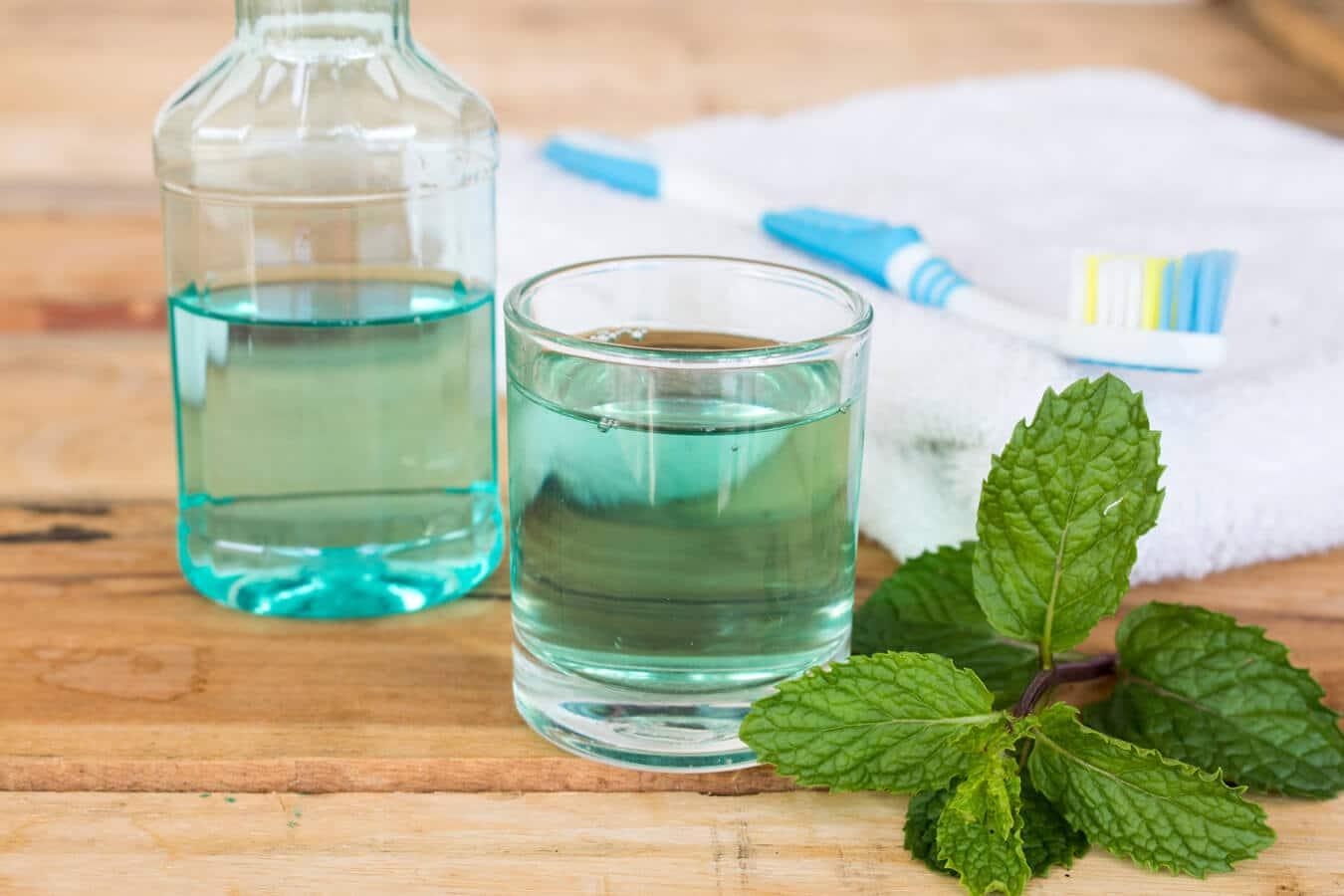
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
4 วิธีรักษาอาการปวดฟันที่บ้าน
หากคุณเคยปวดฟัน คุณจะรู้ว่าการปวดฟันไม่ใช่เรื่องสนุก หากคุณไม่สามารถรับการรักษาทางทันตกรรมได้ในทันที ให้ลองใช้วิธีรักษาอาการปวดฟันที่บ้านด้วยสมุนไพร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม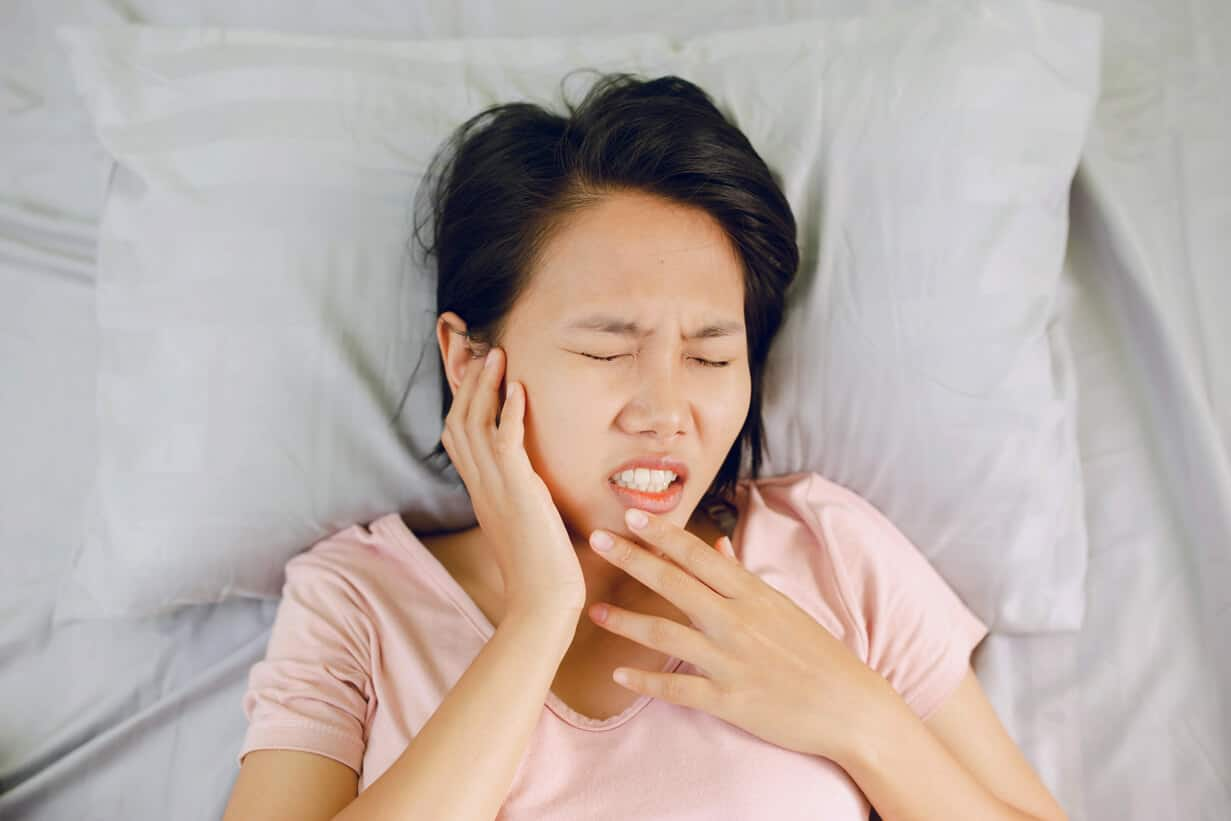
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ห้าสาเหตุหลักของอาการปวดฟันมาก
มีบางสิ่งบางอย่างที่เจ็บปวดและน่ารำคาญใจกับอาการปวดฟันแต่เมื่อใดกันที่อาการปวดฟันเพิ่มมากขึ้นยังคงเป็นปัญหาที่คุณควรเริ่มกังวลใจเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม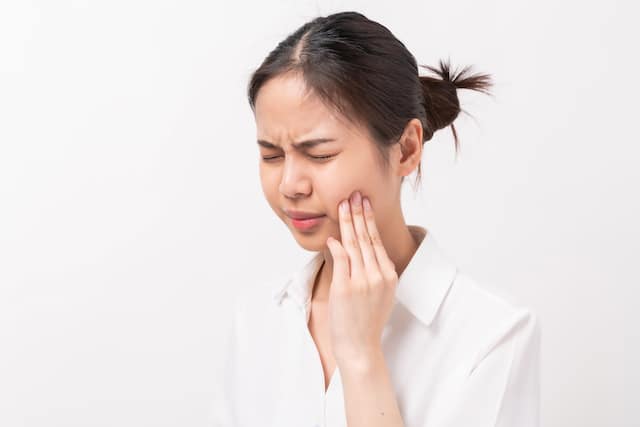
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
อาการปวดนอกตำแหน่งฟันคืออะไร?
บางครั้งอาการปวดฟันก็ไม่ใช่อย่างที่คิด ความเจ็บปวดที่คิดว่ามาจากฟันอาจเป็นอาการปวดนอกตำแหน่งฟัน เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ผู้สูงอายุที่ดูแลตัวเองได้
ผู้สูงอายุกับปัญหาช่องปากเป็นเรื่องที่ดูแลกันได้ โดยเฉพาะผู้สูงอายุที่ดูแลตัวเองได้ มีเทคนิคการดูแลช่องปากอย่างไรบ้าง มาดูเพิ่มเติมครบครันที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
คู่มือสำหรับผู้สูงอายุที่มีผู้ดูแล
คู่มือสำหรับผู้สูงอายุที่มีผู้ดูแล จะช่วยบอกวิธีในการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันของผู้สูงอายุอย่างถูกต้อง เพื่อคุณภาพชีวิตที่ดีของคุณตาคุณยาย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม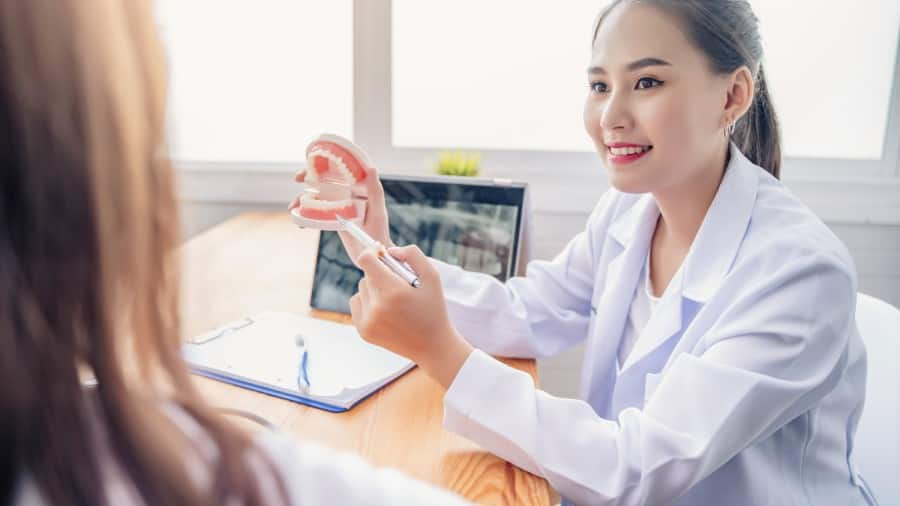
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
สาเหตุของจุดสีน้ำตาลบนฟัน
จุดสีน้ำตาลบนฟันอาจก่อให้เกิดความกังวลได้ โชคดีที่มีหลากหลายวิธีที่คุณสามารถกำจัดมันได้ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสาเหตุและวิธีรักษาได้ในตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
เคี้ยวสิ่งนี้: บดเคี้ยวน้ำแข็งและฟันของคุณ
น้ำแข็งสามารถทำลายฟัน ชั้นเคลือบฟัน และเหงือกได้ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตประเทศไทยตอนนี้และเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการเคี้ยวน้ำแข็งจะสามารถทำลายฟันของคุณได้อย่างไร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
วิธีการบรรเทาอาการฟันมีหนอง
หากช่องปากของคุณนั้นมีอาการปวดอย่างรุนแรง จะมีวิธีที่คุณสามารถรักษาฝีหนองที่ฟันของคุณได้ที่บ้านหรือไม่? เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
สาเหตุของฟันสึกกร่อนคืออะไร
การสึกกร่อนของฟันเป็นปัญหาทางทันตกรรมที่พบได้บ่อย การรู้วิธีป้องกันฟันสึกกร่อนจะสามารถช่วยให้ฟันของคุณแข็งแรงและมีสุขภาพดีได้ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
การดูแลสุขภาพฟัน: มีอะไรบ้างและมีความสำคัญต่อคุณอย่างไร
จริงๆแล้วสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันคืออะไร และมีความสำคัญอย่างไรต่อคุณ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้ในแง่มุมหลักๆ และความสำคัญของการดูแลรักษาสุขภาพในช่องปากและฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
แปรงทำความสะอาดลิ้นกับ แปรงสีฟัน: อันไหนดีกว่ากัน
แปรงทำความสะอาดลิ้น หรือที่ขูดลิ้นนั้นอาจช่วยทำความสะอาดลิ้นได้ดีและทั่วถึงกว่าแปรงสีฟันส่วนใหญ่ ทำไมน่ะเหรอ? เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
อันตรายจากการใช้ที่ขูดหินปูนที่บ้าน
แม้ว่าการกำจัดคราบจุลินทรีย์จะเป็นสิ่งสำคัญต่อสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี แต่นี่ไม่ใช่เรื่องที่คุณสามารถทำเองได้ ทิ้งที่ขูดหินปูนให้ทันตแพทย์ของคุณ แล้วมาเรียนรู้ถึงเหตุผลได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ฟันโยก เกิดขึ้นจากสาเหตุอะไร? สามารถรักษาและเก็บฟันไว้ได้หรือไม่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (18 ปีขึ้นไป)
ยาแก้ปวดฟัน มีกี่ประเภท? ควรเลือกใช้อย่างไร เพื่อรักษาอาการปวดฟันแบบถูกวิธี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

รากฟันเทียม
การฝังรากเทียมคืออะไร
ในการทำทันตกรรมรากฟันเทียม ทันตแพทย์ของคุณจะปลูกรากฟันเทียมทดแทนรากฟันจริง โดยรากฟันเทียมมีอยู่หลายชนิด สามารถดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
รากฟันเทียม
การปลูกถ่ายกระดูกเพื่อฝังรากฟันเทียม: ทำความเข้าใจความเป็นไปได้
ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับทันตกรรมรากฟันเทียม สำหรับผู้ที่สูญเสียฟันตั้งแต่หนึ่งซี่ขึ้นไป เพื่อเรียกคืนรอยยิ้มที่สดใสและความมั่นใจให้กลับมา
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
รากฟันเทียม
รากฟันเทียม: การทดแทนฟันแบบถาวรที่ควรพิจารณา
ทางเลือกหนึ่งที่เป็นที่นิยมของผู้ที่สูญเสียฟัน คือทันตกรรมรากฟันเทียม เพราะเป็นทางเลือกที่สะดวกสบาย ถาวร และสวยงามเหมือนฟันธรรมชาติ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม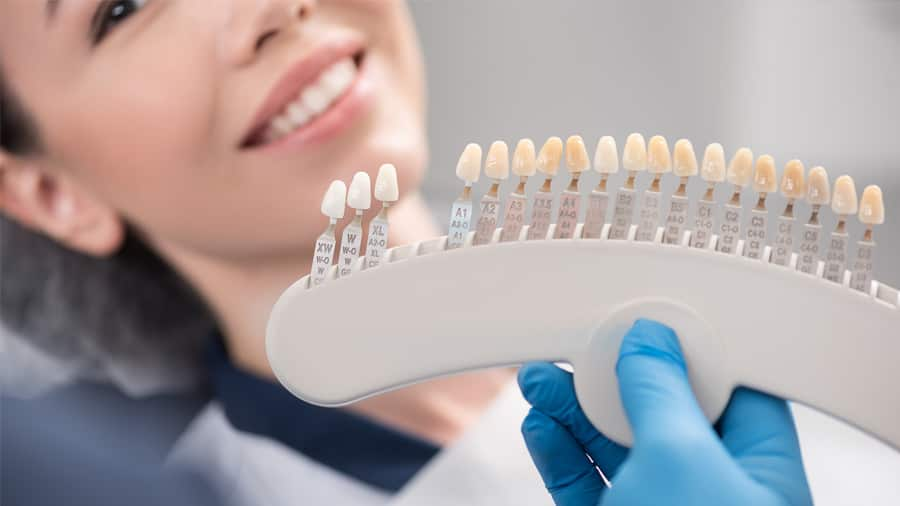
รากฟันเทียม
อาการเจ็บหลังใส่รากฟันเทียมเป็นเรื่องปกติหรือไม่
หลังจากผ่าตัดใส่รากฟันเทียม เป็นเรื่องปกติที่จะมีอาการเจ็บบ้าง บางกรณีอาจเป็นสัญญาณแสดงถึงสิ่งที่ร้ายแรงกว่านั้น อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์
สุขภาพช่องปากของเด็กตั้งแต่ช่วงอยู่ในครรภ์มารดาจนถึงช่วงหัดเดิน
การดูแลสุขภาพฟันของลูกเป็นสิ่งสำคัญไม่ยิ่งหย่อนไปกว่ากัน ในความเป็นจริงแม่ควรดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากของลูกก่อนที่เด็กจะคลอดด้วยซ้ำ ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์
อาการเสียวฟันระหว่างตั้งครรภ์: สิ่งที่อาจเกิดขึ้นและวิธีรับมือ
ร่างกายของคุณมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงในระหว่างตั้งครรภ์ ฟันของคุณก็เช่นกัน อาการเสียวฟันในระหว่างตั้งครรภ์เป็นเรื่องปกติ แต่คุณสามารถลดการระคายเคืองได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์
การดูแลรักษาสุขภาพและช่องปากในหญิงมีครรภ์
ในระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์ ฟัน เหงือก และช่องปากระหว่างตั้งครรภ์ต้องดูแลเป็นพิเศษ เบื้องต้นดูแลด้วยการแปรงฟันและใช้ไหมขัดฟัน และอื่นๆ ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์
เหงือกบวมระหว่างตั้งครรภ์
เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการดูแลเหงือกบวมในระหว่างตั้งครรภ์และคำถามสำคัญเพื่อปรึกษาทันตแพทย์ของคุณ อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากระหว่างการตั้งครรภ์
สุขภาพช่องปากในระหว่างตั้งครรภ์
ปัญหาสุขภาพช่องปากของคนท้องหรือกำลังตั้งครรภ์นั้น อาจก่อให้เกิดผลกระทบต่อสุขภาพเด็กในครรภ์และคุณแม่ เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับวิธีการหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาเหล่านี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
รากฟัน
เรื่องจริงเกี่ยวกับความเจ็บปวดในการรักษาคลองรากฟัน
ความเจ็บปวดที่บริเวณคลองรากฟัน มีสาเหตุจากอะไรได้บ้าง และมีขั้นตอนการรักษา รวมทั้งวิธีการดูแลหลังรักษาได้อย่างไร ดูเพิ่มเติมได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
รากฟัน
การรักษารากฟัน
เพราะรากฟันมีความสำคัญต่อความแข็งแรงของฟัน ชวนทำความรู้จักกับการรักษารากฟัน และทำความเข้าใจว่าเมื่อไรที่ควรไปพบทันตแพทย์เพื่อรักษารากฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
รากฟัน
รักษาคลองรากฟันคืออะไร?
ฟันที่ผุมากและฟันที่แตกร้าวอาจทำให้เกิดการติดเชื้อในโพรงประสาทฟันได้ มาเรียนรู้วิธีการรักษารากฟันหรือคลองรากฟันจากทันตแพทย์เพื่อสุขภาพฟันที่แข็งแรงของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม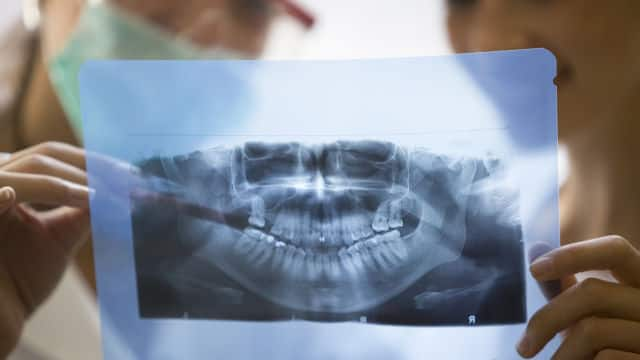
การเอ็กซเรย์
การเอ็กซ์เรย์ฟัน
การเอ็กซเรย์ฟันเป็นส่วนสำคัญของการวางแผนการดูแลใด ๆ ในช่องปาก สามารถช่วยในการตัดสินใจทางทันตกรรมได้ เรียนรู้เรื่องการเอ็กซเรย์ฟันเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม







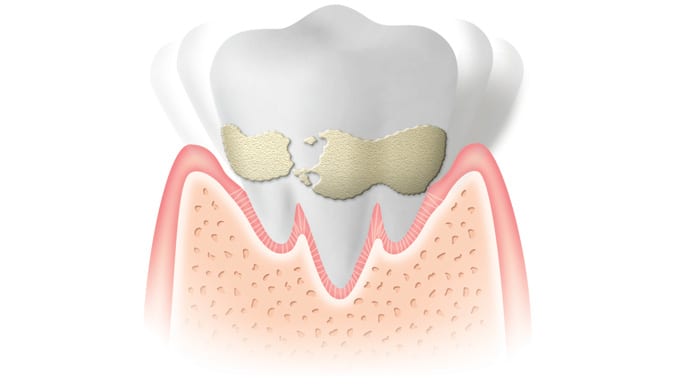


คราบจุลินทรีย์และหินปูน
ปกป้องช่องปากจาก หินปูน เสียวฟัน เหงือกเลือดออก ด้วยนวัตกรรมใหม่จากคอลเกต ยาสีฟันเกลือ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
คราบจุลินทรีย์และหินปูน
หินปูนเกิดจากอะไร? รู้จักที่มาของคราบหินปูนสีดำและทำไมต้องขูดออก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
อาการเจ็บปวดข้อต่อขากรรไกร (TMD)
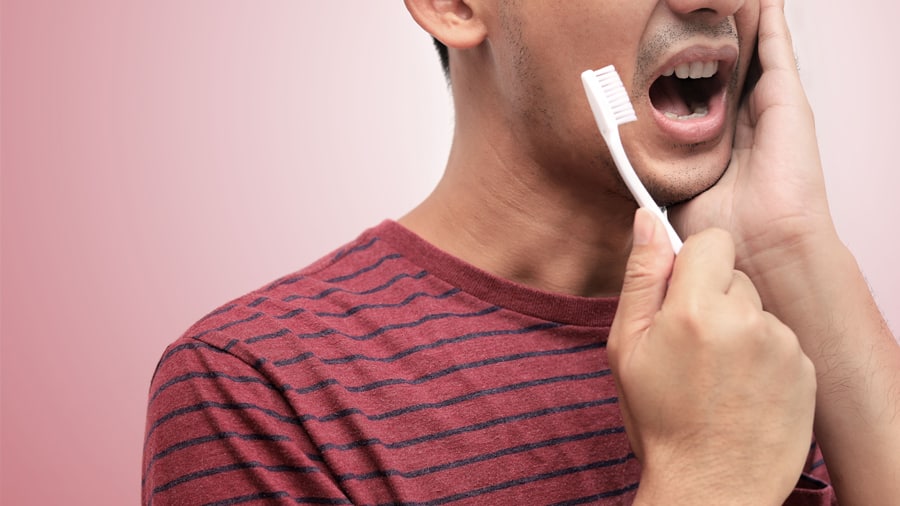
อาการปวดกราม: สาเหตุและการรักษา
มีสภาวะเจ็บป่วยมากมายที่เป็นปัจจัยให้เกิดอาการปวดกรามได้ โดยส่งผลให้การวินิจฉัยและการรักษายากขึ้นพบสาเหตุและการรักษา อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟัน
เคล็ดลับในการเคี้ยวหลังจากอุดฟัน
หลังจากอุดฟัน คุณอาจจะเกิดอาการเสียวฟันบริเวณที่อุดซึ่งอาจลาดยาวไปหลายวัน ทำให้ดื่มน้ำและกินอาหารลำบาก คอตเกตมีเคล็ดลับการเคี้ยวอาหารหลังอุดฟันมาฝาก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟัน
ข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับการอุดฟัน
เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับขั้นตอนในการกรอกอึดปากและสิ่งที่คาดหวังเจะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อคุณเยี่ยมชมพบหมอฟันของคุณจะได้รับการบรรจุเพื่ออุดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟัน
ปวดฟันหลังอุดฟันเป็นเรื่องปกติหรือไม่? สาเหตุที่พบบ่อยและวิธีแก้ไข
มีหลายสาเหตุที่ทำให้คุณมีอาการปวดฟันหลังอุดฟัน เป็นเรื่องปกติหรือไม่? ทำอย่างไรต่อไปดี ค้นหาสาเหตุและเรียนรู้ จากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟัน
การอุดฟันคืออะไร
คุณรู้จักการอุดฟันดีแล้วหรือยังว่า การอุดฟันคืออะไร มีวิธีการอย่างไร และวัสดุอุดฟันมีชนิดไหนให้คุณเลือกบ้าง มาดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมที่นี่เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม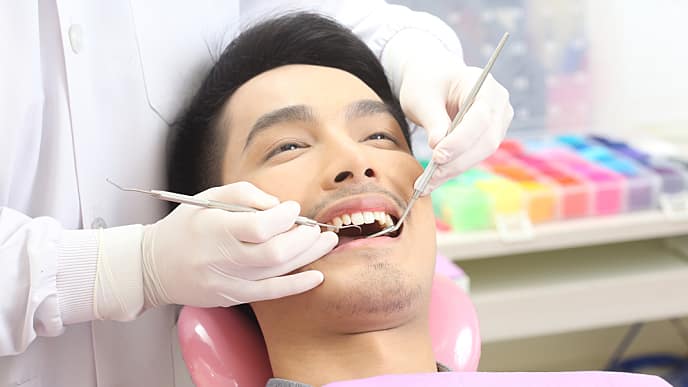
การอุดฟัน
ถ้าคุณต้องการรักษาฟันผุ อย่ารอช้า
รู้ถึงสาเหตุที่ทำให้เกิดอาการปวดฟันเหงือกบวมอันเนื่องมาจากฟันผุ สัญญาณและความรุนแรงของอาการฟันผุ และแนวทางการรักษาและป้องกันฟันผุเ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟัน
สิ่งที่ลูกอาจต้องเผชิญระหว่างการอุดฟัน
อาการเสียวฟันพบได้บ่อยหลังการอุดฟัน คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้สิ่งที่ลูกอาจต้องเผชิญระหว่างการอุดฟันเพื่อช่วยให้ลูกไม่กลัวการไปหาหมอฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันปลอม
คุณจะทำอย่างไรถ้าฟันหัก
เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับตัวเลือกที่สามารถทางเลือกในการแก้ไขปัญหาการสูญเสียฟันหัก เช่น ทันตกรรมการทำรากฟันเทียม, สะพานฟัน และฟันปลอม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันปลอม
ฟันปลอมทั้งปาก ฟันปลอมบางส่วน การดูแลรักษา ฟันปลอม - เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม
มาทำความรู้จักกับชนิดต่าง ๆ ของฟันปลอม ทั้งฟันปลอมบางส่วน ฟันปลอมถาวร และฟันปลอมที่มีความยืดหยุ่น เพื่อเลือกใช้ให้เหมาะกับแต่ละบุคคล
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันปลอม
ฟันปลอมคืออะไร
หากคุณต้องสูญเสียฟัน การใส่ฟันปลอมสามารถช่วยทำให้คุณรู้สึกดีขึ้นได้ เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับชนิดของฟันปลอม และเคล็ดลับสำหรับการดูแลฟันปลอมของคุณ ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันปลอม
ฟันปลอมแบบไหนเหมาะกับคุณที่สุด?
ฟันปลอมเป็นอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้แทนฟันแท้ที่หลุดออกไป ซึ่งมีทั้งฟันปลอมแบบติดแน่นและแบบถอดได้ เรียนรู้วิธีการดูแลและวิธีเลือกฟันปลอมที่เหมาะกับคุณที่สุดได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
ฟันปลอม
ฟันปลอมชั่วคราวคืออะไร
การเชื่อมช่องว่างระหว่างฟันก่อนที่ฟันปลอมถาวรของคุณจะพร้อมใช้งานโดยฟันปลอมชั่วคราวจะช่วยทำให้คุณไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องฟันของคุณอีกต่อไป
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
เหงือกที่ดีต่อสุขภาพฟัน: ดีจนไม่น่าเชื่อว่าเป็นเรื่องจริง
ไม่ว่าจะไปร้านสะดวกซื้อ หรือร้านขายของชำ คุณจะต้องซื้อหมากฝรั่งติดมือออกมาเกือบทุกครั้ง มาดูกันว่าหมากฝรั่งช่วยทำความสะอาดฟันของเราอย่างไรบ้าง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
เคล็ดลับ การรับประทานเพื่อสุขภาพ
คอลเกตแนะนำการเลืออาหารที่ทำให้สุขภาพร่างกายดีขึ้น ช่องปากที่ดีขึ้น ป้องกันปัญหา และส่งเสริมให้เด็กและวัยรุ่นมีการเจริญเติบโตที่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
อาหาร ที่มีประโยชน์ต่อฟัน
อาหารมีผลโดยตรงต่อสุขภาพช่องปาก เช่นอาหารที่มีน้ำตาลอาจทำให้เกิดฟันผุได้ คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ว่าคุณควรกินอาหารอะไรเพื่อส่งประโยชน์ต่อฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
อาหารที่มีแคลเซียมสูงเพื่อฟันแข็งแรง: สิ่งที่คุณควรรู้!
คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ว่าอาหารและเครื่องดื่มส่งผลต่อสุขภาพช่องปาก ดังนั้นควรเลือกรับประทานสิ่งที่มีประโยชน์ เช่น อาหารที่มีแคลเซียมสูง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
สมุนไพรเพื่อสุขภาพช่องปาก
มีงานวิจัยและรวบรวมข้อมูลสมุนไพรไทยไว้มากมาย และพบว่ามีหลายชนิดที่มีสรรพคุณช่วยดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากได้เป็นอย่างดี ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
อาหารที่ช่วยป้องกันฟันผุ
ขนมหวาน อาหารว่างและน้ำอัดลมหวานเจี๊ยบล้วนไม่ดีต่อฟันของคุณ แล้วคุณทราบหรือไม่ว่ามีอาหารที่สามารถป้องกันฟันผุได้ด้วย อ่านข้อมูลจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โภชนาการและสุขภาพช่องปาก
หลังถอนฟันกินอะไรได้บ้าง
คุณอาจสงสัยว่าหลังจากการถอนฟัน สามารถกินอาหารอะไรได้บ้าง อาหารบางประเภทสามารถช่วยบรรเทาอาการหลังจากได้รับการถอนฟันลงได้ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมที่คอลเกตได้ตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
คู่มือสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันที่ดีสำหรับครอบครัว
คุณและครอบครัวสามารถมีฟันและเหงือกที่แข็งแรงได้ ด้วยการปฏิบัติตามการดูแลอนามัยช่องปากพื้นฐานเหล่านี้ ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีการแปรงฟันที่ถูกต้อง
มาดูเทคนิคการแปรงฟันที่ถูกต้อง วิธีการเลือกยาสีฟัน และผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ ที่คุณควรใช้ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าคุณจะมีรอยยิ้มสุขภาพดี และสดใส
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ควรใช้ไหมขัดฟันอย่างไร
เรียนรู้เทคนิคการใช้ไหมขัดฟันอย่างถูกวิธี พร้อมเข้าใจประโยชน์ ข้อดี-ข้อเสียของการใช้ไหมขัดฟันในการดูแลช่องปาก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ช่วยลูกคุณแปรงฟัน พร้อมแผนผัง สติกเกอร์ และรางวัลสำหรับการแปรงฟัน!
หากเด็กๆที่บ้านคุณรู้สึกเบื่อหน่ายกับการแปรงฟันแล้วล่ะก็ ลองทำตามเคล็ดลับดีๆต่อไปนี้ที่จะช่วยให้ลูกๆของคุณสนุกสนานกับการแปรงฟันมากขึ้นเพื่อสุขภาพฟันที่ดี.
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
เคล็ดลับสอนเด็กแปรงฟันและใช้ไหมขัดฟันอย่างถูกวิธี
วิธีการแปรงฟันเด็ก นอกจากขั้นตอนที่ถูกต้องแล้ว ยังต้องมีเทคนิคอย่างไรให้เด็กสนุกกับการแปรงฟัน เพื่อเป็นพื้นฐานในการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี ดูที่นี่เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีทำให้การแปรงฟันเป็นเรื่องสนุก
คุณกำลังเจอกับปัญหาชักจูงลูกน้อยแปรงฟันทุกวันไหม ลองทำให้การทำความสะอาดช่องปากเป็นเรื่องง่ายและสนุกวันนี้ด้วยเคล็ดลับจากคอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
เหงือกของคุณมีเลือดออกขณะใช้ไหมขัดฟันหรือไม่
คุณกำลังประสบปัญหามีเลือดออกขณะใช้ไหมขัดฟันหรือไม่ การที่เหงือกมีเลือดไหลขณะขัดฟันนั้นอาจเป็นสัญญาณของโรคเหงือกอักเสบ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีใช้ไหมขัดฟันเพื่อดูแลสุขภาพปากและฟันที่ดี
เรียนรู้วิธีใช้ไหมขัดฟันที่เหมาะสมเพื่อดูแลสุขภาพปากและฟันที่ดี คอลเกต ให้ข้อมุลเพื่อดูแลฟันให้แข็งแรงและสวยงามได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม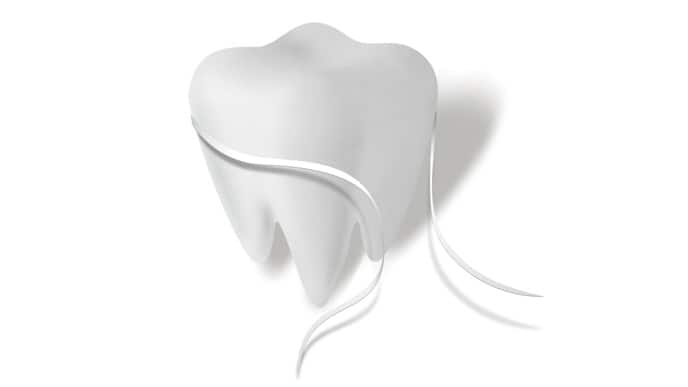
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
การใช้ไหมขัดฟันอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
อย่าละเลยการใช้ไหมขัดฟัน เพราะการใช้ไหมขัดฟันเพียงวันละครั้งก่อนการแปรงฟัน จะช่วยให้การทำความสะอาดซอกฟันมีประสิทธิภาพมากยิ่งขึ้น ป้องกันฟันผุได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
3 วิธีแปรงฟันที่ช่วยให้ฟันสวยและแข็งแรง
การแปรงฟันวันละสองครั้งเป็นการดูแลรักษาสุขภาพช่องปากให้สะอาดปราศจากฟันผุ คอลเกต แนะนำ 3 วิธีแปรงฟันที่ถูกต้องเพื่อฟันสวยได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีทำให้การแปรงฟันเป็นเรื่องน่าสนุก
การแปรงฟันอาจเป็นเหมือนงานที่แสนจะน่าเบื่อ แต่คอลเกตมีเคล็ดลับที่อาจช่วยพลิกการแปรงฟันให้เป็นเรื่องที่น่าสนุกประจำวันของคุณได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ประวัติของแปรงสีฟันและยาสีฟัน
เยี่ยมชมเว็บไซต์คอลเกต เพื่ออ่านประวัติของแปรงสีฟันและยาสีฟัน ค้นหาสินค้าครบถ้วนจากคอลเกต รับรอยยิ้มที่สดใสและสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีแปรงฟัน ใช้ไหมขัดฟันและรับประทานอาหารเพื่อสุขภาพฟันที่ดี
การแปรงฟันอย่างถูกวิธี การใช้ไหมขัดฟันและการเลือกรับประทานอาหารเป็นปัจจัยสำคัญของสุขอนามัยช่องปากที่ดี คอลเกตเล่าให้รู้ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
การแปรงฟันซี่แรกของทารก
การแปรงฟันซี่แรกให้ลูกน้อยเป็นขั้นตอนสำคัญสู่การสร้างสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี นี่คือเทคนิคเมื่อฟันของลูกน้อยเริ่่มขึ้น ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
จบปัญหา คราบหินปูน เหงือกร่น กลิ่นปาก ได้ด้วย Colgate Water Flosser
อยากจบปัญหาคราบหินปูน เหงือกร่น กลิ่นปาก ต้องเริ่มจากการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก ด้วย Colgate Water Flosser(ไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ)
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
จัดฟันต้องรู้! ไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำและเทคนิคดูแลฟันหลังรับประทานอาหาร
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ควรเลือกใช้แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าหรือควรใช้แปรงสีฟันธรรมดาดี
ควรเลือกใช้แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าหรือควรใช้แปรงสีฟันธรรมดาดีมาดูกันว่าทำไมแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าจึงเป็นตัวเลือกที่เหมาะสมต่อการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
เคล็ดลับการมีรอยยิ้มสวย ฟันขาว ในวันออกเดท
มาดูเคล็ดไม่ลับในการเตรียมตัวไปออกเดทสำคัญ ทำให้คู่เดทประทับใจได้ด้วยการมีรอยยิ้มสวย ฟันขาว สดใส ด้วยตัวช่วยอย่างแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีเลือกซื้อแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า
มาดูทุกเรื่องที่คุณต้องรู้ในการเลือกซื้อแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าที่เหมาะกับคุณ ทำความรู้จักว่ามีกี่ชนิด คุณสมบัติที่ควรต้องมี เพื่อการดูแลสุขภาพปากและฟันของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม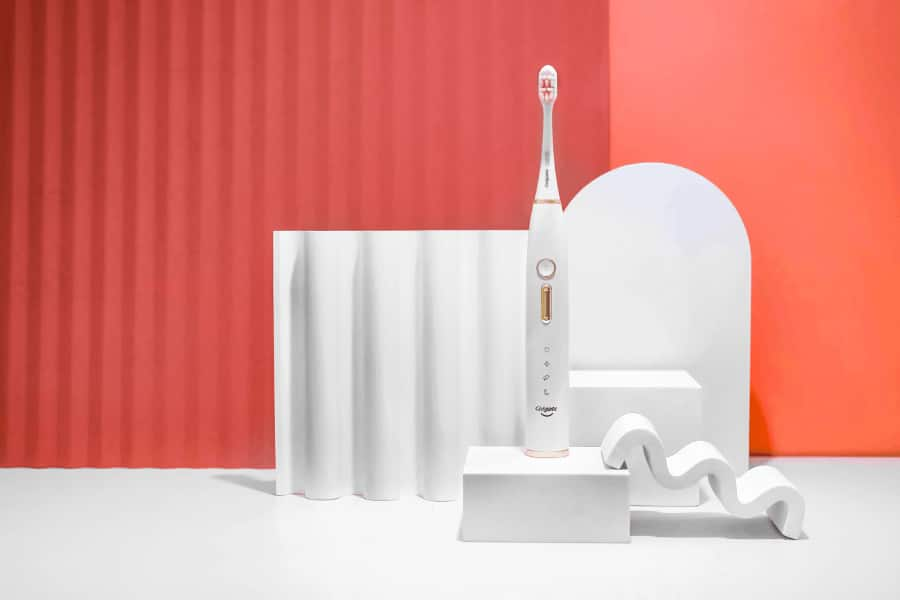
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
การเลือกแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า สำหรับคนจัดฟัน
หากคุณจัดฟันอยู่ แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าอาจเป็นทางเลือกที่คุ้มค่า เราจะช่วยแนะนำทุกเรื่องเกี่ยวกับการเลือกซื้อแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า เพื่อให้คุณตัดสินใจได้ง่ายขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
คู่มือการพกพา แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า ระหว่างเดินทางท่องเที่ยว
การพกพาแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าเวลาไปเที่ยวไม่ใช่เรื่องยาก คอลเกตมีเคล็ดลับดีๆ ตั้งแต่การจัดกระเป๋าไปจนถึงการทำความสะอาดมาฝาก คุณจะได้มีรอยยิ้มที่สดใสตลอดทริป!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม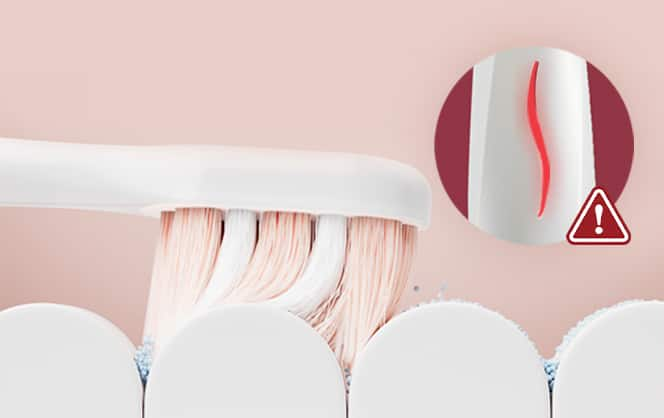
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าพร้อมเซ็นเซอร์อัจฉริยะ เพื่อผู้ที่มีอาการเสียวฟัน
ถ้าคุณกังวลกับอาการเสียวฟัน แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าพร้อมเซ็นเซอร์ตรวจจับแรงกด อาจเป็นคำตอบที่คุณตามหา ทำความรู้จักแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า ที่จะตอบโจทย์การดูแลฟันของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
สร้างวินัยที่ดีเพื่อช่องปากที่สะอาด ด้วยแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า
จุดเริ่มต้นของช่องปากที่สะอาด มาจากสร้างวินัยการแปรงฟัน ทำให้เป็นนิสัยได้ง่ายๆ และสะดวกกว่าที่เคย ด้วยตัวจับเวลาจากแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า
อ่านเพิ่มเติม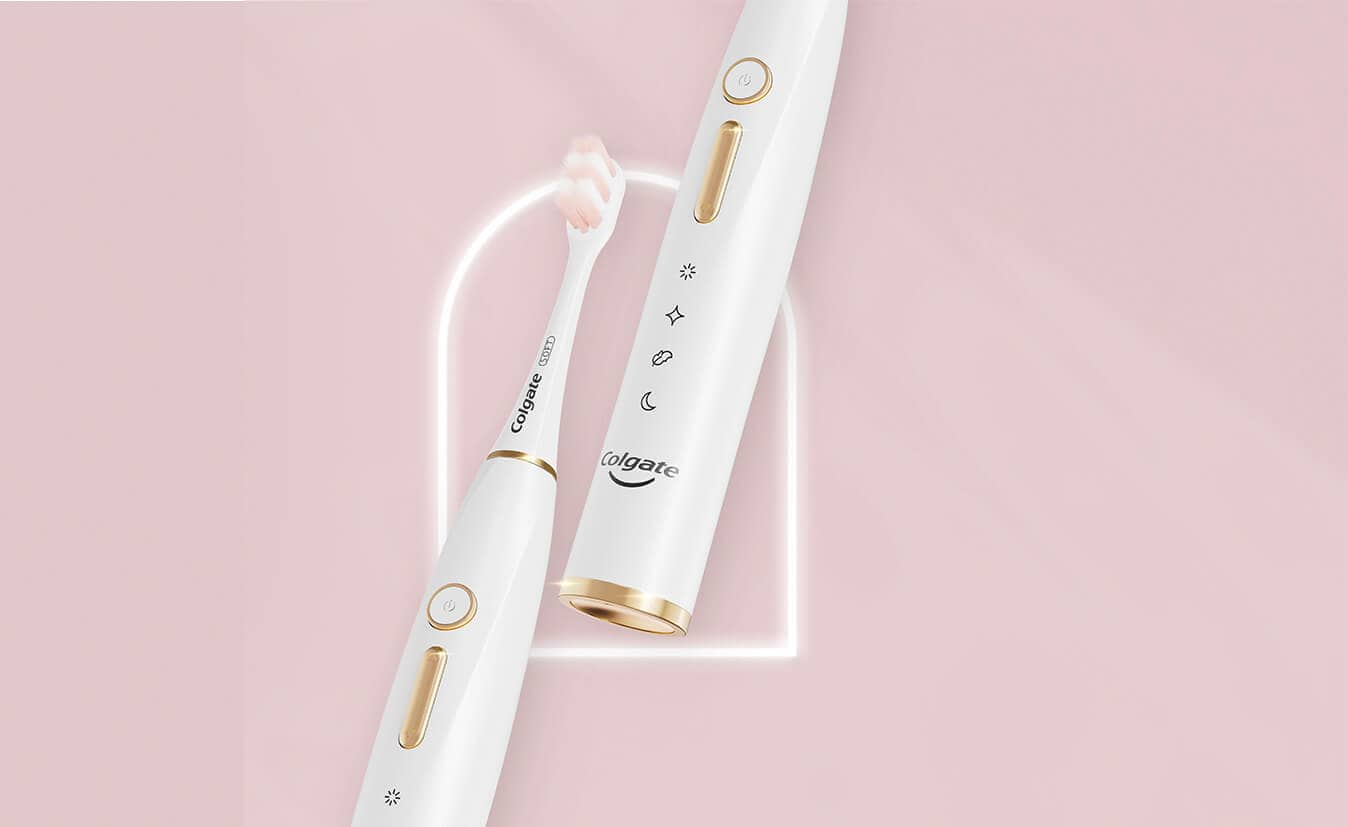
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าแบบโซนิคคืออะไร สำคัญต่อสุขภาพฟันของคุณอย่างไร
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าแบบโซนิค แตกต่างกับแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าทั่วไปอย่างไร มาดูฟังก์ชันการทำงานต่าง ๆ รวมถึงประสิทธิภาพในการทำความสะอาดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม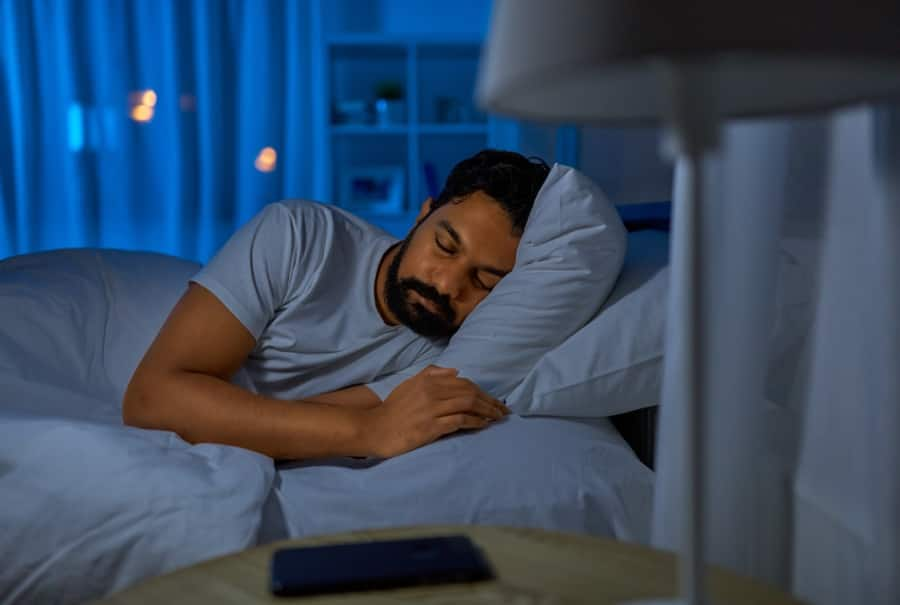
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ไหมขัดฟันไฟฟ้าช่วยให้ขัดฟันได้ง่ายขึ้นหรือไม่
การขัดฟันเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นต่อการรักษาสภาพช่องปากในชีวิตประจำวัน การใช้เครื่องขูดหินปูนไฟฟ้านั้นอาจช่วยให้ขั้นตอนนี้ง่าย และมีความสะดวกมากยิ่งขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม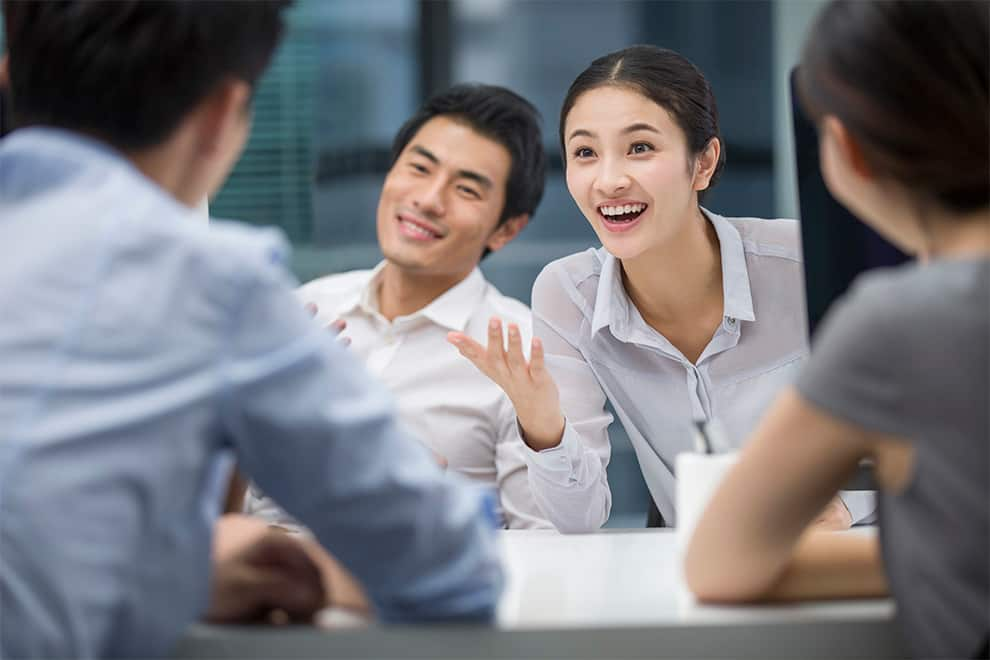
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
การแปรงฟันหลังรับประทานอาหารดีสำหรับคุณหรือไม่
การแปรงฟันหลังมื้ออาการที่เร็วเกินไปนั้น สามารถทำลายชั้นเคลือบฟันได้รับความเสียหายได้ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับเวลาที่เหมาะสมต่อการแปรงฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม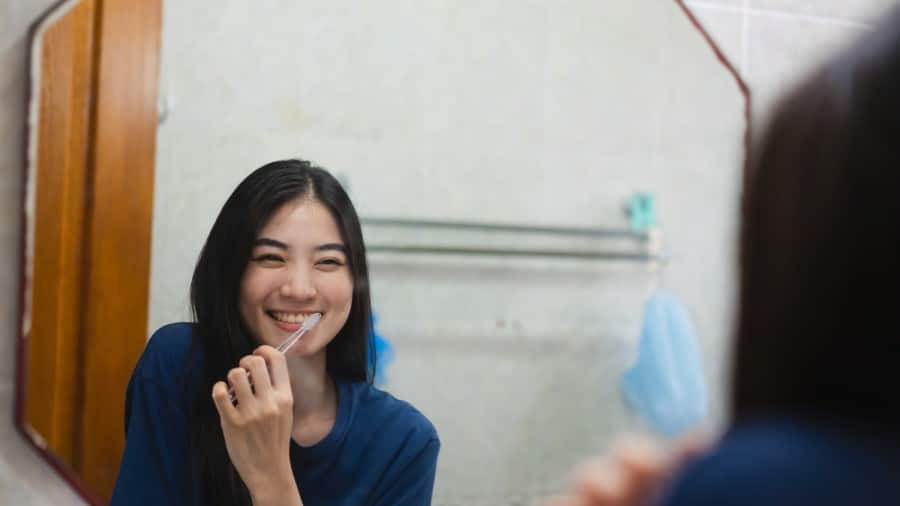
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ได้เวลาเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟันใหม่แล้ว
ดูแลรักษาฟันของคุณด้วยการหมั่นเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟันอันใหม่อย่างสม่ำเสมอ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตและ เรียนรู้ข้อควรคำนึงเกี่ยวกับแปรงสีฟัน และสุขภาพฟันของคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีการใช้ไหมขัดฟันที่ถูกต้องเป็นอย่างไร
คุณอาจจะเคยได้ยินมาว่าการใช้ไหมขัดฟันนั้นจะทำให้คุณมีสุขภาพช่องปากและฟันที่ดี แต่คุณอาจสงสัยว่าเพราะอะไร หรือสงสัยว่าวิธีการใช้ที่ถูกต้องคืออะไร
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
นี่คือสิ่งที่จะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อคุณไม่แปรงฟัน
คุณคงเคยได้ยินมาหลายครั้งแล้วว่าการแปรงฟันทุกวันนั้นเป็นสิ่งที่จำเป็น แล้วจะเกิดอะไรขึ้นถ้าหากคุณไม่แปรงฟัน เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
ถึงเวลาเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟันของคุณแล้ว!
เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้เพื่อค้นหาคำตอบว่าคุณควรจะเปลี่ยนหัวแปรงสีฟันเมื่อไหร่ และความสำคัญของการมีแปรงที่สะอาดเพื่อสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดีของคุณมีอะไรบ้าง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
วิธีเลือกแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าให้เหมาะกับตัวเอง
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
คนจัดฟันจำเป็นต้องใช้แปรงไฟฟ้าไหม?
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
เทคนิคการใช้แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า เพื่อดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
5 ข้อดีของการใช้แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าเพื่อสุขภาพปากและฟัน
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
เชื่อมั้ย กลิ่นปากแก้ไขได้ด้วยการใช้แปรงไฟฟ้า
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
แปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้า ช่วยดูแลปัญหาสุขภาพเหงือกได้อย่างไร
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การแปรงฟันและการขัดฟัน
หัวแปรงสีฟันไฟฟ้าเปลี่ยนบ่อยแค่ไหนถึงจะดี?
หนึ่งในปัญหาใหญ่ของคนดัดฟันคือ เศษอาหารติดตามซอกฟัน ชวนมารู้จักไหมขัดฟันพลังน้ำ ทางเลือกของการทำความสะอาดฟันอย่างล้ำลึกและอ่อนโยนสำหรับคนดัดฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกอักเสบที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกับโรคอื่นๆ
การอักเสบของช่องปากและเหงือกไม่เพียงแต่บ่งบอกถึงสุขภาพช่องปากที่อ่อนแอลง แต่ยังเป็นตัวบ่งชี้ปัญหาสุขภาพด้านอื่นๆ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม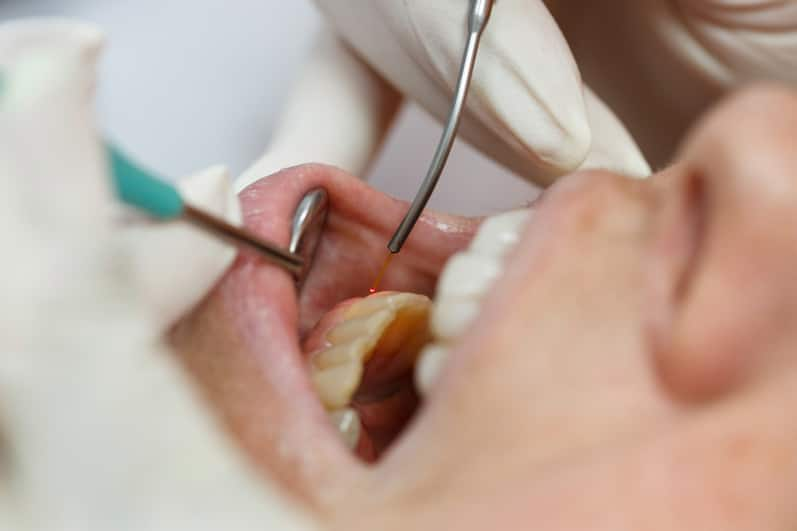
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
แก้ไขปัญหาเหงือกด้วยเลเซอร์ได้อย่างไร
ปัญหาเหงือกคืออาการอักเสบบริเวณเหงือกที่อาจส่งผลกระทบต่อกระดูกซึ่งเป็นส่วนรองรับฟันของคุณ ค้นพบสาเหตุของปัญหาเหงือกและวิธีป้องกันเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ปริทันตวิทยาเบื้องต้น
ปริทันตวิทยาเป็นสาขาทางทันตกรรมที่เน้นการป้องกันและรักษาปัญหาเหงือก เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับปริทันตวิทยาและปริทันตทันตแพทย์ กับคอลเกตเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การรักษาเหงือกร่น: ทางเลือกของการผ่าตัดเหงือกร่น
เหงือกร่นอาจนำไปสู่ปัญหาสุขภาพช่องปากที่รุนแรงกว่าได้หากปัญหาถูกละเลยหรือไม่ได้รับการรักษาอย่างทันท่วงที อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม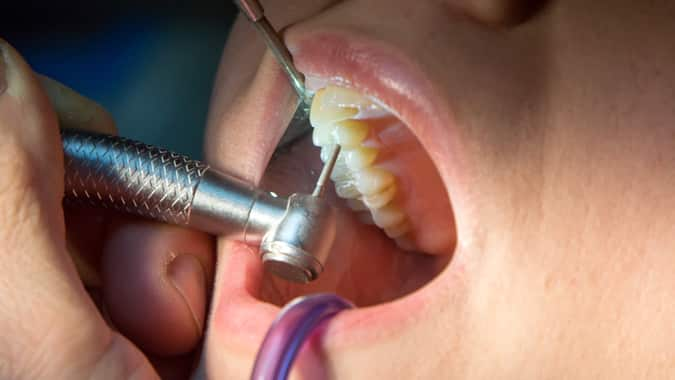
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การทำความสะอาดผิวรากฟันคืออะไรและจำเป็นไหม
ทันตแพทย์ของคุณอาจแนะนำให้คุณทำความสะอาดผิวรากฟัน แต่จริงๆ แล้วมันคืออะไรและทำไมเราจึงควรทำ? สิ่งที่แสดงถึงปัญหาเหงือกมีดังนี้:
อ่านเพิ่มเติม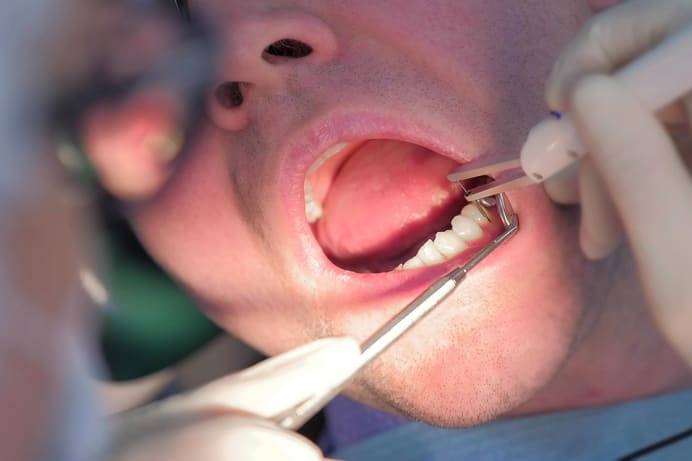
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ร่องลึกปริทันต์คืออะไร?
โรคเหงือกคือการอักเสบบริเวณเหงือกที่อาจส่งผลกระทบต่อกระดูกซึ่งรองรับฟันของคุณ ค้นพบสาเหตุของโรคเหงือกและวิธีป้องกัน จากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม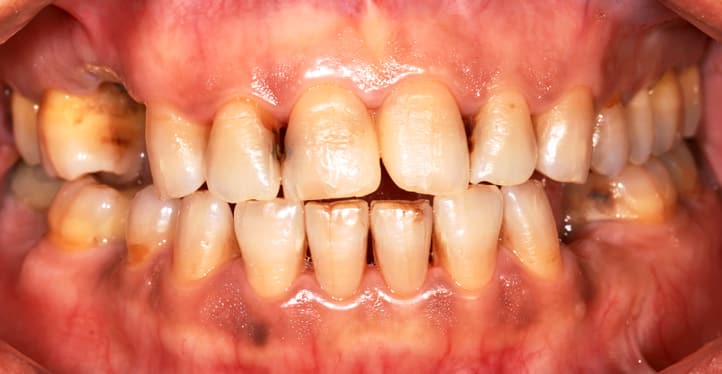
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
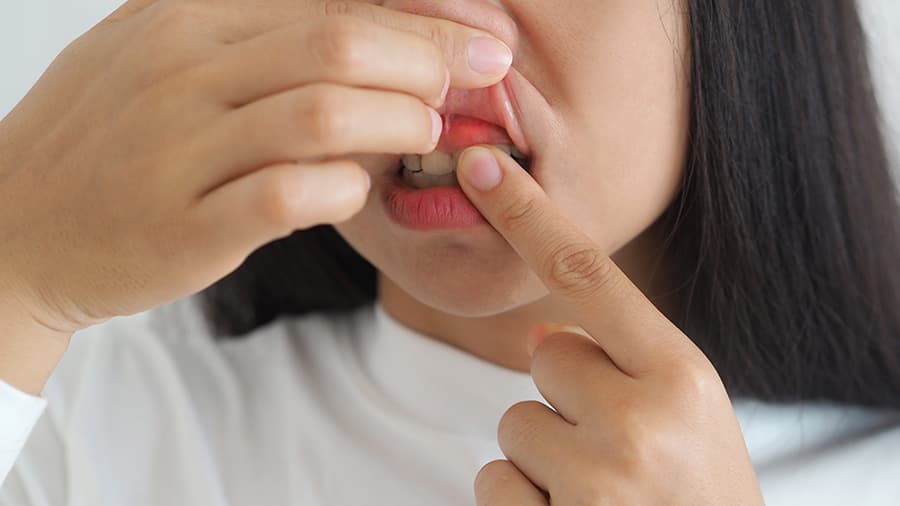
จุดสีดำบนเหงือกมีสาเหตุมาจากอะไร?
เหงือควรมีสีชมพูสุขภาพดี แต่ถ้าบนเหงือกมีจุดสีดําเกิดขึ้น อาจมีสาเหตุได้หลากหลาย ลองมาดูสาเหตุที่อาจเป็นไปได้ก่อนที่จะไปพบทันตแพทย์ของคุณ ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกอักเสบหายเองได้ไหม วิธีรักษาเหงือกอักเสบ
หากเหงือกของคุณบวม อักเสบ หรืออ่อนนุ่มเมื่อคุณแปรงฟัน คุณอาจมีปัญหาเหงือกอักเสบ มองหาวิธีการรักษาปัญหาเหงือกอักเสบที่บ้าน อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม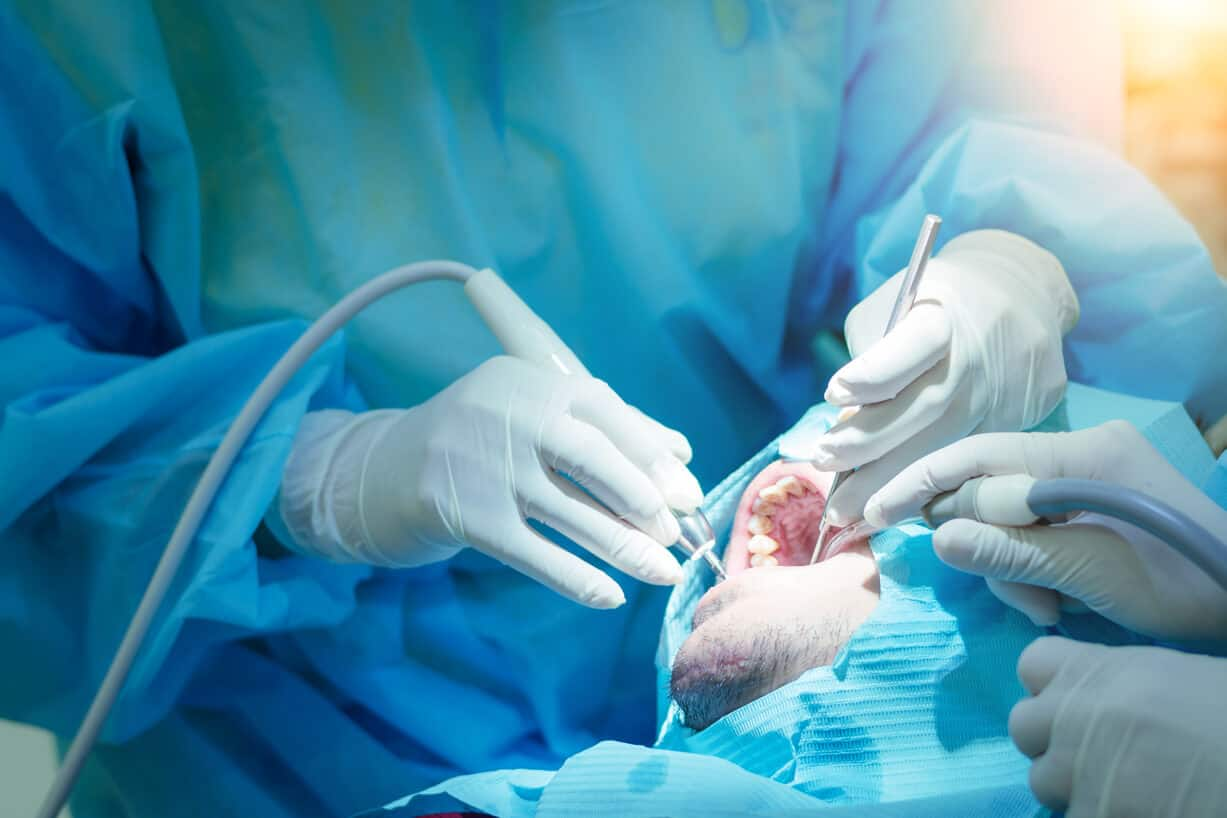
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
สาเหตุของโรคปริทันต์และวิธีป้องกัน
โรคปริทันต์คือการติดเชื้อและอักเสบของเหงือก เอ็นยึดปริทันต์ รวมถึงกระดูกรอบฟัน หากคุณรู้สาเหตุ วิธีรักษา เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
วิธีรักษาเหงือกอักเสบ
รูู้ได้อย่างไรว่าเป็นเหงือกอักเสบ? มาดูอาการที่สังเกตได้ สาเหตุปัจจัยของเหงืออักเสบ วิธีการรักษา รวมถึงวิธีการบรรเทาอาการด้วยตัวเองที่บ้าน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม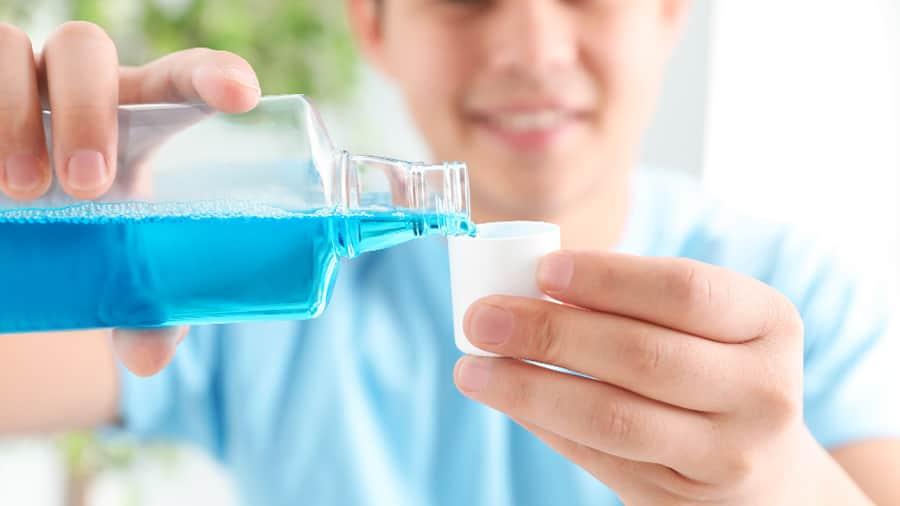
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
4 คำถามเกี่ยวกับน้ำยาบ้วนปากคลอเฮกซิดีนกลูโคเนต
น้ำยาบ้วนปาก คลอเฮกซิดีนกลูโคเนตใช้รักษาเหงือกอักเสบ หรือที่เรียกว่าโรคเหงือกแบบไม่รุนแรง ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม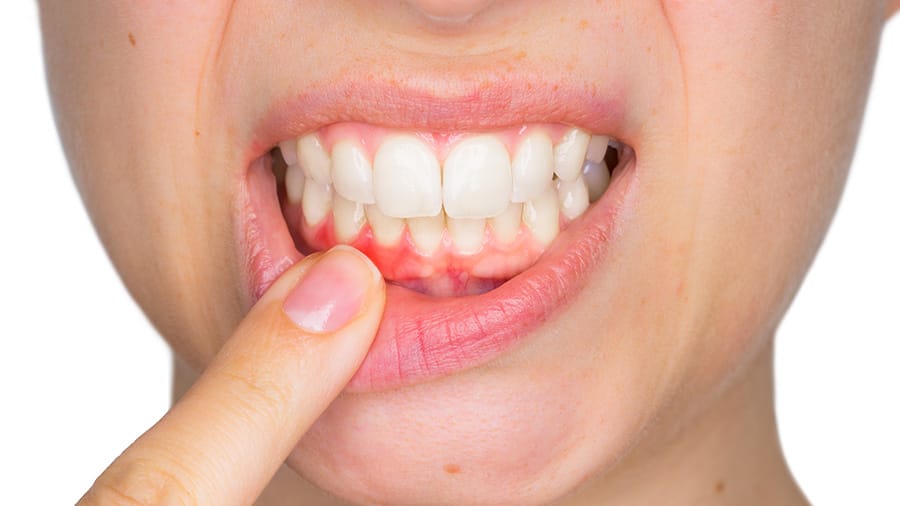
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
อาการของโรคเหงือกที่คุณควรรู้ พร้อมวิธีป้องกันรักษา
อาการของโรคเหงือก คุณจะสามารถรับมือได้ทันทีที่เกิดปัญหา เรียนรู้เรื่องอาการของโรคเหงือก วิธีการรักษา และการป้องกัน ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
วิธีเลือกยาสีฟันเกลือ แก้ปัญหาตรงจุด ป้องกันเหงือกเลือดออก
วิธีแก้ปัญหาเหงือกเลือดออกจากคราบหินปูน การอมน้ำเกลือหรือกินวิตามินซีอาจไม่ใช่คำตอบ รู้วิธีแก้ปัญหาเหงือกเลือดออกอย่างตรงจุดด้วยยาสีฟันเกลือที่คิดค้นมาโดยเฉพาะ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
อาการคันเหงือกเกิดจากอะไร
นอกจากการคันเหงือกจากคราบพลัคตามซอกฟันแล้วนั้น อาการคันเหงือกสามารถเกิดขึ้นได้จากหลายสาเหตุ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสาเหตุ และวิธีการรักษาได้ตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เลือดออกตามไรฟัน: 5 สาเหตุที่คุณควรรู้และวิธีแก้ไขง่ายๆ
การที่มีเลือดออกตามไรฟันขณะแปรงหรือขัดฟันอาจเป็นสัญญาณเตือนบางอย่าง สาเหตุของการที่มีเลือดออกตามไรฟันนั้นมีอะไรบ้าง เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมที่คอลเกตได้ในตอนนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การรักษาเลือดออกตามไรฟัน
การที่มีเลือดออกตามไรฟันขณะที่แปรงหรือขัดฟันนั้นมักเป็นอาการของโรคเหงือกอักเสบที่สามารถนำไปสู่โรคเหงือกในนั้นรุนแรงได้ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมตอนนี้ได้ที่คอลเกต
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การผ่าตัดเหงือก: สิ่งที่คุณจำเป็นต้องรู้
การผ่าตัดเหงือกคือหนึ่งในการผ่าตัดที่จะช่วยในเรื่องปัญหาโรคปริทันต์ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้เพื่อเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับขั้นตอนและวิธีการผ่าตัด
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกบวมเกิดจากอะไรได้บ้าง? รวมสาเหตุการเกิดเหงือกบวม
คุณรู้ไหมว่าเหงือกบวมเกิดจากหลายสาเหตุ มาดูกันว่าเหงือกบวมเกิดจากอะไร? รู้ไว้เพื่อป้องกันการเกิดอาการเหงือกบวม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
วิธีรักษาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ ด้วยการเลือกใช้แปรงสีฟันที่เหมาะสม
แปรงสีฟันและผลิตภัณฑ์สำหรับคนที่มีปัญหาเหงือกอักเสบควรเลือกแบบใด? เพื่อเป็นวิธีรักษาเหงือกบวมอย่างเหมาะสม และส่งเสริมสุขภาพช่องปากให้ดีขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกบวม แต่ไม่เจ็บ ต้องไปหาหมอไหม?
อาการเหงือกบวม เป็นสัญญาณของโรคทางช่องปากอื่นๆ แล้วจะรู้ได้อย่างไรว่าอาการเหงือกบวมที่คุณกำลังเผชิญอยู่ จำเป็นต้องพบทันตแพทย์หรือไม่ หาคำตอบได้ที่นี่!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกบวม เจ็บเหงือก สัญญาณที่เตือนอันตรายของโรคเหงือกอักเสบ
เหงือกบวม เจ็บเหงือก เป็นหนึ่งในอาการของโรคเหงือกอักเสบ ที่ส่งสัญญาณถึงปัญหาสุขภาพช่องปาก โรคเหงือกอักเสบมีกี่ระยะ? สามารถดูแลรักษาเบื้องต้นได้อย่างไรบ้าง?
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
วิธีรักษาเหงือกบวมตรงฟันกราม ยุ่งยากไหม?
หากรู้สาเหตุและวิธีรักษาเหงือกบวมด้านใน บริเวณฟันกราม ก็สามารถบรรเทาอาการและมีสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดียิ่งขึ้นได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
วิธีรักษาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ เบื้องต้นด้วยตัวเอง
การรักษาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ หากเป็นในระยะแรกและอาการไม่รุนแรงมากนัก สามารถรักษาให้หายได้ด้วยตัวเอง ภายใน 2 สัปดาห์ คอลเกตนำมาฝากได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ลองเช็กดู เหงือกบวมประมาณนี้ เป็นรากฟันอักเสบหรือเปล่า?
เช็กดูให้แน่ใจ ว่าปัญหาเหงือกบวมที่คุณเผชิญอยู่ เกิดจากรากฟันอักเสบหรือไม่? เพื่อพบทันตแพทย์และรักษาได้ทันท่วงที ก่อนต้องสูญเสียฟันไป
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ดูแลช่องปากแค่วันละ 4 นาที ก็ป้องกันเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบได้
วิธีนี้แหละเวิร์ค! ดูแลช่องปาก เพียงวันละ 4 นาที ช่วยป้องกันตัวเองจากความเจ็บปวดของเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ และปัญหาช่องปากอื่นๆ ที่อาจตามมาได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ถึงเวลาเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟัน เพื่อการดูแลรักษาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ
รู้ไหมว่า หากคุณมีปัญหาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบควรเปลี่ยนแปรงสีฟันบ่อยแค่ไหน เพื่อช่วยในการดูแลรักษาเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ ป้องกันได้ เมื่อเลือกใช้แปรงสีฟันขนนุ่ม
ทำไมต้องทนความเจ็บปวดจากเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ? ในเมื่อเราป้องกันได้ มาดูเคล็ดลับเลือกแปรงสีฟันขนนุ่ม เพื่อสุขภาพเหงือกที่ดีได้ที่นี่!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกร่นสามารถงอกใหม่ได้หรือไม่?
เหงือกร่นเกิดขึ้นได้จากหลายสาเหตุ ตั้งแต่การแปรงฟันที่แรงเกินไปไปจนถึงการบดฟันของคุณ เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสาเหตุที่ทำให้เหงือกร่นและวิธีการรักษาได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ลดคราบแบคทีเรียและป้องกันเหงือกอักเสบ ด้วยยาสีฟันรักษาโรคเหงือก
ดูแลสุขภาพเหงือกด้วยยาสีฟันรักษาเหงือกที่ช่วยลดการสะสมของคราบแบคทีเรีย ป้องกันเหงือกอักเสบ พร้อมคำแนะนำการดูแลช่องปากอย่างครบถ้วนจากคอลเกต!
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
สาเหตุและอาการเหงือกบวม เหงือกอักเสบ พร้อมวิธีป้องกันและรักษาก่อนพบแพทย์
ทำความเข้าใจอาการเหงือกบวมและเหงือกอักเสบ รวมถึงสาเหตุที่ทำให้เกิด เช่น การแปรงฟันแรง พร้อมวิธีป้องกันและรักษาเพื่อสุขภาพเหงือกที่แข็งแรง อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
สาเหตุของโรคเหงือกอักเสบ บรรเทาอาการเหงือกอักเสบด้วยเองได้หรือไม่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม.png)
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ทางเลือกในการรักษาโรคเหงือก
ชาวอเมริกันนับล้านมีปัญหาเหงือกแต่ไม่รู้ตัวเลยว่าตนเองมีการติดเชื้ออย่างรุนแรง โรคปริทันต์คือการติดเชื้อของเนื้อเยื่อเหงือก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การปลูกถ่ายเหงือกสำหรับเหงือกร่น
เหงือกร่นเป็นกระบวนการที่ค่อยๆ เกิดขึ้นโดยไม่ทันสังเกต การปลูกถ่ายเหงือกเป็นการป้องกันไม่ให้เกิดการสูญเสียเหงือกมากไปกว่าเดิม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
ข้อควรรู้เกี่ยวกับการผ่าตัดเหงือก?
หลังการผ่าตัดเหงือก เป็นเรื่องสำคัญมากที่ปริทันตทันตแพทย์หรือทันตานามัยจะบอกคุณเกี่ยวกับวิธีทำความสะอาดฟันและเนื้อเยื่อเหงือก ด้วยแปรงสีฟันและยาสีฟันผสมฟลูออไรด์ที่มีสารต้านแบคทีเรีย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
.png)
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
เหงือกแข็งแรง: กุญแจสู่สุขภาพที่ดี
สุขภาพช่องปากเป็นส่วนประกอบสำคัญของสุขภาพร่างกายโดยรวม ซึ่งรวมถึงการรักษาเหงือกให้แข็งแรงด้วย ต่อไปนี้คือวิธีสังเกตและรับมือกับขอบเหงือกที่อักเสบ:
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
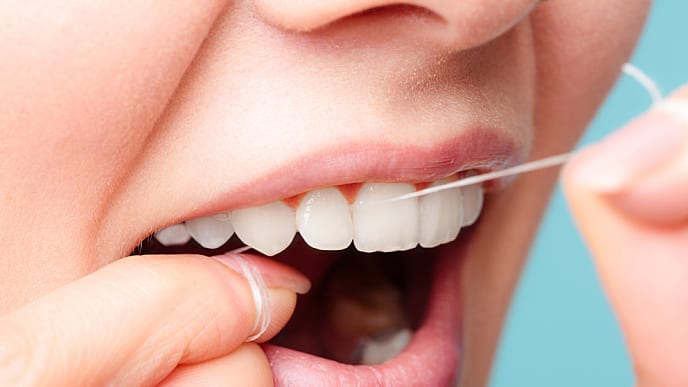
.png)
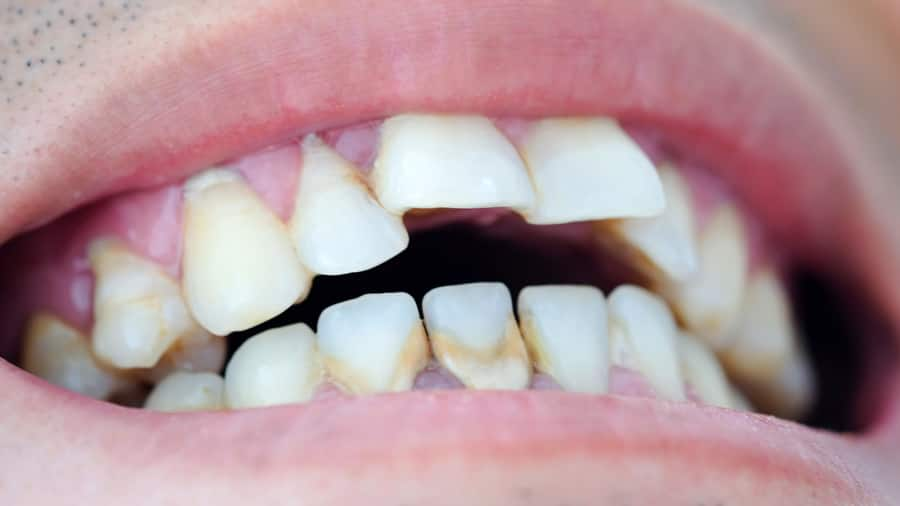

โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การรักษาโรคเหงือกอักเสบโดยผู้เชี่ยวชาญและการดูแลเมื่ออยู่ที่บ้าน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม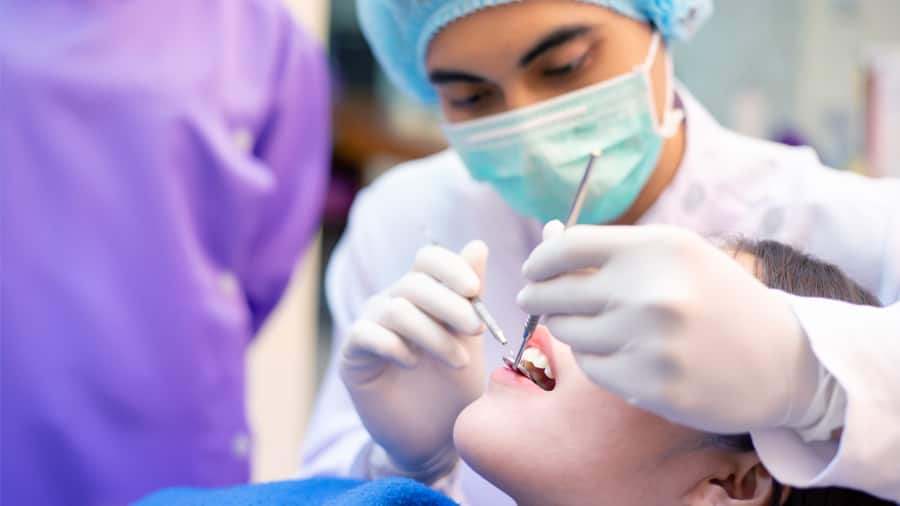

โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
3 ระยะของปัญหาปริทันต์
ตรวจสอบทางการแพทย์โดย Colgate Global Scientific Communication
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
อะไรคือสัญญาณของปัญหาเหงือก?
ตรวจสอบทางการแพทย์โดย Colgate Global Scientific Communication
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
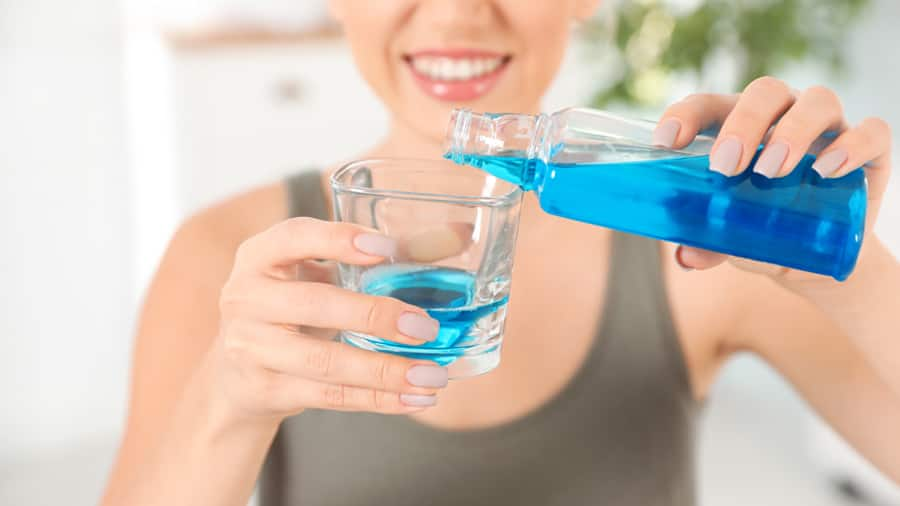




.jpg)
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การทำความสะอาดผิวรากฟันของคุณช่วยป้องกันปัญหาเหงือกขั้นรุนแรงได้อย่างไร
ภาวะเหงือกอักเสบเป็นหนึ่งปัญหาที่พบได้บ่อย เมื่อถึงจุดหนึ่ง การทำความสะอาดผิวรากฟันสามารถลดการติดเชื้อและกำจัดหินปูนเพื่อช่วยให้เหงือกของคุณหายดีได้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
โรคเหงือก (เหงือกอักเสบ)
การผ่าตัดปลูกถ่ายเหงือก: ข้อมูลสำหรับเตรียมพร้อมและวิธีลดอาการเจ็บเหงือก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
ทางเลือกในการรักษา อาการเสียวฟัน
วิธีดูแลอาการเสียวฟันของคุณให้บรรเทาลง มีทั้งแบบทำเองที่บ้าน และไปพบทันตแพทย์ ลองดูวิธีที่เหมาะกับคุณได้เลย ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
ทำไมเกิดอาการเสียวฟัน
อาการเสียวฟัน เกิดขึ้นจากอะไรได้บ้าง? จะมีวิธีการอย่างไรในการป้องกันการเสียวฟัน หรือมีผลิตภัณฑ์ใดบ้างในการบรรเทาอาการ คลิกมาดูคำตอบได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
อาการเสียวฟันคืออะไร
ภาวะเนื้อฟันไวเกิน หรือการเสียวฟัน อาจหมายถึงอาการเจ็บปวดเมื่อสัมผัสกับความร้อน ความเย็น ความหวาน แล้วจะมีวิธีการรักษาอย่างไร มาดูเพิ่มเติมได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
สาเหตุที่ทำให้คุณ ‘เสียวฟัน’ พร้อมวิธีป้องกันและรักษาอาการเสียวฟัน
เมื่อคุณรู้สึกเสียวฟัน มีวิธีจัดการกับอาการฟันเสียวอย่างไรบ้าง? มาดูสาเหตุ วิธีป้องกัน และการรักษาอาการที่ถูกต้อง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
การสึกของเคลือบฟันและอาการเสียวฟัน – คุณจะทำอย่างไร
มาดูวิธีการปฏิบัติตัวเมื่อเคลือบฟันสึก จนทำให้เกิดการเสียวฟัน เพื่อให้คุณใช้ฟันได้อย่างปกติอีกครั้ง ดูเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
การสึกของเคลือบฟัน มีผลต่อฟันของคุณอย่างไร
เคลือบฟันสึก อาจเกิดจากอาหารที่ทานเป็นกรดมากเกินไป หรือความเจ็บป่วยเช่น โรคกรดไหลย้อน ซึ่งสามารถแก้ไขได้ ดูเพิ่มเติม คลิก
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
เหงือกไม่แข็งแรง? ค้นพบ 3 สาเหตุที่ทำให้เหงือกอ่อนแอ
แปรงฟันแรง เหงือกเป็นแผล คือหนึ่งในสาเหตุที่ทำให้เหงือกอ่อนแอ และอักเสบได้ แต่ยังมีสาเหตุอื่นๆ อีกด้วย เรียนรู้ถึงสาเหตุหลักและการป้องกันเบื้องต้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
คุณควรทำอย่างไรเมื่อมีอาการเสียวฟัน
อาการเสียวฟันพบในคนทุกวัย และทางเลือกในการรักษาอาการเสียวฟันมีอะไรบ้าง คอลเกตจะเล่าให้คุณรู้การรักษาอาการเสียวฟันในคลินิกและที่บ้าน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
ควรทำอย่างไรเมื่อเสียวฟันเพราะความเย็น
มีวิธีต่างๆรักษาการปวดฟันที่เกิดหลังกินน้ำเย็น เช่นการใช้ยาสีฟันสูตรฟลูออไรด์ เป็นต้น อ่านข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นจากคอลเกตได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
วิธีบรรเทาและแก้อาการเสียวฟันง่ายๆแบบธรรมชาติ
การปรับเปลี่ยนกิจวัตรประจำวันเพียงเล็กน้อยสามารถบรรเทาอาการเสียวฟันได้และไม่ปวดฟันในอนาคต คอลเกตแนะนำวิธีธรรมชาติได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
ยาสีฟันลดอาการเสียวฟันที่ดีควรมีส่วนผสมอะไร?
ยาสีฟันสำหรับอาการเสียวฟันสามารถช่วยลดภาวะเสียวฟันได้ในระยะเวลาเพียงแค่สองอาทิตย์ คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้ส่วนผสมที่ช่วยปกป้องเคลือบฟัน
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
บรรเทาอาการเสียวฟัน
อาการเสียวฟัน เป็นอาการเจ็บแปลบของฟันอันเกิดจากการสูญเสียของผิวฟัน หรืออาจเกิดจากภาวะเหงือกร่นก็เป็นได้ มาดูวิธีการบรรเทาอาการเสียวฟันได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
วิธีรักษาอาการเสียวฟัน
ตอนที่รากฟันถูกเปิดออก การกินอาหารร้อนหรือเย็นอาจส่งสัญญาณไปที่โพรงประสาทฟันซึ่งทำให้รู้สึกเสียวฟัน คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม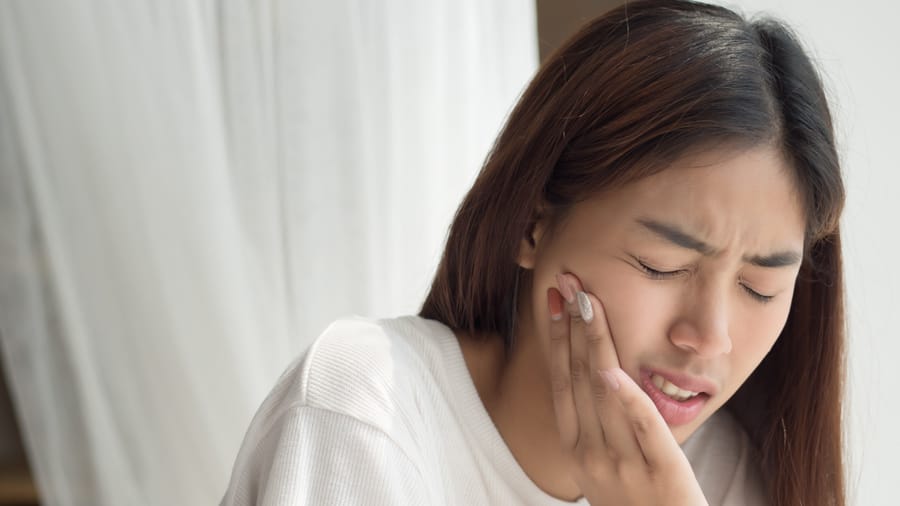
การเสียวฟัน
สาเหตุและการรักษาอาการเสียวฟัน
อาการเสียวฟันเกิดจากสิ่งปกติเช่นอาหารร้อนหรือเย็นได้ และเกิดจากอาการหนักก่วาเช่นฟันโยกหรือเหงือกบวมได้ด้วย คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
อาการเจ็บเหงือกและอาการเสียวฟัน
คุณรู้ไหมว่าอาการเจ็บปวดในช่องปากของคุณเกิดจากอาการเจ็บเหงือกหรือปวดฟัน และควรใช้วิธีใดรักษา คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มเต็มได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
สาเหตุและวิธีรับมือเมื่อมีอาการเสียวฟัน
เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอาการเสียวฟัน ว่าอะไรคือสาเหตุของการเสียวฟัน รวมถึงวิธีการรักษาอาการและการป้องกัน ค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
อาการปวดฟัน หมายถึงอะไร?
คุณพบทันตแพทย์ทุกหกเดือน คุณไม่มีฟันผุ แล้วทำไมถึงยังมีอาการปวดฟันได้ล่ะ? เรียนรู้สาเหตุของอาการปวดฟันจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
อาการปวดฟันเกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไร
อาการปวดฟันที่รุนแรงมีหลายรูปแบบ ได้แก่ อาการปวดตื้อ ปวดตุบๆ เป็นเวลานาน หรือจู่ๆ ปวดแปล๊บขึ้นมาอย่างกะทันหันค้นหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
4 เคล็ดลับแก้ปัญหาอร่อยปาก แต่เสียวฟันแปล๊บไปถึงทรวง
ไม่ว่าจะกินของร้อน ของเย็น ก็เสียวฟันแปล๊บๆ ทุกที จะดีกว่าไหม? ถ้าแก้ปัญหาเสียวฟันได้อย่างตรงจุด กลับมาใช้ชีวิตประจำวันได้อย่างมีความสุข ไร้อาการเสียวฟันกวนใจ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
Topic: สายกินต้องระวัง ทำยังไงเมื่อกรดไหลย้อนทำให้เสียวฟัน พร้อมวิธีแก้ปัญหาด้วยยาสีฟันเกลือที่ดีจากคอลเกต
กรดไหลย้อนหนึ่งในโรคฮิตที่อาจทำให้เกิดอาการเสียวฟันโดยไม่รู้ตัว แก้ปัญหาด้วยยาสีฟันเกลือสูตรช่วยบรรเทาอาการเสียวฟัน ได้ตั้งแต่วันนี้
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
ฟันของคุณไวต่อน้ำตาลหรือไม่
คุณทราบหรือไม่ว่าน้ำตาลสามารถให้คุณมีอาการเสียวฟันได้ เยี่ยมชมคอลเกตตอนนี้และเรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับอาการเตือนของการปวดหรือเสียวฟันและ วิธีการรักษาอาการเหล่านั้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การเสียวฟัน
สาเหตุของอาการปวดฟันกราม พร้อมวิธีดูแลรักษาช่องปากที่คุณทำเองได้
ไม่ว่าคุณจะใส่ใจกับการดูแลช่องปากของคุณมากแค่ไหนก็ตาม บางทีสักครั้งหนึ่งในชีวิต คุณก็อาจต้องเจอกับประสบการณ์นี้...อ่านเพิ่มเติม
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลุ่มอาการฟันร้าว
คุณมีฟันแตกบ้างไหม
คุณมีฟันแตกบ้างไหม? แตกฟันแตกอาจเกิดขึ้นจะง่ายกว่าที่คุณคิด เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับฟันแตกและสิ่งที่จะทำอย่างไรข้อควรปฏิบัติถ้าหากคุณมีฟันแตก, ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
กลุ่มอาการฟันร้าว
ต้องทำอย่างไรหาก ฟันกรามแตก
ฟันแตก เกิดขึ้นได้จากหลายสาเหตุ ทั้งเกิดจากการบดเคี้ยว หรืออุบัติเหตุ ลองมาดูกันว่าสัญญาณว่าฟันของคุณจะแตก และขั้นตอนในการซ่อมแซมรอยแตกมีอย่างไรบ้าง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟัน
อุดฟันหน้าสำหรับฟันหน้าห่าง
ฟันห่างเกิดจากฟันมีพื้นที่ระหว่างฟัน 2 ซี่มากกว่าปกติ มักพบที่ฟันหน้าสองซี่ซึ่งแก้ไขได้ด้วยการอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟันเพื่อคืนรอยยิ้มที่สดใสให้กับคุณ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟัน
ไม่ใช่ว่าทุกคนจะสามารถทำการฟอกฟันขาวได้
ไม่ใช่ทุกคนที่ต้องได้รับการฟอกสีฟัน โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งถ้าคุณมีการอุดฟันด้วยสี คอลเกตจะช่วยให้คุณตรวจสอบ และหาทางเลือกอื่น ๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม

การอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟัน
การอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟัน
การอุดฟันด้วยวัสดุสีเหมือนฟัน คือวิธีการทางทันตกรรมเพื่อความงามที่ใช้วัสดุอุดฟันเรซิน (พลาสติก) ที่มีสีเหมือนฟัน ซ่อมแซมฟันที่ผุ บิ่น แตก หรือเปลี่ยนสี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: วัยรุ่น (13-17 ปี)
การให้ความรู้เกี่ยวกับสุขอนามัยในช่องปากแก่วัยรุ่น
เคล็ดลับเล็กๆ น้อยๆ เพื่อให้วัยรุ่นหันมาสนใจการดูแลสุขอนามัยในช่องปาก เพราะการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากเป็นเรื่องสำคัญสำหรับคนทุกวัย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: วัยรุ่น (13-17 ปี)
วัยรุ่นจะมีรอยยิ้มที่สดใสได้อย่างไร
ปัญหาทันตกรรมอะไรบ้างที่วัยรุ่นควรตระหนักและให้ความสำคัญ เพื่อการมีรอยยิ้มที่สดใสของวัยรุ่น เตรียมพร้อมรอยยิ้มให้ก้าวไปสู่วัยผู้ใหญ่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: วัยรุ่น (13-17 ปี)
ทำความรู้จักกับการดัดฟันและการดูแลรักษา
มาทำความรู้จักกับทันตกรรมจัดฟัน ที่ช่วยจัดให้ฟันและขากรรไกรที่เบียดกัน อยู่สูงกว่า หรือต่ำกว่าตำแหน่งขบฟัน ให้อยู่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องอย่างที่ควรจะเป็น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (55 ปีขึ้นไป)
สี่วิธีในการดูแลสุขอนามัยในช่องปากเมื่ออายุมากขึ้น
เมื่ออายุมากขึ้น สุขภาพร่างกายก็เปลี่ยนแปลง เช่นเดียวกับสุขภาพช่องปาก มาเรียนรู้วิธีการดูแลสุขอนามัยในช่องปาก เพื่อให้ฟันและเหงือกของคุณแข็งแรง
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (55 ปีขึ้นไป)
วิธีดูแลรักษาสุขภาพช่องปากเมื่ออายุมากขึ้น
เมื่ออายุมากขึ้น ช่องปากก็เริ่มมีปัญหาไปตามอายุที่เพิ่มขึ้น มาดูวิธีดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากสำหรับผู้สูงอายุอย่างถูกต้องกัน คลิกเลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ผู้ใหญ่ (55 ปีขึ้นไป)
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากสำหรับผู้สูงวัย
มาทำความเข้าใจว่าจะเกิดอะไรขึ้นกับช่องปากบ้างเมื่อคนเรามีอายุมากขึ้น เพื่อการดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากอย่างถูกต้อง ให้ผู้สูงอายุได้มีสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดี
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
ความสำคัญของการดูแลรักษาสุขภาพช่องปากของเด็ก
ในการดูแลสุขภาพฟันน้ำนมของเด็กนั้น ควรเริ่มต้นการฝึกสุขอนามัยช่องปากของลูกอย่างเร็วที่สุด อ่านเพิ่มเติมได้ที่ Colgate.co.th
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
การดูแลฟันของทารก
มาดูวิธีการที่ถูกต้องในการดูแลฟันของเด็กทารกขั้นพื้นฐาน รวมถึงข้อมูลที่ควรรู้เกี่ยวกับฟันผุจากขวดนม, ฟลูออไรด์ เพื่อฟันชุดแรกของลูกมีใช้งานได้นาน ๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
ฟันผุในวัยเด็ก
ฟันผุกับเด็กอาจจะดูเป็นเรื่องปกติ แต่จะดีกว่ามากถ้าฟันไม่ผุ ลองมาดูเทคนิคการป้องกันฟันผุในเด็ก เพื่อให้ฟันน้ำนมอยู่คู่กับเด็ก ๆ ไปนาน ๆ
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
การงอกของฟันน้ำนม: สัญญาณและการดูแลรักษา
พ่อแม่ควรทำอย่างไรเมื่อลูกน้อยรู้สึกเจ็บที่ฟันน้ำนมซี่แรกจะงอก คอลเกตแนะนำเคล็ดลับเกี่ยวกับการดูแลฟันน้ำนมที่งอกใหม่ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
คู่มือสำหรับคุณพ่อคุณแม่เพื่อสุขภาพฟันของลูก
การดูแลใส่ใจสุขภาพฟันสำหรับเด็ก ๆ มีความสำคัญไม่แพ้การดูแลสุขภาพร่างกาย คุณพ่อคุณแม่จึงต้องเข้าใจทุกเรื่องของสุขภาพฟันของลูกให้มากที่สุด
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากวัยเรียน
เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับการดูแลช่องปากสำหรับเด็ก ได้แก่ วิธีแปรงฟันเด็กๆ ให้ถูกต้อง แปรงสีฟันเด็ก และอื่นๆ อีกมากมายจากคอลเกต ได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม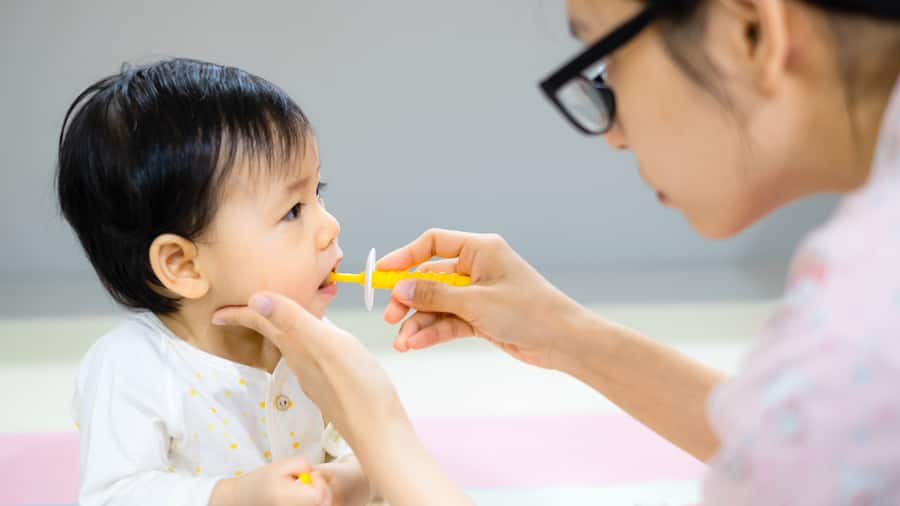
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
ข้อมุลเกี่ยวกับเด็กฟันผุ
พ่อแม่รู้ไหมว่าฟันผุในเด็กเล็กอาจก่อให้เกิดปัญหาอื่นๆสำหรับสุขภาพช่องปากในอนาคตได้ คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
การพาลูกน้อยไปพบทันตกรรมเด็กเป็นครั้งแรก
กุมารแพทย์และทันตแพทย์สำหรับเด็กส่วนใหญ่แนะนำว่าพ่อแม่ควรพาลูกน้อยไปพบตั้งแต่ในช่วงขวบปีแรก คอลเกต ให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มขึ้นได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
วิธีแปรงฟันเด็กวัยหัดเดิน
การแปรงฟันของลูกน้อยวัยหัดเดินอย่างถูกวิธี จะช่วยสร้างนิสัยสุขภาพช่องปากที่ดีได้ในอนาคต คอลเกตให้ข้อมุลเพิ่มเต็มได้ที่นี่
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
สิ่งที่คุณควรรู้เกี่ยวกับการสูญเสียฟันน้ำนมของลูกน้อย
คุณพ่อคุณแม่ไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องลูกฟันน้ำนมหลุด เพราะคอลเกตมีวิธีการดูแลลูกน้อยอย่างถูกต้องเมื่อฟันน้ำนมของลูกเริ่มหลุดมาบอก มาดูกันได้เลย
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปาก: ทารก (0-4)
ฟันน้ำนมซี่แรกของลูกน้อย
ระหว่างช่วงอายุ 4 ถึง 6 เดือน ลูกน้อยกำลังเริ่มมีฟันน้ำนมงอกขึ้นมา คอลเกต เล่าให้รู้วิธีบรรเทาอาการเจ็บปวดช่วงที่ฟันลูกกำลังขึ้น
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
พบกับการจับคู่ที่ลงตัวเพื่อรอยยิ้มของคุณ
พบกับหลากหลายผลิตภัณฑ์และโซลูชันที่ไม่มีอะไรเทียบได้ที่รองรับด้วยศาสตร์การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับเป้าหมายการเผยรอยยิ้มของคุณ ใช้เครื่องมือของเราและหาคู่ที่ลงตัว!
พบกับการจับคู่ที่ลงตัวเพื่อรอยยิ้มของคุณ
พบกับหลากหลายผลิตภัณฑ์และโซลูชันที่ไม่มีอะไรเทียบได้ที่รองรับด้วยศาสตร์การดูแลสุขภาพช่องปากที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับเป้าหมายการเผยรอยยิ้มของคุณ ใช้เครื่องมือของเราและหาคู่ที่ลงตัว!
แบบทดสอบเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพช่องปาก
อะไรคือสิ่งที่อยู่เบื้องหลังรอยยิ้มของคุณ
ทำแบบประเมินสุขภาพช่องปากของเราเพื่อให้กิจวัตรการดูแลช่องปากของคุณเกิดประโยชน์มากที่สุด
แบบทดสอบเกี่ยวกับสุขภาพช่องปาก
อะไรคือสิ่งที่อยู่เบื้องหลังรอยยิ้มของคุณ
ทำแบบประเมินสุขภาพช่องปากของเราเพื่อให้กิจวัตรการดูแลช่องปากของคุณเกิดประโยชน์มากที่สุด





