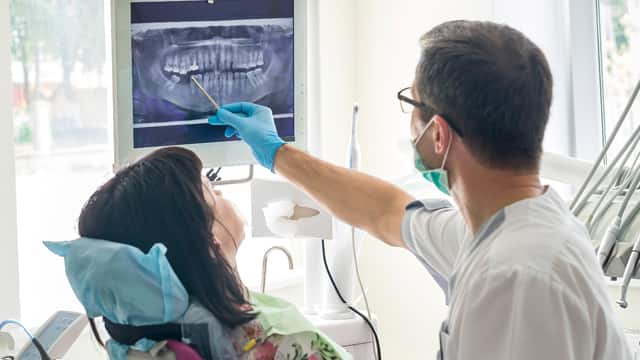
Definition
Any trauma to the mouth that may cause bleeding and lacerations to the gums, and dislodge, or fracture teeth, and may require immediate medical attention.
Signs and Symptoms
As with any trauma to the mouth, you should consult your dentist immediately to determine if treatment is required. The dentist will examine the affected area and may take X-rays.
If you are in pain from a broken, cracked or chipped tooth, you may be able to take an over-the-counter pain reliever. If possible, keep any part of the tooth that has broken off and take it with you to the dentist.
Cause
Whether the result of an accident or biting on a piece of food that’s too hard, mouth injuries can cause teeth to become cracked, broken, or knocked out/dislodged.
Diagnosis
If a tooth is completely knocked out of the mouth by an injury, take the tooth to your dentist as soon as possible. It may be possible for your tooth to be placed back into your mouth, a procedure called re-implantation.
Prevention
If you’re playing any contact sports, wearing a mouthguard can help protect your teeth from injury and trauma. Mouthguards are available at most sporting goods stores; however, to ensure a mouthguard fits properly, contact your dentist for a consultation to have one custom made to protect the teeth.
To help protect your teeth from injury while eating, avoid biting hard candies and ice.
Complications
An untreated infection can spread to the surrounding gum tissue of other teeth and into your jawline. It could even spread to different parts of your body, leading to other health issues and diseases. Signs of an infection include swelling around the site of the broken tooth and nearby tissue, throbbing pain and sometimes a fever.
Related Conditions
Left untreated, a dental emergency can lead to more serious complications. A cracked tooth, for instance, can leave a fracture in the tooth, a decayed tooth can cause a hole or opening in the tooth, and both are vulnerable to bacteria and decay. A jaw injury or possible fracture needs immediate attention at your dentist's office or in the emergency room.
Oral Care Center articles are reviewed by an oral health medical professional. This information is for educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist, physician or other qualified healthcare provider.
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine
ORAL HEALTH QUIZ
What's behind your smile?
Take our Oral Health assessment to get the most from your oral care routine






.png)