-
-

FLUORIDE
What Is Stannous Fluoride Toothpaste?Discover what is Stannous Fluoride Toothpaste and its importance to prevent cavities and other oral health problems.

TEETH WHITENING
Whitening toothpaste - hydrogen peroxide vs. carbamide peroxideIf you lose one or more of your front teeth due to injury or decay, you may feel ...
-
Science & InnovationOral Health Commitment
- Oral Health Commitment
- Bright Smiles, Bright Futures
- Educational Resources
- Mobile Dental Van
- Volunteer
- ORAL HEALTH CHECK
- PRODUCT MATCH
- Oral Health and Dental Care | Colgate®
- Oral Health
- Excessive Saliva? What It Could Mean (And How To Deal)


If someone uses the phrase “mouth-watering,” it’s usually a compliment or a sign that they’re appreciating good food. But if your mouth is literally watering, that’s a little different. Excessive saliva, known as hypersalivation, can cause you discomfort and embarrassment and might also lead to other complications. Find out what causes excessive saliva and how to treat it.
What Is Saliva and What Is Its Purpose?
Saliva is derived from blood, which helps maintain the health of hard and soft tissues in your mouth. Healthy saliva flow can wash food away from the teeth and gums, breaks down food for easy swallowing, enhances your ability to taste, and prevents cavities and other infections. Saliva even keeps the surface of your teeth strong by contributing high levels of calcium and fluoride. So, while reduced saliva flow, known as dry mouth, can cause swallowing and digestion problems, excessive saliva in your mouth is also a cause for concern.
Causes of Excessive Saliva
Drooling in infants and toddlers is normal and may often happen while they’re teething. Drooling or hypersalivation in adults is usually associated with infections or nervous system disorders.
Hypersalivation in adults is primarily caused by:
- Mononucleosis or sinus infections
- Strep throat or tonsillitis
- Allergies
- Heartburn or GERD
- Pregnancy
- Use of certain medicines
- Reaction to pesticide poisoning or snake or insect venom
- Nervous system disorders that cause difficulty with swallowing, like cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, multiple sclerosis, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, autism, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Some people who have excessive saliva are at an increased risk of aspirating saliva, foods, or fluids into their lungs. This can cause problems if they’re also facing issues with bodily reflexes, for example, coughing or gagging. Excessive saliva over time can also cause skin breakdown around the chin and lip area.
How to Treat Excessive Saliva
Treatment for excessive saliva depends on your overall health and other symptoms that you may be having. It is best accomplished by a multidisciplinary team, from primary care physicians to speech therapists, neurologists, and dentists. If you find yourself having excessive saliva in your mouth, it’s essential to consult with your doctor to determine the best treatment plan.
A study in New Approaches in Diagnostics and Treatment recommends that treatment interventions, including speech and swallowing therapy, medications, Botox, and use of oral prosthetic devices, among other things, be used. MedlinePlus notes that a speech therapist can determine if hypersalivation increases the risk of you breathing foods or fluids into your lungs.
Having excessive saliva can be quite uncomfortable, so you must seek out treatment as soon as possible. Consult with your doctor so that together you can find a treatment plan that manages the excessive saliva and makes you feel comfortable and confident.
Oral Care Center articles are reviewed by an oral health medical professional. This information is for educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist, physician or other qualified healthcare provider.
Related Articles
Adult Oral Care
Causes Of Brown Spots On TeethBrown spots on teeth may worry you, but there's plenty you can do to fix them. Your dentist can offer a solution based on the following causes.

Adult Oral Care
4 Tooth Pain Home RemediesIf you've ever had a toothache, you know tooth pain isn't fun. If you're unable to receive dental attention right away, try some tooth pain home remedies.

Adult Oral Care
Bumps on the Back of the Tongue: Normal or Abnormal?Bumps on the back of the tongue can occur due to sores and infections among other conditions. Consult your dentist if you notice abnormal bumps.

Adult Oral Care
Chattering Teeth: What's Behind It?Your chattering teeth could just be a sign that you're cold. Though there may be underlying causes that are a little more serious. Learn more here.
Related Products

Colgate Total Active Prevention Whitening Toothbrush is a soft toothbrush with charcoal infused spiral and Floss-Tip bristles (1). This soft bristle toothbrush fights the root cause* of cavities, plaque, gingivitis, bad breath, tartar buildup**, and stains*** and also helps remove surface stains to prevent stain buildup.
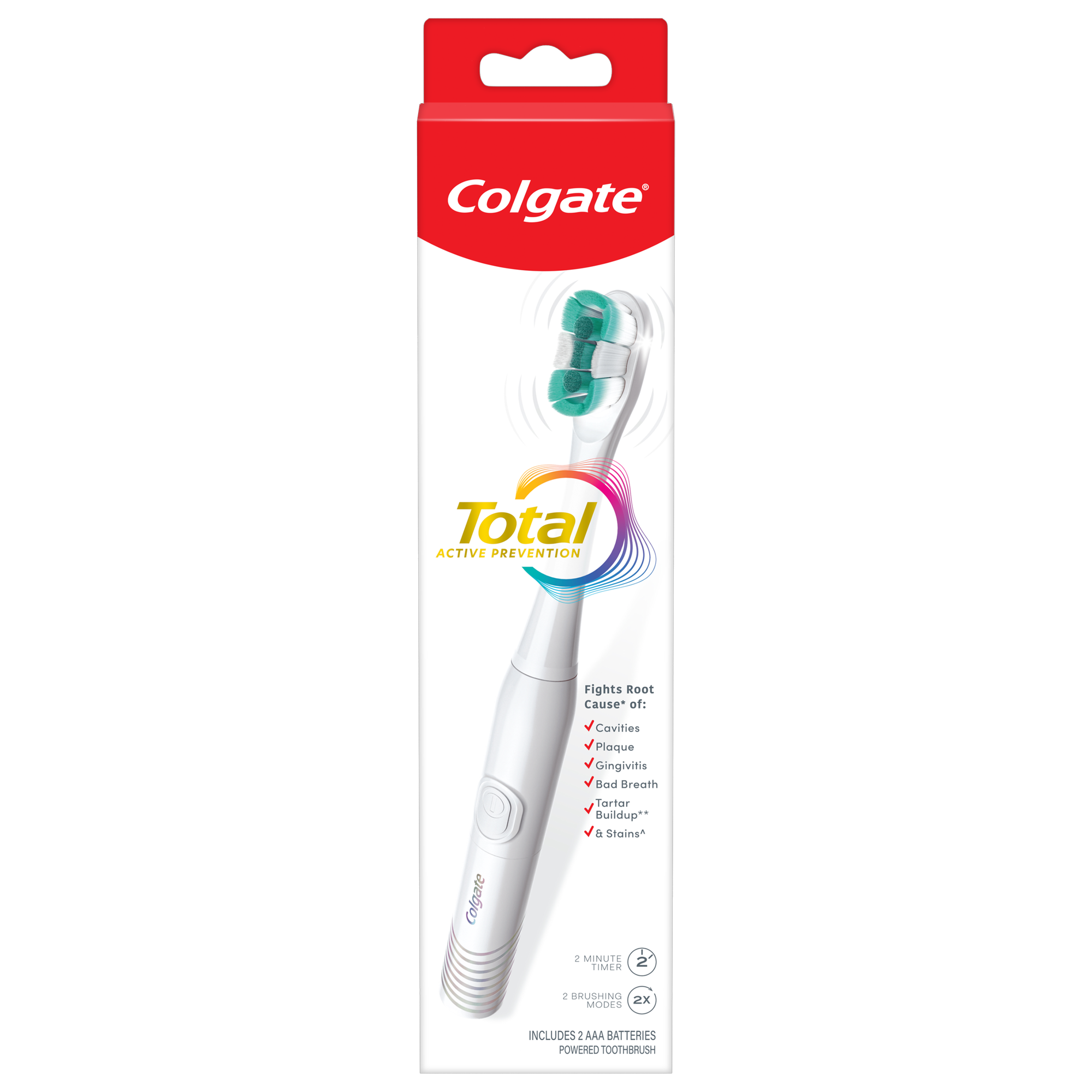
Power away plaque with Colgate Total Battery Powered Toothbrush. This battery operated toothbrush for adults fights the root cause* of cavities, plaque, gingivitis, bad breath, tartar buildup**, and stains***. Plus, this battery toothbrush has a built in 2 minute timer and features two cleaning modes, Sensitive and Regular, to cater to your unique oral care needs.

The Colgate Total® Active Prevention Foaming Clean Soft Bristle Toothbrush is specially designed to tackle the root cause* of cavities, plaque, gingivitis, bad breath, tartar buildup**, and stains***.

Colgate Total Alcohol Free* Gum Health Mouthwash delivers 24-hour protection** against bacteria and also helps prevent gum problems

Helping dental professionals
More professionals across the world trust Colgate. Find resources, products, and information to give your patients a healthier future




